Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Post2019 CS-1011
Uploaded by
Jaume SanahujaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Post2019 CS-1011
Uploaded by
Jaume SanahujaCopyright:
Available Formats
Microfracture with synthetic extracellular matrix application as a viable treatment option for first metatarsophalangeal joint osteochondritis dessicans
Nicole A. Bauerly, DPM, FACFAS, Kimberly L. Bobbitt, DPM, FACFAS, Matthew J. Tschudy, DPM
Hennepin Healthcare, Minneapolis, MN CS-1011
]
Statement of Purpose Methodology and Procedure Continued Surgical technique continued Patient is currently in regular shoe gear and ambulating with minimal
Subchondral drilling with application of a synthetic extracellular cartilage Each patient underwent subchondral drilling along with the application of Results Continued pain, but is unable to return to full sporting activity level.
matrix for the treatment of traumatic osteochondral defects are an extracellular cartilage matrix. Calcaneal bone mineral aspirate (BMA)
routinely performed in other joints, however reported less common in was harvested and mixed with the extracellular matrix. Four of the six
the first metatarsal phalangeal joint (1st MTPJ) . To determine if this is a patients had additional decompressive osteotomies or cheilectomies
viable treatment option – preventing the advancement of osteoarthritis performed. Analysis and Discussion:
(OA) and return patients back to pre-injury activity and pain levels.
The goals of this procedure were to reduce pain, to increase function,
Literature Review Surgical Technique and to prevent long-term joint arthrosis. This case series shows that
Osteochondral lesions or osteochondritis dessicans, usually leads to microfracture with biocartilage application with BMA could be a viable
Patients were placed in the Supine position. Prior to inflation of the treatment option for osteochondral defect of the first metatarsal head.
progressive osteoarthritis. These lesions in the 1st MTPJ are either tourniquet BMA was harvested from the calcaneus, see figure 2.
biomechanical, years of wear and tear, or trauma and can lead to hallux Current data shows that 5/6 have returned to pre injury activity level
limitus/rigidus. In the literature lesions of the knee and ankle are well with minimal to no pain. One patient who continues to have ongoing pain
described with good treatment modalities, with results favoring following surgery has returned to regular shoe gear but not to full
Figure 5. Application of BMA with extracellular matrix into defect with Figure 7. Pre operative MRI of patient 3 showing a 0.5 cm in diameter by 0.2 activity. Patient is likely to need a 1st metatarsal phalangeal joint fusion,
microfracturing with extracellular matrix. However lesions of the 1st application of fibrin glue
metatarsal are not well described. Most lesions of the 1st metatarsal are cm deep lesion in the central metatarsal head. but at this time patient does not want to proceed with any further
thought to originate from trauma, this will likely leade to progressive surgery. A larger population of patients with a longer follow up is needed
Following the procedure patients were recommended a non to determine if this is a viable option to help decrease the chance of
arthritis and hallux limitus in the future. Osteochondral lesions treated weightbearing period of 4 weeks.
with subchondral drilling, curettage, microabrasion, microfracture of the Patient underwent the procedure outlined along with a cheilectomy. needing a 1st metatarsal phalangeal join fusion following an
talus have shown mixed results. In mid-term results these lesions have Intraoperative images are shown in figure 8. Patient was back to normal osteochondral lesion of the 1st MPJ. However current results and data
commonly progressed with further destruction of surrounding cartilage, Results shoe gear at 5 weeks and had returned to pre injury activity level. are promising.
