KLE Technological University Page |1
MACHINE LEARNING HANDS-ON PROGRAMS
Program 1: Linear Regression – Single Variable Linear Regression
Description About Dataset :
Performing the Linear regression for Single variable by using Salary_Data.csv which is consists of two
features that is Salary, [Link] column contains 30 rows of information. Feature “Salary”
describes Each person salary according to his/her year of experience.
//Python code to perform Single variable linear regression
from [Link] import drive
[Link]('/content/drive')
import numpy as np
import [Link] as plt
import pandas as pd
"""**Importing the dataset**"""
dataset=pd.read_csv('/content/drive/My Drive/Machine Learning/Chapter1/Salary_Data.csv')
X = [Link][:, :-1].values
y = [Link][:, -1].values
print(y)
print(X)
"""**Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set**"""
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 1/3, random_state = 0)
"""**Training the Simple Linear Regression model on the Training set**"""
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
regressor = LinearRegression()
[Link](X_train, y_train)
y_pred = [Link](X_test)
print(y_pred)
[Link](X_train, y_train, color = 'red')
[Link](X_train, [Link](X_train), color = 'blue')
[Link]('Salary vs Experience (Training set)')
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University Page |2
[Link]('Years of Experience')
[Link]('Salary')
[Link]()
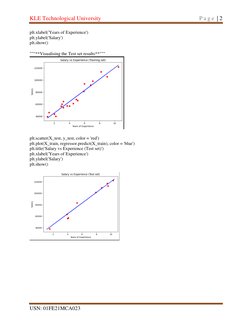
"""**Visualising the Test set results**"""
[Link](X_test, y_test, color = 'red')
[Link](X_train, [Link](X_train), color = 'blue')
[Link]('Salary vs Experience (Test set)')
[Link]('Years of Experience')
[Link]('Salary')
[Link]()
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University Page |3
Program 2: Linear Regression – Multi Variable Linear Regression
Description About Dataset:
Performing the linear regression using multi linear regression on 50_Startups.csv which is consist of 5
features that is R&D, Marketing, Spend, Administration, Spend, State, Profit. Each column contains 50
rows of information.
//Python code to perform Multi variable linear regression
from [Link] import drive
[Link]('/content/drive')
# Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import [Link] as plt
import pandas as pd
# Importing the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/My Drive/Machine Learning/Chapter1/MachineLearning-
master/Multiple Linear Regression Code [Link] (Unzipped Files)/50_Startups.csv')
X = [Link][:, :-1].values
y = [Link][:, -1].values
# Encoding categorical data
from [Link] import ColumnTransformer
from [Link] import OneHotEncoder
ct = ColumnTransformer(transformers=[('encoder', OneHotEncoder(), [3])], remainder='passthrough')
X = [Link](ct.fit_transform(X))
print(X)
#Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2, random_state = 0)
# Training the Multiple Linear Regression model on the Training set
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
regressor = LinearRegression()
[Link](X_train, y_train)
# Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = [Link](X_test)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
print([Link]((y_pred.reshape(len(y_pred),1), y_test.reshape(len(y_test),1)),1))
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University Page |4
Program 3: Classification – Logistic Regression
Description About Dataset:
Performing the Logistic Regression on Social_Network_Ads. csv which is consists of three features that is
Age, EstimatedSalary, purchased. Each column contains 400 rows of information. Feature “Age” describes
Each person age and according to his/ Estimated Salary . depending on which he/she will decide to purchase
a particular item or not.
