Professional Documents
Culture Documents
600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-2
600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-2
Uploaded by
april0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
179 views10 pagesOriginal Title
2. 600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3)-part-2 (1)-part-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
179 views10 pages600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-2
600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-2
Uploaded by
aprilCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
106 Cost Accounting
Problem 4 ’s total fi
Green Meadows makes three types portable coolers. \ Sass or cach pe
Cost P!,080,000. Selling prices, variable costs, and sales ps
of cooler follow:
MODEL SELLING VARIABLE Pune
PRICE cost Mone
X100 P 8,800 P 7,600 ie
X950 14,800 12,000 50%
C 800 24,000 20,000 20%
|.What is the company’s break-even point in units and pesos?
2.1f the company has a target of IM how many units of each type of cooler must
be sold
Problem 5
Alonzo owns a barber where he employs five barbers and pays each a base rate of
2,000 per month. One of the barbers act as the manager and receives an extra
P3,000 per month. In addition to the base rate, each barber is paid a commission of
P20 per haircut. A barber can do an average of 6 haircuts a day. The barber shop
is open 24 days a month. Other costs incurred are as follows:
Advertising P 1,000 per month
Rent 4,000 per month
Barber supplies 400 per month
Utilities 1,750 per month and
25 per haircut
Magazines
/ 250 per month
Cleaning Supplies 15 per haircut
Currently Alonzo charges P100 per haircut
Required
1.Compute the break-even point ns a) number of haircut:
2.In March, 1400 haircuts were given, Compute the net
3.Alonzo wants a net income of P25,000, compute the
must be given
4.1f Alonzo wants a net income of P40,000, an ; |
much must be the amount charged per haircut 41,500 haircuts were given, how
's snd in (b) total pesos
Income
© number of haircuts that
vy
Chapter 4 Cost Volume Profit Analysis 107
Problem 6
Guiller Company’s projected profit for the coming year follows
TOTAL PER UNIT
Sales P2,480,000 — P.20.00
Variable costs 1,488,000 12.00
Contribution margin 992,000 Pb. 8.00
Fixed cost 626,400
Operating income P 365,600
Required
1,Compute the break-even point in units
2.Compute the break-even point in pesos
3.Compute the contribution margin ratio
4.Using the projected sales for the coming year, compute the margin of safety and -
margin of safety ratio.
Problem 7
Statement of Comprehensive Income for Brooklyn Company for the current year is
Sales P 750,000
Variable cost 600,000
Contribution margin 150,000
Fixed cost 100,000
Operating income P _50,000
Required
1.Compute the break-even point
2.Compute the margin of safety
3.Compute the margin of safety ratio
4.Compute the degree of operating leverage — ; .
S.Suppose the company experiences a 30% increase in revenues, compute for the
percentage change in profits
108 Cost Accounting
MULTIPLE CHOICE - THEORIES i .
1. The systematic examination of the relationship among selling prices, volume of
sales and production costs and profits is called
a, contribution margin analysis
b. cost-volume-profit analysis
c. budgetary analysis
d, gross profit analysis
2. CVP analysis allows management to determine the relative profitability of a
product by
a. determining potential bottlenecks in the production process :
b. determining the contribution margin per unit and projected profits at different
levels of production. a
¢. assigning costs to a product in a manner. that maximizes the contribution
margin
d. keeping fixed costs in an absolute minimum
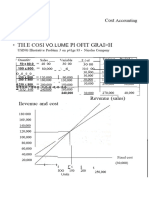
3. The most important information derived from a breakeven chart is the
a, amount of sales needed to cover the variable cost
b. amount of sales needed to cover the fixed cost
c. relationship among revenues, variable costs, fixed costs at different levels of
activity. ,
“d. volume or output level at which the enterprise breaks even
4, Companies with a high degree of operating leverage
a, will have a more significant shift in income as sales volume
b. have fewer fixed costs’
c. have low contribution margin ratios
d, are less dependent on volume to add profits
changes
5.A company’s break-even point would be increased bu
a. an increase in fixed costs
b, a decrease in contribution margin ratio
c. a decrease in selling price
d. a decrease in variable cost per unit
Chapter 4 Cost Volume Profit Analysis 109
6. If the variable cost per unit decreases while selling price decreases, the new
variable Cost ratio in relation to the old variable cost ratio will be
a. higher
b. lower
c. the same
d. not enough information provided
CVP analysis is a simple but powerful tool to assist management at different
stages of the decision making process, Which of the following does not
; ‘represent a primary of the CVP model>
a. Ability to compute the break even point
b. Ability to find target sales volume
c. Aids in evaluating tax planning alternatives
4. Aids in determining optimal pricing policies
8. A decrease in the margin of safety would be caused by
a.an increase in total fixed cost
b.in increase in total actual sales
c.a decrease in variable cost per unit
d.a decrease in the selling price per unit
1.8. Ifthe fixed cost for a product decrease and the variable cost (as a percentage of
peso sales) decrease, what will be the effect on the contribution margin ratio
and the break-even point respectively
Contribution margin ratio Break-even point
a. Deceased Increased
b. Increased Decreased
c, Decreased “Decreased
d. Increased Increased
10. If the sales mix shifts toward the higher contribution margin products, what
would happen to the break-even point
a. decreases
b. increases
¢. remains constant
d. requires additional information
110 Cost Accounting
MULTIPLE CHOICE - PROBLEMS
The Avengers Company is trying to do cost volume profit analysis with the
following information for the month of August
Sales rte
Total Fixed cost 7
Total variable costs =} 960,009
Unit price 40
I. The operating income of the Avengers Company is
a. P160,000
b. P190,000
ce. P240,000
d. P440,000
2.What is the break-even point in units?
