Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I. Overview
I. Overview
Uploaded by
Ali AshrafOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I. Overview
I. Overview
Uploaded by
Ali AshrafCopyright:
Available Formats
Gluconeogenesis and the
chapter
7 Maintenance of Blood
Glucose Levels
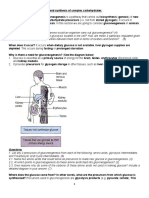
I. OVERVIEW (FIGURE 7-1)
A. Gluconeogenesis, which occurs mainly in the liver and to a small degree in the kidney, is the syn-
thesis of glucose from compounds that are not carbohydrates.
B. The major precursors for gluconeogenesis are lactate, amino acids (which form pyruvate or tri-
carboxylic acid [TCA] cycle intermediates), and glycerol (which forms dihydroxyacetone phos-
phate [DHAP]). Even-chain fatty acids do not produce any net glucose.
C. Gluconeogenesis involves several enzymatic steps that do not occur in glycolysis; thus, glucose is
not generated by a simple reversal of glycolysis.
D. The synthesis of 1 mole of glucose from 2 moles of pyruvate requires the energy equivalent of
about 6 moles of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
E. Blood glucose levels are maintained within a very narrow range, even though the nature of a per-
son’s diet may vary widely, and the normal person eats periodically during the day and fasts
between meals and at night. Even under circumstances when a person does not eat for extended
periods of time, blood glucose levels decrease only slowly.
F. The major hormones that regulate blood glucose are insulin and glucagon.
G. After a meal, blood glucose is supplied by dietary carbohydrate. However, during fasting, the liver
maintains blood glucose levels by the processes of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
H. All cells use glucose for energy; however, the production of glucose during fasting is particularly
important for tissues such as the brain and red blood cells.
I. During exercise, blood glucose is also maintained by liver glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
II. REACTIONS OF GLUCONEOGENESIS
A. Conversion of pyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate (Figure 7-2)
1. In the liver, pyruvate is converted to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in two steps.
2. Pyruvate (produced from lactate, alanine, and other amino acids) (Step 1) is first converted to
oxaloacetate (OAA) (Step 2) by pyruvate carboxylase, a mitochondrial enzyme that requires bi-
otin and ATP.
109
You might also like
- Gluconeogenesis and Cori CycleDocument21 pagesGluconeogenesis and Cori CycleAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- Group Presentation (A) Group Presentation : Health Science (Gen. Nursing) Biochemistry Gluconeogenesis DR SujuudDocument31 pagesGroup Presentation (A) Group Presentation : Health Science (Gen. Nursing) Biochemistry Gluconeogenesis DR SujuudIbrahim WarsameNo ratings yet
- 2.7 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Gluconeogenesis - Better PicturesDocument12 pages2.7 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Gluconeogenesis - Better Pictureslovelots1234No ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument62 pagesGlycolysisafuaserwaa489No ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: Unit 2Document7 pagesGluconeogenesis: Unit 2Vaishali PathakNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: Location of GluconeogenesisDocument31 pagesGlycolysis: Location of GluconeogenesisTahera AhmedNo ratings yet
- Location of GluconeogenesisDocument4 pagesLocation of GluconeogenesisAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- 13 Cau Hoa SinhDocument37 pages13 Cau Hoa SinhTran Danh NhanNo ratings yet
- Group Presentation: Course: Biochemistry Topic: GlycolysisDocument31 pagesGroup Presentation: Course: Biochemistry Topic: GlycolysisIbrahim WarsameNo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument48 pagesGluconeogenesisQshyanNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument27 pagesReportJasmin BarriosNo ratings yet
- 2.4gluconeo IVDocument51 pages2.4gluconeo IVsabirinaly30No ratings yet
- Utilization of Carbohydrates and Glycolysis: Dr. E.Y. ALIDocument74 pagesUtilization of Carbohydrates and Glycolysis: Dr. E.Y. ALIAbdulrhManNo ratings yet
- 3 Glikolisis 9Document17 pages3 Glikolisis 9Rafi Ahmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- The Role of Liver in Metabolism An Updated ReviewDocument6 pagesThe Role of Liver in Metabolism An Updated Reviewرشاد خالد عماد Rashad Khaled EmadNo ratings yet
- 2.6 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Glycogen MetabolismDocument10 pages2.6 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Glycogen Metabolismlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Backwards ReasoningDocument40 pagesBackwards Reasoningharshit chaudharyNo ratings yet
- 3.2. Carbo-Meta - Short VersionDocument29 pages3.2. Carbo-Meta - Short VersionLong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Endocrine Control On MetabolismDocument79 pagesIntroduction To The Endocrine Control On Metabolisminka.elseNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Importance of Carbohydrate (2015)Document38 pagesBiochemical Importance of Carbohydrate (2015)Agnes Treyssia SandewaNo ratings yet
- 8glycogen Metabolism2013 PDFDocument90 pages8glycogen Metabolism2013 PDFNazeer Baig MogalmearjaNo ratings yet
- C454 Lect3 ViewDocument66 pagesC454 Lect3 ViewAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- METABOLISM of CARBOHYDRATESDocument62 pagesMETABOLISM of CARBOHYDRATESmohaysin pirinoNo ratings yet