//Python code to perform Classification – Logistic Regression
import numpy as np
import [Link] as plt
import pandas as pd
from [Link] import drive
[Link]('/content/drive')
# Importing the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/My Drive/Machine Learning/Chapter1/MachineLearning-
master/Social_Network_Ads.csv')
X = [Link][:, :-1].values
y = [Link][:, -1].values
# Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
print(X_train)
print(y_train)
print(X_test)
print(y_test)
# Feature Scaling
from [Link] import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = [Link](X_test)
print(X_train)
print(X_test)
# Training the Logistic Regression model on the Training set
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
classifier = LogisticRegression(random_state=0)
[Link](X_train, y_train)
#Predict the result for Age = 30 and EstimatedSalary = 87000
print([Link]([Link]([[30, 87000]])))
#Predicting the Test Set results
y_pred = [Link](X_test)
print(y_pred)
print([Link]((y_pred.reshape(len(y_pred),1),
y_test.reshape(len(y_test),1)),1))
# Making the Confusion Matrix
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University Page |5
from [Link] import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print(cm)
accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
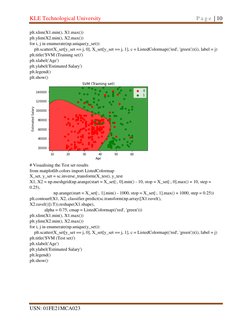
# Visualising the Training set results
from [Link] import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = sc.inverse_transform(X_train), y_train
X1, X2 = [Link]([Link](start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 10, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 10, step =
0.25),
[Link](start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1000, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1000, step = 0.25))
[Link](X1, X2, [Link]([Link]([Link]([[Link](),
[Link]()]).T)).reshape([Link]),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
for i, j in enumerate([Link](y_set)):
[Link](X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1], c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
[Link]('Logistic Regression (Training set)')
[Link]('Age')
[Link]('Estimated Salary')
[Link]()
[Link]()
# Visualising the Test set results
from [Link] import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = sc.inverse_transform(X_test), y_test
X1, X2 = [Link]([Link](start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 10, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 10, step =
0.25),
[Link](start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1000, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1000, step = 0.25))
[Link](X1, X2, [Link]([Link]([Link]([[Link](),
[Link]()]).T)).reshape([Link]),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
for i, j in enumerate([Link](y_set)):
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University Page |6
[Link](X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1], c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
[Link]('Logistic Regression (Test set)')
[Link]('Age')
[Link]('Estimated Salary')
[Link]()
[Link]()
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University Page |7
Program 4: Classification – Support Vector Machines (SVM)
Description About Dataset:
Performing the Support Vector Machines on Social_Network_Ads. csv which is consists of three features
that is Age, EstimatedSalary, purchased. Each column contains 400 rows of information. Feature “Age”
describes Each person age and according to his/ Estimated Salary . depending on which he/she will decide
to purchase a particular item or not.
//Python code to perform Classification – Support Vector Machines (SVM)
from [Link] import drive
[Link]('/content/drive')
# Support Vector Machine (SVM)
# Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import [Link] as plt
import pandas as pd
# Importing the dataset
dataset = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/My Drive/Machine Learning/Chapter1/MachineLearning-
master/Social_Network_Ads.csv')
X = [Link][:, :-1].values
y = [Link][:, -1].values
# Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
print(X_train)
print(y_train)
print(X_test)
print(y_test)
# Feature Scaling
from [Link] import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = [Link](X_test)
print(X_train)
print(X_test)
# Training the SVM model on the Training set
from [Link] import SVC
classifier = SVC(kernel = 'linear', random_state = 0)
[Link](X_train, y_train)
# Predicting a new result
print([Link]([Link]([[30,87000]])))
# Predicting the Test set results
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University Page |8
y_pred = [Link](X_test)
print([Link]((y_pred.reshape(len(y_pred),1), y_test.reshape(len(y_test),1)),1))
# Making the Confusion Matrix
from [Link] import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print(cm)
accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
# Visualising the Training set results
from [Link] import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = sc.inverse_transform(X_train), y_train
X1, X2 = [Link]([Link](start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 10, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 10, step =