possibly due to the in adequacy of the fibrocartilage and scar tissue Patient 1 who was as 66 year old male who fell from a height of 4 feet
commonly formed with these techniques. It is possible that this may be and sustained an injury to his right great to 4 months prior to being seen
the same with the 1 MTPJ and will ultimately lead to hallux rigidus. in our clinic. Patient continued to have pain across his first metatarsal
Treatment for the ankle which include osteochondral grafting, frozen phalangeal joint throughout range of motion. It was determined to obtain
osteochondral allografts or extracellular matrix help prevent hallux an MRI given the duration of the symptoms. Patient was noted to have a References
rigidus. However very few of these studies have been published in the 0.5 cm x 0.9 cm osteochondral defect of the 1st metatarsal head seen in
Figure 2. Harvesting BMA from calcaneus with Jamshidi Needle Clinical Comparison of the Osteochondral Autograft Transfer System and
literature. figure 1. Patient had an uneventful post operative period and return to Subchondral Drilling in Osteochondral Defects of the First Metatarsal Head Yong
regular shoe gear at 6 weeks and pre operative activity level with Sang Kim, MD, Eui Hyun Park, MD, Ho Jin Lee, MD, Yong Gon Koh, MD, Jin
Next the 1st metatarsal phalangeal joint was accessed through minimal pain at 18 weeks. Patient then returned to clinic at 7 months Woo Lee, MD, PhD, The American Journal of Sports Medicine Vol 40, Issue 8, pp.
standard dorsal technique. The joint was then inspected and the post operative with minimal pain to his operative side while golfing. An 1824 – 1833
Methodology and Procedure osteochondral lesion was identified (figure 3). Next using a curette the MRI was obtained (figure 6) showing resolution of patients prior Figure 8. Patient 3 intraoperative lesion in central metatarsal head after Hopson M, Stone P, Paden M. First metatarsal head osteoarticular transfer system
At Hennepin Health we have now been using Microfacture with lesion was prepared by removing the loose cartilage and curetting to osteochondral lesion. Patient had no pain with any other activities. extracellular matrix application for salvage of a failed hemicap-implant: a case report. J Foot Ankle
application of synthetic extracellular cartilage matrix for several obtain 90 degrees at all borders (figure 4). Next, subchondral drilling Surg. 2009;48(4):483-487.
patients who can recall a specific traumatic event leading to acute 1st was performed using a 0.045 k-wire. The primary surgeon then Osteochondral autogenous transplantation for an osteochondral defect of the first
MTPJ pain. Currently 6 patients have presented with acute 1st MTPJ pain determined the need for a decompressive osteotomy or cheilectomy metatarsal head: A case report, Alan B. Kravitz, DPM FACFAS, The Journal of Foot
and radiographic or MRI confirmed osteochondral defect (OCD). based on biomechanical joint structure or extent of the lesion. Finally, and Ankle Surgery, Vol. 44, Iss. 2, March - April, 2005, pp. 152-155.
the extracellular matrix combined with BMA was applied into the doi:10.1053/J.JFAS.2005.01.009
lesion. Care was taken to maintain the curvature of he metatarsal Giannini S, Vannini F. Operative treatment of osteochondral lesions of the talar
head (figure 5). Next a fibrin glue was placed over the defect. The dome: current concepts review. Foot Ankle Int. 2004;25(3):168-175.
joint was held distracted for 5 minutes to allow for the glue to dry. Surgical Treatment of a Tibial Osteochondral Defect With Debridement, Marrow
Stimulation, and Micronized Allograft Cartilage Matrix: Report of an All-
Arthroscopic Technique.Sarang DesaiJ Foot Ankle Surg. 2016 Mar-Apr; 55(2): 279–
282. Published online 2014 Sep 8. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2014.07.011
Financial Discolosures
Figure 6. MRI follow up on patient 1, 7 months from original surgery None
Table 1 shows the results of our 6 patients who underwent microfacture
with application of extracellular cartilage matrix. The average age of our
Patient 3 was a 36 year old female who had a prior bunion surgery 16
patients and time out from surgery was 45 years old and 18 months Contact Information
years prior who injured her great toe 1 month prior when falling. An MRI
was also obtained prior to surgery (figure 7.). respectively. Of our 6 patients 5 (83%) have returned to their pre injury Matthew Tschudy, DPM
activity level. Patient 6 who sustained and open fracture of the base of
Figure 1. (Patient 1) Pre operative MRI revealing OCD of the 1st metatarsal the proximal phalanx and extensor hallucis longus tendon rupture is the Matthew.Tschudy@hcmed.org
head measuring 0.5 cm x 0.9 cm. Figure 3. Identification of the Figure 4. Preparation of the lesion only patient who has not fully returned to pre injury activity level.