- Topic: Glyconeogenesis: Biochemistry IIDocument5 pagesTopic: Glyconeogenesis: Biochemistry IINaiomiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes 2Document903 pagesBiochemistry Notes 2madhu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Gluco Neo GenesisDocument16 pagesGluco Neo Genesiswaldo_reyes_1No ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument40 pagesLECTURE 3 - Carbohydrate Metabolismmuhammedgmdidra95No ratings yet
- Carbhydrate MetabolimsDocument25 pagesCarbhydrate MetabolimsM sarauta TvNo ratings yet
- 10 CH26 Nutrition and Metabolism 2 2015Document29 pages10 CH26 Nutrition and Metabolism 2 2015AbdullionNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism and BiosynthesisDocument44 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism and BiosynthesisEmman RegondolaNo ratings yet
- Met of CHODocument43 pagesMet of CHOKiya AlemuNo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument11 pagesGluconeogenesisChymuul MarthaNo ratings yet
- (ENDOCRINE) Tugas Biochemistry Week 2 Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Document4 pages(ENDOCRINE) Tugas Biochemistry Week 2 Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Jeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- B314 AssignmentDocument23 pagesB314 AssignmentPalesa NtsekalleNo ratings yet
- Lec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismDocument12 pagesLec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismyanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 22 Gluconeogenesis, Glycogen Metabolism, and The Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 22 Gluconeogenesis, Glycogen Metabolism, and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Generation of ATP by GlycolysisDocument3 pagesGeneration of ATP by GlycolysisYousif AlaaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis For NursesDocument17 pagesGlycolysis For NursesAaron WallaceNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism (Unit 2) : Gluconeogenesis Continued .Document22 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism (Unit 2) : Gluconeogenesis Continued .qwerty123No ratings yet
- GlucagonDocument4 pagesGlucagonElenanana100% (1)
- 13 - GluconeogenesisDocument23 pages13 - GluconeogenesischeckmateNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Storage and Synthesis in Liver and Muscle: GlycogenDocument40 pagesCarbohydrate Storage and Synthesis in Liver and Muscle: GlycogenJay R PlogioNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument36 pagesGlycolysisAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument23 pagesGlycolysiskrazy lrkaNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024-B3502-Lecture 17-Carbohydrate Metabolism-Gluconeogenesis and Oxidative Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument15 pages2023-2024-B3502-Lecture 17-Carbohydrate Metabolism-Gluconeogenesis and Oxidative Pentose Phosphate Pathwaypitsolerato60No ratings yet
- MFN-002 Unit 6Document52 pagesMFN-002 Unit 6NaveenNo ratings yet
- Define GlycolysisDocument3 pagesDefine GlycolysisjhanensuarezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Second Gluconeogenesis PDFDocument26 pagesLecture 8 Second Gluconeogenesis PDFMadani TawfeeqNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument43 pagesGlycolysisAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- 2023 BCH313 Gluconeogenesis and Synthesis of Complex Carbohydrates NotesDocument9 pages2023 BCH313 Gluconeogenesis and Synthesis of Complex Carbohydrates NotesNOLUBABALONo ratings yet
- Gluco Neo GenesisDocument19 pagesGluco Neo GenesisessaNo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument9 pagesGluconeogenesisPankaj Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle: CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesCitric Acid Cycle: CharacteristicsYahya Daham Zafeer SakhrNo ratings yet
- Bio Chem LMRP 2019Document36 pagesBio Chem LMRP 2019skNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument42 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismLennieka A NickleNo ratings yet
- Recitation - Metabolic Fate of Glucose and Fatty AcidsDocument2 pagesRecitation - Metabolic Fate of Glucose and Fatty AcidshoythereNo ratings yet
- Bch242-Bch252 2021 CarbohydrateDocument31 pagesBch242-Bch252 2021 CarbohydrateEmmanuella OffiongNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesMetabolism of Carbohydrateskathleenmaisiedevilla.021105No ratings yet
- GlucolysisDocument11 pagesGlucolysisMohamed SalahNo ratings yet
- 2003 KS3 SC 5-7 Paper1Document28 pages2003 KS3 SC 5-7 Paper1Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- I. The Tricarboxylic Acid CycleDocument8 pagesI. The Tricarboxylic Acid CycleAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Pneumatics and Hydraulics - Notes - 2015Document2 pagesPneumatics and Hydraulics - Notes - 2015Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- I. Protein Synthesis Translation of Messenger RNADocument5 pagesI. Protein Synthesis Translation of Messenger RNAAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- I. General Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument3 pagesI. General Mechanisms of Hormone ActionAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- I. General OverviewDocument1 pageI. General OverviewAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- III. Synthesis of RNA TranscriptionDocument5 pagesIII. Synthesis of RNA TranscriptionAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- IB-Chem SAQ AnswersDocument64 pagesIB-Chem SAQ AnswersAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- II. Synthesis of DNA ReplicationDocument6 pagesII. Synthesis of DNA ReplicationAli AshrafNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE EssentialBiology SyllabusMatchingGridDocument4 pagesCambridge IGCSE EssentialBiology SyllabusMatchingGridAli AshrafNo ratings yet