0.25),
[Link](start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1000, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1000, step = 0.25))
[Link](X1, X2, [Link]([Link]([Link]([[Link](),
[Link]()]).T)).reshape([Link]),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
for i, j in enumerate([Link](y_set)):
[Link](X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1], c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
[Link]('SVM (Training set)')
[Link]('Age')
[Link]('Estimated Salary')
[Link]()
[Link]()
# Visualising the Test set results
from [Link] import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = sc.inverse_transform(X_test), y_test
X1, X2 = [Link]([Link](start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 10, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 10, step =
0.25),
[Link](start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1000, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1000, step = 0.25))
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University Page |9
[Link](X1, X2, [Link]([Link]([Link]([[Link](),
[Link]()]).T)).reshape([Link]),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
for i, j in enumerate([Link](y_set)):
[Link](X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1], c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
[Link]('SVM (Test set)')
[Link]('Age')
[Link]('Estimated Salary')
[Link]()
[Link]()
# Training the SVM model on the Training set
from [Link] import SVC
classifier = SVC(kernel = 'rbf', random_state = 0)
[Link](X_train, y_train)
# Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = [Link](X_test)
print([Link]((y_pred.reshape(len(y_pred),1), y_test.reshape(len(y_test),1)),1))
# Visualising the Training set results
from [Link] import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = sc.inverse_transform(X_train), y_train
X1, X2 = [Link]([Link](start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 10, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 10, step =
0.25),
[Link](start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1000, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1000, step = 0.25))
[Link](X1, X2, [Link]([Link]([Link]([[Link](),
[Link]()]).T)).reshape([Link]),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 10
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
for i, j in enumerate([Link](y_set)):
[Link](X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1], c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
[Link]('SVM (Training set)')
[Link]('Age')
[Link]('Estimated Salary')
[Link]()
[Link]()
# Visualising the Test set results
from [Link] import ListedColormap
X_set, y_set = sc.inverse_transform(X_test), y_test
X1, X2 = [Link]([Link](start = X_set[:, 0].min() - 10, stop = X_set[:, 0].max() + 10, step =
0.25),
[Link](start = X_set[:, 1].min() - 1000, stop = X_set[:, 1].max() + 1000, step = 0.25))
[Link](X1, X2, [Link]([Link]([Link]([[Link](),
[Link]()]).T)).reshape([Link]),
alpha = 0.75, cmap = ListedColormap(('red', 'green')))
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
[Link]([Link](), [Link]())
for i, j in enumerate([Link](y_set)):
[Link](X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j, 1], c = ListedColormap(('red', 'green'))(i), label = j)
[Link]('SVM (Test set)')
[Link]('Age')
[Link]('Estimated Salary')
[Link]()
[Link]()
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 11
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 12
Program 5: Classification using Neural Networks
Description About Dataset:
Performing the Classification using Neural Networks on [Link] which is consists of
nine features that is X1,X2,X3,X4,X5,X6,X7,X8,X9 . Each column contains 767 rows of information.
//Python code to perform Classification using Neural Networks
from [Link] import drive
[Link]('/content/drive')
# first neural network with keras tutorial
from numpy import loadtxt
from [Link] import Sequential
from [Link] import Dense
# load the dataset
dataset = loadtxt('/content/drive/My Drive/[Link]', delimiter=',')
# split into input (X) and output (y) variables
X = dataset[:,0:8]
y = dataset[:,8]
[Link]
(768, 9)
[Link]
(768, 8)
[Link]
(768,)
# define the keras model
model = Sequential() #calling default constructor
#First Hidden Layer (along with input layer)
[Link](Dense(12, input_dim=8, activation='relu')) #adding input layer along with the 1st hidden layer
#1st hidden layer has 12 activation units, input layer has 8 units for 8 features
#activation function used in the 1st layer is ReLU
#Adding the 2nd Hidden layer with 8 activation nodes and ReLU function
[Link](Dense(12, activation='relu'))
#Adding output layer with 1 activation unit (binary classification) and with Sigmoid function
[Link](Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
# compile the keras model
#Loss means computing the error or cost function (using algorithm - binary_crossentropy)
#Algorithm used is 'adam' - Stochastic gradient descent algorithm
#Evaluating the performance of the model will be done using 'accuracy'
[Link](loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# fit the keras model on the dataset
