Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Python - List Comprehension
Python - List Comprehension
Uploaded by
ahmed salemOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Python - List Comprehension
Python - List Comprehension
Uploaded by
ahmed salemCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorials Exercises Get Certified Services Bootcamps Spaces Sign Up Log in
Dark mode
Dark code
HTML CSS JAVASCRIPT SQL PYTHON JAVA PHP BOOTSTRAP HOW TO W3.CSS C C++ C# REACT R JQUERY DJANGO
Python Tutorial
Python HOME ADVERTISEMENT
Python Intro
Python Get Started
Python Syntax
Python Comments
Python Variables
Python Data Types
Python - List Comprehension
Python Numbers
❮ Previous Next ❯
Python Casting
Python Strings
Python Booleans
Python Operators List Comprehension
Python Lists
Python Lists List comprehension offers a shorter syntax when you want to create a new list based on the values of an existing list.
Access List Items Example:
Change List Items
Based on a list of fruits, you want a new list, containing only the fruits with the letter "a" in the name.
Add List Items
Remove List Items Without list comprehension you will have to write a for statement with a conditional test inside:
Loop Lists
List Comprehension
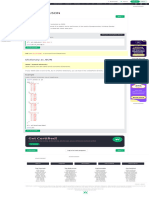
Example Get your own Python Server
Sort Lists
Copy Lists fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "kiwi", "mango"]
Join Lists newlist = []
List Methods
for x in fruits:
if "a" in x:
newlist.append(x)
print(newlist)
Try it Yourself »
With list comprehension you can do all that with only one line of code:
Example
COLOR PICKER
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "kiwi", "mango"]
newlist = [x for x in fruits if "a" in x]
print(newlist)
Try it Yourself »
ADVERTISEMENT
The Syntax
newlist = [expression for item in iterable if condition == True]
The return value is a new list, leaving the old list unchanged.
Condition
The condition is like a filter that only accepts the items that valuate to True . ADVERTISEMENT
Example
Only accept items that are not "apple":
newlist = [x for x in fruits if x != "apple"]
Try it Yourself »
The condition if x != "apple" will return True for all elements other than "apple", making the new list contain all fruits except
"apple".
The condition is optional and can be omitted:
Example
With no if statement:
newlist = [x for x in fruits]
Try it Yourself »
Iterable
The iterable can be any iterable object, like a list, tuple, set etc.
Example
You can use the range() function to create an iterable:
newlist = [x for x in range(10)]
Try it Yourself »
Same example, but with a condition:
Example
Accept only numbers lower than 5:
newlist = [x for x in range(10) if x < 5]
Try it Yourself »
Expression
The expression is the current item in the iteration, but it is also the outcome, which you can manipulate before it ends up like a
list item in the new list:
Example
Set the values in the new list to upper case:
newlist = [x.upper() for x in fruits]
Try it Yourself »
You can set the outcome to whatever you like:
Example
Set all values in the new list to 'hello':
newlist = ['hello' for x in fruits]
Try it Yourself »
The expression can also contain conditions, not like a filter, but as a way to manipulate the outcome:
Example
Return "orange" instead of "banana":
newlist = [x if x != "banana" else "orange" for x in fruits]
Try it Yourself »
The expression in the example above says:
"Return the item if it is not banana, if it is banana return orange".
❮ Previous Log in to track progress Next ❯
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Spaces Upgrade Newsletter Get Certified Report Error
Top Tutorials Top References Top Examples Get Certified
HTML Tutorial HTML Reference HTML Examples HTML Certificate
CSS Tutorial CSS Reference CSS Examples CSS Certificate
JavaScript Tutorial JavaScript Reference JavaScript Examples JavaScript Certificate
How To Tutorial SQL Reference How To Examples Front End Certificate
SQL Tutorial Python Reference SQL Examples SQL Certificate
Python Tutorial W3.CSS Reference Python Examples Python Certificate
W3.CSS Tutorial Bootstrap Reference W3.CSS Examples PHP Certificate
Bootstrap Tutorial PHP Reference Bootstrap Examples jQuery Certificate
PHP Tutorial HTML Colors PHP Examples Java Certificate
Java Tutorial Java Reference Java Examples C++ Certificate
C++ Tutorial Angular Reference XML Examples C# Certificate
jQuery Tutorial jQuery Reference jQuery Examples XML Certificate
FORUM | ABOUT
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we
cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.