a. 14,000 units
b. 25,000 units
c. 28,000 units
d. 35,000 units
3.If the company desires a profit of P80,000, how many must be sold?
a. 30,000 units
b, 35,000 units
c. 36,000 units
d, 45,000 units
4.The margin of safety is
a. P100,000
b. P200,000
c. P300,000
d. P400,000
‘The Orange Company plans to sell a new product. The s
be P 150 per unit. The company is able to produce 15
marketing manager feels that a more realistic level of
Variable cost is estimated at P70 per unit. Total fi;
elling price is expected to
2000 units but the company’s
sales would be 12,000 units.
xed costs will be P 900,000
Chapter 4 Cost Volume Profit Analysis i
5.The break-even sales
a. 10,000 units
b, 11,250 units
c. 16,000 units
d. 18,000 units
6. How much is the income
a. P (87,500) °
b. P122,500
c. P300,000
d. P330,000
(loss) if the company sells all the units it can produce
7. If the company desires to earn P400,000 before tax at full capacity, what selling
price must be charged
a. P 80.00
b.P 90.00
c.P 95.00
d. P100.00
Donna Company manufactures and sells two products: Product A and Product B.
The two products have the following characteristics
. Product A Product B
Selling price per unit P 50.00 P30.00
Sales revenue 750,000 900,000
Variable cost per unit 30.00 24.00
Total fixed cost for the company was P320,000 but increase to P400,000 at
production levels over 100,000. Selling price and variable cost per unit are the
same at all production levels
8.Assuming a constant product mix, what is the break-even in units?
a, 10,000 units
b. 16,000 units
¢, 25,000 units
4. 30,000 units
Cost Accounting
112
. it product mi:
9.For the company to eam a profit of P400,000, assuming constant PFOSNS! mis,
how many units must be sold
a, 25,000 units
b. 37,500 units
¢. $0,000 units
4. 75,000 units
The following costs have ben estimated based otal SON ao
Direct materials P 300,000 ne
Direct labor 250,000 100
Manufacturing overhead 250,000 a
Selling and administrative 150,000 30
10. What selling price will result in a 40% contribution margin.
a. P33.25 :
b. P3958
©. P52.78
d, P60.00
1
. What selling price will yield a projected income of PS0,000?
a. P35.20
b. P36.94
c. P4180
d, P42.25
Happy Face Company has fixed cost of P500,000 per year, variable cost of P30
per unit, and a selling price of PSO per unit,
12. At a production level of 30,000 units, how much is the
a. P 50,000
b. P 100,000
c. P 150,000
d. P 200,000
Operating income?
13. The break-even sales in units
a. 10,000 uits
b. 25,000 units
c. 27,500 units
d, 30,000 units
Chapter 4 Cost Volume Profit Analysis 113
14, The number of units the company must sell to earn an income of P100,000?
a. 10,000 units
b. 25,000 units
c. 27,500 units
d. 30,000 units
Alexis Company Operated at normal capacity during the current year producing
50,000 of. its single Product... Sales totaled 40,000 units at a selling price of P20
per unit. Variable manufacturing cost were P& per unit and variable selling and
administrative were P 4 per unit, Fixed cost were incurred uniformly throughout
the year and amounted to P188,000 for manufacturing and P64,000 for.P64,000 for
selling and administrative.
15.The break-even point in pesos is
a. P 420,000
b. P 470,000
c.P 630,000
d. P 732,000
The Presley Company manufactures two products, Product X and Product Y.. The
following are projections for the coming year,
Product X Product Y
Sales P 100,000 P 112,500
Sales in units 10,000 7,500
Expenses
Fixed P 20,000 P 24,000
Variable 60,000 75,000
Projected profit 20.000 14,000
16.Assuming that the facilities are not jointly used, the breakeven output (in
units)for Product X would be
a. 8,000
b. 7,000
c. 6,000
d. 5,000
Cost Accounting
114
unit. The variable cost is
The Power Company sells its product at P15.00 pet inted to P45,000
° les amou
P9.00 per unit. Total fixed cost is P12,000. Current sal
17.1f sales decrease by 500 units, by how much would fixed expenses have to be
reduced to maintain the current net income?