# Batch size is for updating the weights. Weights are updated after every 10 rows are executed.
[Link](X, y, epochs=200, batch_size=40)
Epoch 1/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5050 - accuracy: 0.7591
Epoch 2/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 963us/step - loss: 0.5148 - accuracy: 0.7435
Epoch 3/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5155 - accuracy: 0.7396
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 13
Epoch 4/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5197 - accuracy: 0.7565
Epoch 5/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5281 - accuracy: 0.7578
Epoch 6/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5223 - accuracy: 0.7526
Epoch 7/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5092 - accuracy: 0.7513
Epoch 8/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5072 - accuracy: 0.7617
Epoch 9/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5241 - accuracy: 0.7552
Epoch 10/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5311 - accuracy: 0.7292
Epoch 11/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5194 - accuracy: 0.7539
Epoch 12/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5436 - accuracy: 0.7292
Epoch 13/200
...
Epoch 199/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.4924 - accuracy: 0.7383
Epoch 200/200
77/77 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.4948 - accuracy: 0.7617
Accuracy: 76.56
# make probability predictions with the model
predictions = [Link](X)
# round predictions
rounded = [round(x[0]) for x in predictions]
# make class predictions with the model
predictions = model.predict_classes(X)
# make class predictions with the model
predictions = model.predict_classes(X)
# summarize the first 5 cases
for i in range(5):
print('%s => %d (expected %d)' % (X[i].tolist(), predictions[i], y[i]))
[6.0, 148.0, 72.0, 35.0, 0.0, 33.6, 0.627, 50.0] => 0 (expected 1)
[1.0, 85.0, 66.0, 29.0, 0.0, 26.6, 0.351, 31.0] => 0 (expected 0)
[8.0, 183.0, 64.0, 0.0, 0.0, 23.3, 0.672, 32.0] => 1 (expected 1)
[1.0, 89.0, 66.0, 23.0, 94.0, 28.1, 0.167, 21.0] => 0 (expected 0)
[0.0, 137.0, 40.0, 35.0, 168.0, 43.1, 2.288, 33.0] => 1 (expected 1)
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 14
Program 6: Unsupervised Learning – K-Means Clustering
Description About Dataset:
Performing the K-Means Clustering which is the technique of unsupervised learning by using
Mall_Customers.csv which is consists of four e features that is CustomerID, Genre, Age, Annual Income,
Spending Score (1-100). Each column contains 200 rows of information. Features used to describes whether
person will purchase a particular item or not based on persons age, genre and Annual Income.
//Python code to perform Unsupervised Learning – K-Means Clustering
import numpy as np
import [Link] as plt
import pandas as pd
from [Link] import drive
[Link]('/content/drive')
dataset = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/My Drive/Machine Learning/Chapter1/MachineLearning-
master/Mall_Customers.csv')
X = [Link][:, [3, 4]].values
# y = [Link][:, 3].values
# Using the elbow method to find the optimal number of clusters
from [Link] import KMeans
wcss = []
for i in range(1, 11):
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters = i, init = 'k-means++', max_iter = 300, n_init = 10, random_state = 42)
[Link](X)
[Link](kmeans.inertia_)
[Link](range(1, 11), wcss)
[Link]('The Elbow Method')
[Link]('Number of clusters')
[Link]('WCSS')
[Link]()
# Fitting K-Means to the dataset
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters = 5, init = 'k-means++', max_iter = 300, n_init = 10, random_state = 42)
y_kmeans = kmeans.fit_predict(X)
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 15
# Visualising the clusters
[Link](X[y_kmeans == 0, 0], X[y_kmeans == 0, 1], s = 100, c = 'red', label = 'Cluster 1')
[Link](X[y_kmeans == 1, 0], X[y_kmeans == 1, 1], s = 100, c = 'blue', label = 'Cluster 2')
[Link](X[y_kmeans == 2, 0], X[y_kmeans == 2, 1], s = 100, c = 'green', label = 'Cluster 3')
[Link](X[y_kmeans == 3, 0], X[y_kmeans == 3, 1], s = 100, c = 'cyan', label = 'Cluster 4')
[Link](X[y_kmeans == 4, 0], X[y_kmeans == 4, 1], s = 100, c = 'magenta', label = 'Cluster 5')
[Link](kmeans.cluster_centers_[:, 0], kmeans.cluster_centers_[:, 1], s = 300, c = 'yellow', label =
'Centroids')
[Link]('Clusters of customers')
[Link]('Annual Income (k$)')
[Link]('Spending Score (1-100)')
[Link]()
[Link]()
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 16
Program 7: Convolution Neural Networks Application
Description About Dataset:
Performing the Convolution Neural Networks Application on image dataset to predict between black-
diamond watermelon and caroline watermelon. Training_set contain the images of both the types of
watermelons. One folder containing image dataset of both the watermelons which is divided as test and
training dataset. Training_set folder contains black-diamond watermelon (500) images and caroline
watermelon (500) images and Test image dataset contains black-diamond watermelon (100), caroline
watermelon (100) images.