lesion
RESEARCH POSTER PRESENTATION DESIGN © 2012
www.PosterPresentations.com
You might also like
- The Bodyweight Warrior Program PDFDocument33 pagesThe Bodyweight Warrior Program PDFMarco Lami91% (11)
- Module 1-Ergonomics and Facilities PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 1-Ergonomics and Facilities Planninglei melendrez100% (6)
- Mind Map. Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageMind Map. Skeletal SystemMayeliz Urvina50% (2)
- Perfect Workout For WomenDocument6 pagesPerfect Workout For Women-MidsummerMan-100% (6)
- Carte de Abstracte Cimsc 2017 1Document135 pagesCarte de Abstracte Cimsc 2017 1Remus BobârnacNo ratings yet
- The METEOR Trial: No Rush To Repair A Torn Meniscus: Interpreting Key TrialsDocument7 pagesThe METEOR Trial: No Rush To Repair A Torn Meniscus: Interpreting Key TrialsLuis MiguelNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and TX Pelvic Metastases Injury07Document12 pagesEvaluation and TX Pelvic Metastases Injury07Antonio PáezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 PDFDocument23 pagesModule 2 PDFRui ViegasNo ratings yet
- Cureus 0012 00000008747Document8 pagesCureus 0012 00000008747Gustavo FredericoNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument8 pagesOsteomyelitiskenapayaNo ratings yet
- Residual Limb Complications and Management StrategiesDocument9 pagesResidual Limb Complications and Management StrategiesTarushi TanwarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fracture Management: A Review of Rehabilitation ConceptsDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fracture Management: A Review of Rehabilitation ConceptsInas MellanisaNo ratings yet
- Management of Aseptic Tibial NonunionDocument11 pagesManagement of Aseptic Tibial NonunionJawad KhanNo ratings yet
- Plantar FascitisDocument10 pagesPlantar FascitisDeffy Frans SiallaganNo ratings yet
- PR 2021 Cureus 13-1-E12870 1-9Document9 pagesPR 2021 Cureus 13-1-E12870 1-9aditya galih wicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Total Knee Arthroplasty - Opioid-Free Analgesia in A Patient With Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia A Case ReportDocument3 pagesTotal Knee Arthroplasty - Opioid-Free Analgesia in A Patient With Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia A Case ReportChristian SihiteNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation Following Meniscal Repair: A Systematic ReviewDocument12 pagesRehabilitation Following Meniscal Repair: A Systematic ReviewJulenda CintarinovaNo ratings yet
- Deena Horn DPM AACFAS, John Doolan DPM FACFAS, Adam Cirlincione FACFAS DPM Joseph Larsen DPM FACFASDocument1 pageDeena Horn DPM AACFAS, John Doolan DPM FACFAS, Adam Cirlincione FACFAS DPM Joseph Larsen DPM FACFASbaoNo ratings yet
- Prospective Study of Management of Close or CompouDocument5 pagesProspective Study of Management of Close or CompoumaudiaNo ratings yet
- Low Back Neck Pain Paper JBMTDocument8 pagesLow Back Neck Pain Paper JBMTMariusz IdzikowskiNo ratings yet
- The Rationale of Surgical Treatment in Pediatric Spine TuberculosisDocument6 pagesThe Rationale of Surgical Treatment in Pediatric Spine TuberculosisSpica KentNo ratings yet
- A 12-Week Exercise Therapy Program in Middle-Aged Patients With Degenerative Meniscus Tears: A Case Series With 1-Year Follow-UpDocument13 pagesA 12-Week Exercise Therapy Program in Middle-Aged Patients With Degenerative Meniscus Tears: A Case Series With 1-Year Follow-UpJacinta SeguraNo ratings yet
- Jkfs 32 102Document5 pagesJkfs 32 102Filip starcevicNo ratings yet
- Case Report Stensrud2012Document13 pagesCase Report Stensrud2012marcus souzaNo ratings yet