Copyright 1999-2023 by Refsnes Data. All Rights Reserved.
W3Schools is Powered by W3.CSS.
You might also like
- Powershell Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pagePowershell Cheat Sheet PDFzC6MuNiW100% (1)
- Microstrategy Test BreakdownDocument19 pagesMicrostrategy Test BreakdownmicrostrategyhydNo ratings yet
- Python - Access List ItemsDocument1 pagePython - Access List Itemsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python For LoopsDocument1 pagePython For Loopsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python RegExDocument1 pagePython RegExahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python - Join SetsDocument1 pagePython - Join Setsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python Data TypesDocument1 pagePython Data Typesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python - Loop DictionariesDocument1 pagePython - Loop Dictionariesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- NumPy Ufuncs - ProductsDocument1 pageNumPy Ufuncs - Productsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python RegExDocument11 pagesPython RegExFoxNo ratings yet
- Python NumbersDocument1 pagePython Numbersahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python ArraysDocument1 pagePython Arraysahmed salemNo ratings yet
- IS231: Web Technology Python: By: Neamat El TaziDocument79 pagesIS231: Web Technology Python: By: Neamat El Taziahmed karamNo ratings yet
- List Tuple Dictionary BooleanDocument7 pagesList Tuple Dictionary Booleansandeep sharmaNo ratings yet
- NumPy Joining ArrayDocument1 pageNumPy Joining Arrayahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python - Loop Tuples 1Document8 pagesPython - Loop Tuples 1huzefa.boy.boyNo ratings yet
- WWW W3schools Com Python Python Operators ASPDocument8 pagesWWW W3schools Com Python Python Operators ASPIsac MartinsNo ratings yet
- Python Lesson 6Document12 pagesPython Lesson 6aliNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument17 pagesPythonAli SalamehNo ratings yet
- 2 PythonDocument26 pages2 PythonRedHatNo ratings yet
- Unpack A Collection: "Orange" "Banana" "Cherry"Document37 pagesUnpack A Collection: "Orange" "Banana" "Cherry"Shubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Programing ConceptDocument10 pagesPrograming Conceptsalman ahsanNo ratings yet
- 2.data Types and OperatorsDocument18 pages2.data Types and OperatorsKomal pandeyNo ratings yet
- Pandas - Cleaning Empty CellsDocument1 pagePandas - Cleaning Empty Cellsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument10 pagesPythonManisha SolankiNo ratings yet
- Python Lesson 7Document8 pagesPython Lesson 7z201033725No ratings yet
- Set, String, TupleDocument22 pagesSet, String, Tupleaakimbekov20No ratings yet
- Array List VBADocument3 pagesArray List VBAMak Un NanbanNo ratings yet
- PHP OperatorsDocument10 pagesPHP OperatorsDhanraj pawarNo ratings yet
- NumPy Ufuncs - LogsDocument1 pageNumPy Ufuncs - Logsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Qusetion Bank AnswersDocument9 pagesQusetion Bank AnswersgokulNo ratings yet
- Python AssignmentDocument21 pagesPython AssignmentJayant Deshmukh100% (1)
- NumPy Ufuncs - SummationsDocument1 pageNumPy Ufuncs - Summationsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument26 pagesPythonanimeshNo ratings yet
- Python Lesson 2Document6 pagesPython Lesson 2aliNo ratings yet
- JavaScript ArraysDocument13 pagesJavaScript ArraysVaibhav KaleNo ratings yet
- Python Programming NotesDocument76 pagesPython Programming NotesJayyant ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- JavaScript Array MethodsDocument5 pagesJavaScript Array Methodsursu_padure_scr100% (1)
- Python Range Function: Built-In FunctionsDocument36 pagesPython Range Function: Built-In FunctionsJoffre Ramiro Pesantez VerdezotoNo ratings yet
- Python Lesson 5Document5 pagesPython Lesson 5aliNo ratings yet
- NumPy Ufuncs - Simple ArithmeticDocument1 pageNumPy Ufuncs - Simple Arithmeticahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Elective PythonDocument17 pagesElective PythonHygeia Knoll Cloa BorjaNo ratings yet
