Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algo Bradycardia
Algo Bradycardia
Uploaded by
Andi SanapatiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algo Bradycardia
Algo Bradycardia
Uploaded by
Andi SanapatiCopyright:
Available Formats
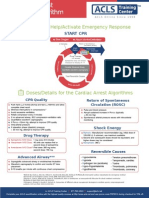
Bradycardia with
a pulse algorithm
Assess appropriateness for clinical condition.
Heart rate typically < 50/min if bradyarrhythmia.
Identify and treat underlying cause
Maintain patent airway; assist breathing as necessary*
If the patient is short of breath, administer oxygen
Oxygen as indicated
Cardiac monitor to identify rhythm; monitor blood pressure and oximetry
IV access
12-lead ECG if available; don’t delay therapy
Persistent bradyarrhythmia causing:
Monitor Hypotension?
and Acutely altered mental status?
Signs of shock?
observe
Ischemic chest discomfort?
Acute heart failure?
Atropine IV dose:
First dose: Atropine 1 mg
Repeat every 3–5 minutes
Maximum: 3 mg
If atropine ineffective:
Transcutaneous pacing**
OR
Dopamine IV infusion:
5–20 mcg/kg per minute
OR
Epinephrine IV infusion:
2–10 mcg per minute
Consider:
Expert consultation
Transvenous pacing
* Dorges V, Wenzel V, Knacke P, Gerlach K, Comparison of different airway management strategies to ventilate apneic, nonpreoxygenated patients. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:800-804 ** Link MS, Atkins DL, Passman RS, Halperin HR, Samson RA,
White RD, Cudnik MT, Berg MD, Kudenchuk PJ, Kerber RE. “Part 6: electrical therapies: automated external defibrillators, defillation, cardioversion, and pacing: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
and Emergency Cardiovascular Care”. Circulation. 2010; 122(suppl 3):S706-S719. http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/122/18_suppl_3/S706
Version control: This document follows 2020
American Heart Association® guidelines for CPR © ACLS Training Center +1 219-255-2255 support@acls.net
and ECC. American Heart Association® guidelines Scan for the latest
are updated every five years. If you are reading Complete your ACLS recertification online with the algorithm cards
this page after December 2025, please contact highest quality course at http://www.acls.net
support@acls.net for an update. Version 2023.07.a
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- ACLS Exam ADocument8 pagesACLS Exam ASean Johnson83% (30)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Janice Krug PMHNP ResumeDocument3 pagesJanice Krug PMHNP Resumeapi-416722296No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Autoclave Cleaning Log Sheet ExampleDocument23 pagesAutoclave Cleaning Log Sheet Exampleankit7588No ratings yet
- CPR and AED Skills Test 1-Rescuer Adult CPR and AED ChecklistDocument1 pageCPR and AED Skills Test 1-Rescuer Adult CPR and AED ChecklistNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Acls - Megacode - UpdatedDocument4 pagesAcls - Megacode - UpdatedDivine Dela Pena100% (1)
- MU323 Image 1Document6 pagesMU323 Image 1Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- MU323 Extra Credit 3Document5 pagesMU323 Extra Credit 3Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- MU323 Assignment 6Document7 pagesMU323 Assignment 6Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- MU323 Group Assignment 1Document5 pagesMU323 Group Assignment 1Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Mu323 HW 1Document7 pagesMu323 HW 1Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- MU323 Info 4Document5 pagesMU323 Info 4Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- MU323 Answer Key 9Document6 pagesMU323 Answer Key 9Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation FinalDocument46 pagesMechanical Ventilation FinalNaven Scorp100% (1)