- Masquelet TechniqueDocument9 pagesMasquelet TechniqueMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNo ratings yet
- The Meniscus Is A Fibercartilagenous Structure, Which Plays A Significant Role in MaintainingDocument7 pagesThe Meniscus Is A Fibercartilagenous Structure, Which Plays A Significant Role in MaintainingStefan StefNo ratings yet
- Management of Osteoarthritis of The Knee in The Active PatientDocument11 pagesManagement of Osteoarthritis of The Knee in The Active PatientAmalia RosaNo ratings yet
- Osteochondroma Fracture in Young Athlete Bfe9f44bDocument4 pagesOsteochondroma Fracture in Young Athlete Bfe9f44bViona Ananda putriNo ratings yet
- Cel MM Derivadas de Almohadilla de Grasa Infrapatelar para Tto de Osteoartritis de RodillaDocument6 pagesCel MM Derivadas de Almohadilla de Grasa Infrapatelar para Tto de Osteoartritis de RodillaDIEGONo ratings yet
- Medicine: Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Acupuncture and GlucocorticoidDocument3 pagesMedicine: Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Acupuncture and Glucocorticoidindra coolNo ratings yet
- Adler 2007Document11 pagesAdler 2007Anand KarnawatNo ratings yet
- E000514 FullDocument6 pagesE000514 FullRenan O. Pravatta PivettaNo ratings yet
- Manual Therapy and Eccentric Exercise in The Management of Achilles TendinopathyDocument10 pagesManual Therapy and Eccentric Exercise in The Management of Achilles TendinopathyDewi YulyantiNo ratings yet
- 12.posterolateral Approach To Tibial Plafond Fractures A Case SeriesDocument4 pages12.posterolateral Approach To Tibial Plafond Fractures A Case SeriesMichael John TedjajuwanaNo ratings yet
- Basics and Best Practices of Multimodal Pain.34Document7 pagesBasics and Best Practices of Multimodal Pain.34QuangTiến ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Treatment Strategyfor Irreparable Rotator Cuff TearsDocument16 pagesTreatment Strategyfor Irreparable Rotator Cuff TearshawkjohnNo ratings yet
- Role of Ligamentotaxis in Management of Comminuted Intra/ Juxta Articular FracturesDocument3 pagesRole of Ligamentotaxis in Management of Comminuted Intra/ Juxta Articular FracturesNidhish PatelNo ratings yet
- Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy: Stroke December 2004Document5 pagesConstraint-Induced Movement Therapy: Stroke December 2004Emilia LaudaniNo ratings yet
- Arthroplasty Today: Original ResearchDocument8 pagesArthroplasty Today: Original ResearchAndhi Riawan Eko WiikramatunggadewaNo ratings yet
- Buck Reapir EPLDocument7 pagesBuck Reapir EPLMacaGumucioNo ratings yet
- ET 4. - Iatrogenic - Segmental - Defect - How - I - Debride.3. JOT 2017Document7 pagesET 4. - Iatrogenic - Segmental - Defect - How - I - Debride.3. JOT 2017Enrique Morales MiguelNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Cyriax Friction Massage Along With Ultrasound Therapy in Patients With Plantar FascitisDocument9 pagesEffectiveness of Cyriax Friction Massage Along With Ultrasound Therapy in Patients With Plantar FascitisLuís CorreiaNo ratings yet
- Mar2012 CC NoyesDocument17 pagesMar2012 CC NoyesJavierLarenasNo ratings yet
- MG GiganteDocument6 pagesMG GiganteomNo ratings yet
- Biological Approaches For Cartilage RepairDocument9 pagesBiological Approaches For Cartilage RepairPoppyA.NamiraNo ratings yet
- Iowaorthj00001 0076Document10 pagesIowaorthj00001 0076alyek92No ratings yet
- Banc Zero W Ski 2014Document16 pagesBanc Zero W Ski 2014Vitória GuimarãesNo ratings yet
- Guarda Nardin 2008Document10 pagesGuarda Nardin 20086mqpjqh2vqNo ratings yet
- Vertical Ridge AurmentationDocument23 pagesVertical Ridge AurmentationPirman SyachNo ratings yet
- Total Hip and Total Knee Replacement Post Operatif Nursing ManagementDocument5 pagesTotal Hip and Total Knee Replacement Post Operatif Nursing ManagementAnas KhafidNo ratings yet