//Python code to perform Convolution Neural Networks Application
from [Link] import drive
[Link]('/content/drive')
import tensorflow as tf
from [Link] import ImageDataGenerator
## Part 1 - Data Preprocessing
### Preprocessing the Training set
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1./255,
shear_range = 0.2,
zoom_range = 0.2,
horizontal_flip = True)
training_set = train_datagen.flow_from_directory('/content/drive/My Drive/training_set',
target_size = (64, 64),
batch_size = 64,
class_mode = 'binary')
### Preprocessing the Test set
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1./255)
test_set = test_datagen.flow_from_directory('/content/drive/My Drive/test_set',
target_size = (64, 64),
batch_size = 64,
class_mode = 'binary')
## Part 2 - Building the CNN
### Initialising the CNN
cnn = [Link]()
### Step 1 - Convolution
[Link]([Link].Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=3, activation='relu', input_shape=[64, 64, 3]))
### Step 2 - Pooling
[Link]([Link].MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2))
### Adding a second convolutional layer
[Link]([Link].Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'))
[Link]([Link].MaxPool2D(pool_size=2, strides=2))
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 17
### Step 3 - Flattening
[Link]([Link]())
### Step 4 - Full Connection
[Link]([Link](units=128, activation='relu'))
### Step 5 - Output Layer
[Link]([Link](units=1, activation='sigmoid'))
## Part 3 - Training the CNN
### Compiling the CNN
[Link](optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'binary_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy'])
### Training the CNN on the Training set and evaluating it on the Test set
[Link](x = training_set, validation_data = test_set, epochs = 10)
Epoch 1/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5050 - accuracy: 0.7591
Epoch 2/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 963us/step - loss: 0.5148 - accuracy: 0.7435
Epoch 3/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5155 - accuracy: 0.7396
Epoch 4/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5197 - accuracy: 0.7565
Epoch 5/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5281 - accuracy: 0.7578
Epoch 6/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5223 - accuracy: 0.7526
Epoch 7/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5092 - accuracy: 0.7513
Epoch 8/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5072 - accuracy: 0.7617
Epoch 9/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5241 - accuracy: 0.7552
Epoch 10/10
16/16 [==============================] - 0s 1ms/step - loss: 0.5311 - accuracy: 0.7292
# Saving the model
[Link]('watermelon.h5')
## Part 4 - Making a single prediction
import numpy as np
from [Link] import image
import [Link] as image
test_image = image.load_img('/content/drive/My Drive/[Link]', target_size = (64, 64))
test_image = image.img_to_array(test_image)
test_image = np.expand_dims(test_image, axis = 0)
result = [Link](test_image)
training_set.class_indices
if result[0][0] == 1:
USN: 01FE21MCA023
�KLE Technological University P a g e | 18
prediction = 'caroline watermelon '
else:
prediction = 'black diamon watermelon '
print(prediction)
USN: 01FE21MCA023




![KLE Technological University
P a g e | 6
USN: 01FE21MCA023
plt.scatter(X_set[y_set == j, 0], X_set[y_set == j](https://screenshots.scribd.com/Scribd/252_100_85/326/676894927/6.jpeg)