- Toolkit End-Trafficking Oct 2012Document4 pagesToolkit End-Trafficking Oct 2012Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Borang Soal SelidikDocument4 pagesBorang Soal SelidikNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- End Trafficking Toolkit: Get Informed: What Is Human Trafficking?Document4 pagesEnd Trafficking Toolkit: Get Informed: What Is Human Trafficking?Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Human Trafficking and Study Abroad: Taylor S. ParkerDocument12 pagesHuman Trafficking and Study Abroad: Taylor S. ParkerNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Human Trafficking Guide OPIA 2017Document67 pagesHuman Trafficking Guide OPIA 2017Naven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Job ApplicationDocument2 pagesJob ApplicationNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Schools and Anti-Trafficking Awareness: Education/Training Key Influencers & StudentsDocument32 pagesSchools and Anti-Trafficking Awareness: Education/Training Key Influencers & StudentsNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- List The Roles of Capnography During General AnaesthesiaDocument2 pagesList The Roles of Capnography During General AnaesthesiaNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Human Trafficking CurriculumDocument23 pagesHuman Trafficking CurriculumNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- BMDocument5 pagesBMNaven ScorpNo ratings yet
- Acls DrugsDocument5 pagesAcls DrugsDebby Christiana SNo ratings yet
- Emergency Short Courses in SA - Local 25-3-2021Document1 pageEmergency Short Courses in SA - Local 25-3-2021JacquesNo ratings yet
- Defibrillators Type Comparison: External, Automated, Semi AutomatedDocument39 pagesDefibrillators Type Comparison: External, Automated, Semi AutomatedEng.AymanNo ratings yet
- 99 Topics For The CCFPDocument134 pages99 Topics For The CCFPalexidr100% (2)
- Materi Dr. Yuddy Imowanto, SP - EMDocument64 pagesMateri Dr. Yuddy Imowanto, SP - EMAni ArdiantiNo ratings yet
- Part 5: Neonatal ResuscitationDocument30 pagesPart 5: Neonatal ResuscitationAngela Giselle Garcia RuizNo ratings yet
- Course Exercise - ACLS Precourse Self-Assessment and Precourse Work, International English (IVE)Document637 pagesCourse Exercise - ACLS Precourse Self-Assessment and Precourse Work, International English (IVE)Kia MercadoNo ratings yet
- ACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterDocument1 pageACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterJeane SuyantoNo ratings yet
- Brochure ASCDocument16 pagesBrochure ASCsiddharthNo ratings yet
- 2nd Announcment Ver 03 CompDocument10 pages2nd Announcment Ver 03 CompDea PrazwalithaNo ratings yet
- Practice of NCC Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in AdultsDocument24 pagesPractice of NCC Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in AdultsAna Rica Santiago Navarra-CruzNo ratings yet
- ACLS Provider Manual Supplementary MaterialDocument86 pagesACLS Provider Manual Supplementary MaterialEma0% (2)
- Acls FixDocument20 pagesAcls Fixluthfi adityaNo ratings yet
- ACLSDocument39 pagesACLSJason LiandoNo ratings yet
- CPR SeminarDocument73 pagesCPR SeminarAmy Lalringhluani Chhakchhuak100% (6)
- Service Manual: Defibrillator/MonitorDocument172 pagesService Manual: Defibrillator/MonitorArya BondanNo ratings yet
- ACLSDocument26 pagesACLSrobmadereNo ratings yet
- Canadian Fitness Safety Standards PDFDocument103 pagesCanadian Fitness Safety Standards PDFMichel HunterNo ratings yet
- Trauma ArrestDocument12 pagesTrauma ArrestydtrgnNo ratings yet
- RCDSO Standard of Practice Use of Sedation and General AnesthesiaDocument40 pagesRCDSO Standard of Practice Use of Sedation and General AnesthesiaSharjeel ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- SimulationDocument9 pagesSimulationKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Dimension of Development First Aid EducationDocument3 pagesDimension of Development First Aid EducationNovelyn Mitra100% (1)
- ACLS Provider Manual Supplementary Material: © 2020 American Heart AssociationDocument75 pagesACLS Provider Manual Supplementary Material: © 2020 American Heart AssociationpolelNo ratings yet
- Bls CPR LectureDocument12 pagesBls CPR LectureNoona PlaysNo ratings yet
- Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: CPR StartDocument2 pagesShout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: CPR StartdavpierNo ratings yet
- CRASH CART NewDocument11 pagesCRASH CART NewGemstone Dangel NdukaNo ratings yet