- Man Ther 2013 Barra LópezDocument7 pagesMan Ther 2013 Barra LópezRuggiero CannitoNo ratings yet
- Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation TDCS in M - 2024 - International JourDocument5 pagesTranscranial Direct Current Stimulation TDCS in M - 2024 - International JourRonald QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Preprosthetic and Reconstructive SurgeryDocument32 pagesPreprosthetic and Reconstructive Surgeryruoiconmapu100% (1)
- Agonist Antagonist Myoneural InterfaceDocument10 pagesAgonist Antagonist Myoneural InterfaceJorge CamotesNo ratings yet
- Dolor LumbarDocument11 pagesDolor LumbarNataliaNo ratings yet
- Divyanshu KUmar - FINALDocument5 pagesDivyanshu KUmar - FINALSNo ratings yet
- IASTM and Stretching Plantar FasciitisDocument11 pagesIASTM and Stretching Plantar FasciitisNicolás Ayelef ParraguezNo ratings yet
- Effective Use of Viscosupplementation After Knee Arthroscopy: Experience From A Working GroupDocument10 pagesEffective Use of Viscosupplementation After Knee Arthroscopy: Experience From A Working GroupIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Sprain Ankle JurnalDocument9 pagesSprain Ankle JurnalRahmadanii RahmadaniiNo ratings yet
- #PENTING Bell1983Document7 pages#PENTING Bell1983Octapaedi SoetomoNo ratings yet
- Mini FixatorsDocument4 pagesMini FixatorsRajNo ratings yet
- IndianSpineJ22138-5978405 163624Document8 pagesIndianSpineJ22138-5978405 163624Josh JoshiNo ratings yet
- The Direct Superior Approach in Total Hip ArthroplastyDocument5 pagesThe Direct Superior Approach in Total Hip ArthroplastytripodegrandeNo ratings yet
- Principles of Manual Medicine for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Arthrokinematic Approach-Hakata MethodFrom EverandPrinciples of Manual Medicine for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Arthrokinematic Approach-Hakata MethodShigehiko KatadaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Tumor Surgery: A Case-Based ApproachFrom EverandSpinal Tumor Surgery: A Case-Based ApproachDaniel M. SciubbaNo ratings yet
- Medicine The American Journal of SportsDocument11 pagesMedicine The American Journal of SportsJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- DC 1cantDocument7 pagesDC 1cantJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Fencing InjuriesDocument72 pagesFencing InjuriesJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Top 10 MistakesDocument7 pagesTop 10 MistakesJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Pericles: Best With 2 or 4 Players 1 Hour/Turn War Scenario - 3-5 HrsDocument6 pagesPericles: Best With 2 or 4 Players 1 Hour/Turn War Scenario - 3-5 HrsJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
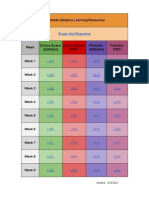
- Free Distance Learning ToolsDocument2 pagesFree Distance Learning ToolsJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- TK 10 Day PlanDocument109 pagesTK 10 Day PlanJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- 6th 10 Day PlanDocument139 pages6th 10 Day PlanJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- K 10 Day PlanDocument154 pagesK 10 Day PlanJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grade 10 Day PlanDocument138 pages2nd Grade 10 Day PlanJaume Sanahuja100% (3)
- 8th Grade 10 Day PlanDocument151 pages8th Grade 10 Day PlanJaume Sanahuja67% (3)