a. P7,500
b. P6,000
¢. P3,000
4. P2000
18.At a break-even point of 400 units, the variable costs 400 and the anced costs
were P200. What will the 401* unit sold contribute to profit before tax?
a.Po ’
b. PO.60.
c. P1.00
d. P1530
The statement of comprehensive income for Blanche Company for the current
year is presented below
Sales P 400,000
Variable costs 125,000
Contribution margin 275,000
Fixed costs 200,000
Income before tax
P 75,000
19.What is the degree of operating leverage of Blanche Company
a.3.67
b.1.45
c. 5.33
d. 1.67
The following information pertains to Ellery Company.
1,000,000, break even sales - P700,000, budgeted oer weet sales —
600,000. ed contribution margin ~
20.The margin of safety for the Ellery Company is
a. P300,000
b. P400.000
c. P500,000
d, P600,000,
ee
Chapter
a ae a ee
JOB ORDER COSTING
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to
Define job order costing and identify the types ©!
most to use this system.
‘© Demonstrate the mechanics of a job order costing system. ;
Differentiate among the forms used in the purchase and issuance - of
Pnterials such as a purchase requisition, a purchase order, @ receiving
report, and a materials requisition. .
«Distinguish between the periodic and perpetual cost accumulation systems
used to account for materials issued to production and for ending materials
inventory. :
«Prepare a job order cost sheet
f industries that would be
The job order cost procedure keeps the costs of various jobs or contracts separate
during their manufacture or construction. The method is applicable to job order
work in factories, workshops, and repair shops as well as to work by builders,
construction engineers, shipbuilders, and printers. The cost unit is the job, the
work order, or the contract; and the records will show the cost of each. The
method presupposes the possibility of physically identifying the jobs produced and
of charging each with its own cost.
A variation of the job order cost method is that of costing orders by lots. A lot is
the quantity of product that can conveniently and economically be produced and
costed. For example, in the shoe manufacturing industry, a contract is divided into
lots, each lot being from 100 to 250 pairs of one size and style of shoe. The costs
are then accumulated for each lot.
In job order costing, each job is an accounting unit to which materials, labor, and
factory overhead costs are assigned by means of job order numbers. The cost f
each order produced for a given customer or the cost of each lot to be pla ai
stock is recorded on a summary sheet called a job order cost sheet, or merel ra cosh
sheet, This mater sheet is designed to collect the costs of material: labo : a
factory overhead applicable to a specific job Sen
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Just-In-Time and Backflush AccountingDocument7 pagesJust-In-Time and Backflush AccountingaprilNo ratings yet
- TH E PL Ofit Grai H: Graph 1Document13 pagesTH E PL Ofit Grai H: Graph 1aprilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Cost AccountingaprilNo ratings yet
- 600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-11Document10 pages600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-11aprilNo ratings yet
- 111-120 - 1. 600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-1 PG 96-105Document10 pages111-120 - 1. 600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-1 PG 96-105aprilNo ratings yet
- Cost - Volume Profit AnalysisDocument14 pagesCost - Volume Profit AnalysisaprilNo ratings yet
- 600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-4Document10 pages600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-4aprilNo ratings yet
- 600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-5Document10 pages600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-5aprilNo ratings yet
- Vol - Jum E: Graph 1 Graj HDocument13 pagesVol - Jum E: Graph 1 Graj HaprilNo ratings yet
- 46 Cost AccountingDocument23 pages46 Cost AccountingaprilNo ratings yet
- Auditing ContractsDocument36 pagesAuditing ContractsaprilNo ratings yet
- 600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-8Document10 pages600070447-Cost-Accounting-and-Control-De-Leon-2019-PART-1 (3) - Part-2 (1) - Part-8aprilNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - CISDocument13 pagesTopic 5 - CISaprilNo ratings yet
- 1-10 OkDocument10 pages1-10 OkaprilNo ratings yet
- 71 100Document30 pages71 100aprilNo ratings yet
- Cis SWDocument3 pagesCis SWaprilNo ratings yet
- 101 110Document10 pages101 110aprilNo ratings yet
- Simbapay 10Document1 pageSimbapay 10aprilNo ratings yet
- Remitly 10Document3 pagesRemitly 10aprilNo ratings yet
- Central Europe 7 Countries 12 Days by TnaDocument1 pageCentral Europe 7 Countries 12 Days by TnaaprilNo ratings yet
- Risk and Control Issues For PurchasingDocument1 pageRisk and Control Issues For PurchasingaprilNo ratings yet
- Cis Audit ReviewerDocument11 pagesCis Audit RevieweraprilNo ratings yet
- Auditing in CIS 1617 2ndsem FEDocument10 pagesAuditing in CIS 1617 2ndsem FEaprilNo ratings yet