- L 3-Python CollectionsDocument57 pagesL 3-Python CollectionsHoney PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Data TypesDocument12 pagesData TypesshantanuNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Linker in TH Translation ProcessDocument31 pagesThe Role of The Linker in TH Translation ProcessMeron McphersonNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesPython Cheat Sheet PDFWisdom BasseyNo ratings yet
- Python Basics: Note The Comma!Document3 pagesPython Basics: Note The Comma!susheelkumarNo ratings yet
- Python Basics: Note The Comma!Document3 pagesPython Basics: Note The Comma!susheelkumarNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesPython Cheat Sheet PDFsusheelkumarNo ratings yet
- R19 Python UNIT - 3 (Ref-2)Document41 pagesR19 Python UNIT - 3 (Ref-2)srinivas pNo ratings yet
- Slides IsabelleDocument186 pagesSlides IsabelleVasudevan ARVNo ratings yet
- Random PermutationsDocument1 pageRandom Permutationsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python FunctionDocument11 pagesPython FunctionSoe Kalayar NaingNo ratings yet
- Python OperatorsDocument10 pagesPython OperatorsnezerakuttehNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument25 pagesUnit 2 NotesarjunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document27 pagesLecture 2Sahil AgarwalNo ratings yet
- UNIT1 - PDS - Basic PythonDocument130 pagesUNIT1 - PDS - Basic PythonAryan bariyaNo ratings yet
- prl1007 - Python Data StructuresDocument4 pagesprl1007 - Python Data StructuresSony AsampalliNo ratings yet
- Python List 02Document27 pagesPython List 02Syed Kamran Ahmad1No ratings yet
- EML4930/EML6934: Lecture 01 - About Python: Basics: Data Types, Math, Logic, If StatementDocument35 pagesEML4930/EML6934: Lecture 01 - About Python: Basics: Data Types, Math, Logic, If StatementKingsley Etornam AnkuNo ratings yet
- Python - Join TuplesDocument1 pagePython - Join Tuplesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python - Copy DictionariesDocument1 pagePython - Copy Dictionariesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python ListsDocument1 pagePython Listsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Matplotlib PlottingDocument1 pageMatplotlib Plottingahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python Machine Learning Scatter PlotDocument1 pagePython Machine Learning Scatter Plotahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Logistic DistributionDocument1 pageLogistic Distributionahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python Machine Learning Linear RegressionDocument1 pagePython Machine Learning Linear Regressionahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python NumbersDocument1 pagePython Numbersahmed salemNo ratings yet
- NumPy Data TypesDocument1 pageNumPy Data Typesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Pandas - Cleaning Empty CellsDocument1 pagePandas - Cleaning Empty Cellsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Pandas - Removing DuplicatesDocument1 pagePandas - Removing Duplicatesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python - Change List ItemsDocument1 pagePython - Change List Itemsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python IteratorsDocument1 pagePython Iteratorsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python InheritanceDocument1 pagePython Inheritanceahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Pandas SeriesDocument1 pagePandas Seriesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Pandas TutorialDocument1 pagePandas Tutorialahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python - Update TuplesDocument1 pagePython - Update Tuplesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- NumPy Ufuncs - SummationsDocument1 pageNumPy Ufuncs - Summationsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- NumPy Creating ArraysDocument1 pageNumPy Creating Arraysahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Pandas Read JSONDocument1 pagePandas Read JSONahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python BooleansDocument1 pagePython Booleansahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python JSONDocument1 pagePython JSONahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python Variables - Assign Multiple ValuesDocument1 pagePython Variables - Assign Multiple Valuesahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Pareto DistributionDocument1 pagePareto Distributionahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Pandas - Cleaning Data of Wrong FormatDocument1 pagePandas - Cleaning Data of Wrong Formatahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python Machine Learning - Logistic RegressionDocument1 pagePython Machine Learning - Logistic Regressionahmed salemNo ratings yet
- NumPy Array Copy Vs ViewDocument1 pageNumPy Array Copy Vs Viewahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Matplotlib HistogramsDocument1 pageMatplotlib Histogramsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python While LoopsDocument1 pagePython While Loopsahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Python MathDocument1 pagePython Mathahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Arc Flash Hazard Calculation in 9 Steps Using IEEE 1584 - EEPDocument4 pagesArc Flash Hazard Calculation in 9 Steps Using IEEE 1584 - EEPShung Tak ChanNo ratings yet
- User Manual of DS-7100&DS-7200HI Series DVRDocument159 pagesUser Manual of DS-7100&DS-7200HI Series DVRarturo0diaz_1No ratings yet
- AdoDocument64 pagesAdofpgrande822No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 The Project Management and Information Technology ContextDocument29 pagesLecture 2 The Project Management and Information Technology ContextEdward ChachaNo ratings yet
- SOC Selected Optimized Coordination IEC Coordination Tables For Motor ProtectionDocument4 pagesSOC Selected Optimized Coordination IEC Coordination Tables For Motor ProtectionSattawat PuntaNo ratings yet
- Metropolis AMS) Release 1.0 Through 7.2 Installation GuideDocument256 pagesMetropolis AMS) Release 1.0 Through 7.2 Installation GuideFireNo ratings yet
- The Title Goes Here With Each Initial Letter Capitalized: Author's Name and Author's NameDocument8 pagesThe Title Goes Here With Each Initial Letter Capitalized: Author's Name and Author's NameAfraaz SyedNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Part 4 AssessmentDocument3 pagesUnit 5 Part 4 AssessmentDonovan DettmerNo ratings yet
- Symmetry-Corrected RMSD Calculations in PythonDocument7 pagesSymmetry-Corrected RMSD Calculations in PythonmayaazwirNo ratings yet
- Climate Models Challenges For Fortran Development ToolsDocument8 pagesClimate Models Challenges For Fortran Development ToolsCarlos EncisoNo ratings yet
- Ibook G4 Hard Drive Replacement - IfixitDocument15 pagesIbook G4 Hard Drive Replacement - IfixitdxbugsNo ratings yet
- KKJJJDocument2 pagesKKJJJAndrosabak communityNo ratings yet
- Pico 8Document21 pagesPico 8Heji ZulkunzNo ratings yet
- NodeB Commission NewDocument20 pagesNodeB Commission NewRonald PitchblackNo ratings yet
- Maintenance: MM-36D6 MM-36D6Document2 pagesMaintenance: MM-36D6 MM-36D6topansaputraNo ratings yet
- Sier BR P Sier-Brochure 20201224Document7 pagesSier BR P Sier-Brochure 20201224yane schmidhamerNo ratings yet
- 5.1.1.7 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesDocument9 pages5.1.1.7 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesAlex Box0% (1)
- Model COC Exam ITSS 2 CODE002Document9 pagesModel COC Exam ITSS 2 CODE002bisrat100% (1)
- Guidelines Imagesv 2Document6 pagesGuidelines Imagesv 2hardikkishan2001No ratings yet
- Certifying Authorities Rules 2000Document27 pagesCertifying Authorities Rules 2000antcbeNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE 1 OCT II Drilling PDFDocument9 pagesPRACTICE 1 OCT II Drilling PDFAmar BenAmarNo ratings yet
- Opentext Enterprise Content Management Ecm Content Server Product OverviewDocument4 pagesOpentext Enterprise Content Management Ecm Content Server Product OverviewUniCluster100% (1)
- In 4Document2 pagesIn 4AngelinNo ratings yet
- At P DesignerDocument46 pagesAt P DesignerdankorankoNo ratings yet
- Panaview ManualDocument128 pagesPanaview ManualShahnawaz SalimNo ratings yet
- Summer IntershipDocument65 pagesSummer IntershipAkshitaNo ratings yet
- Liquor Permit ApplicationDocument1 pageLiquor Permit ApplicationjssoufiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Industrial Robot ProgrammingDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Industrial Robot ProgrammingwreathbearerNo ratings yet
- How To Perform Dunning - SAP F150Document12 pagesHow To Perform Dunning - SAP F150VickyNo ratings yet