- 4th 10 Day PlanDocument106 pages4th 10 Day PlanJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade 10 Day PlanDocument131 pages7th Grade 10 Day PlanJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- 1st Grade Resources For Distance Learning PDFDocument1 page1st Grade Resources For Distance Learning PDFJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Organise PSDocument57 pagesOrganise PSJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Guia Esgrima Per A ParesDocument55 pagesGuia Esgrima Per A ParesJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- ETC Book 2011Document176 pagesETC Book 2011Jaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Guia de Compra Equipament EsgrimaDocument26 pagesGuia de Compra Equipament EsgrimaJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Kit - Remote LearningDocument1 pageEmergency Kit - Remote LearningJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Guia Esgrima Per A ParesDocument55 pagesGuia Esgrima Per A ParesJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Shakespeare SonnetsDocument165 pagesShakespeare SonnetsJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Bodenheimer PrimCareDocument4 pagesBodenheimer PrimCareJaume SanahujaNo ratings yet
- Radiologic History Exhibit Musculoskeletal EponymsDocument19 pagesRadiologic History Exhibit Musculoskeletal EponymsSangeetha KumariNo ratings yet
- Pleural MCQS MedicineDocument17 pagesPleural MCQS MedicineCheryls Raju100% (1)
- Pain and Effusion and Quadriceps Activation and StrengthDocument6 pagesPain and Effusion and Quadriceps Activation and StrengthЯнь НгуенNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report BLSDocument6 pagesNarrative Report BLSSoriano Armenio67% (3)
- Wild Ginger Restaurant Trade Dress Trade Secrets Complaint PDFDocument32 pagesWild Ginger Restaurant Trade Dress Trade Secrets Complaint PDFMark JaffeNo ratings yet
- 4102.0 - Australian Social Trends, 2007Document9 pages4102.0 - Australian Social Trends, 2007tina m fayzaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Document17 pagesThe Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Leo Cordel Jr.No ratings yet
- Case BriefDocument4 pagesCase BriefAnirudh Arora33% (3)
- 17-19 Use of Force, Fitness For Duty (Exonerated)Document14 pages17-19 Use of Force, Fitness For Duty (Exonerated)Whitman County WatchNo ratings yet
- CTEV - Congenital Club FootDocument43 pagesCTEV - Congenital Club FootIrfan Ali ShujahNo ratings yet
- Jarvis: Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 6 EditionDocument6 pagesJarvis: Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 6 Editionaden100% (1)
- UPS2000-A - (1 KVA-3 KVA) User ManualDocument83 pagesUPS2000-A - (1 KVA-3 KVA) User ManualKasirNo ratings yet
- Ward WarrantDocument6 pagesWard WarrantBobby Martinez100% (1)
- Howard Leight Hearing Conservation SeminarDocument89 pagesHoward Leight Hearing Conservation SeminarPhewit TymeNo ratings yet
- Hand and Upper ExtremityDocument722 pagesHand and Upper ExtremityPaul Radulescu - Fizioterapeut88% (8)
- A Bilateral Subdural Hematoma Case Report 2165 7548.1000112 PDFDocument2 pagesA Bilateral Subdural Hematoma Case Report 2165 7548.1000112 PDFPutra GagahNo ratings yet
- Bauer Reversible Hammer Drill 1992e B ManualDocument18 pagesBauer Reversible Hammer Drill 1992e B ManualBinyamin AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Basic Life SupportDocument50 pagesPediatric Basic Life SupportnurmauliarizkyNo ratings yet
- Inguinal CanalDocument22 pagesInguinal CanalAaryan PatelNo ratings yet
- Coaches Checklist For Offensive Game Planning and Goaline Play Calling SeriesDocument10 pagesCoaches Checklist For Offensive Game Planning and Goaline Play Calling Seriesw_dees100% (1)
- Argument EssayDocument4 pagesArgument Essayapi-358284634No ratings yet
- Tyranids: Warhammer 40,000 Codex: Official Update Version 1.2Document5 pagesTyranids: Warhammer 40,000 Codex: Official Update Version 1.2Adam Russell ReevesNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics: Name:Jibran Rarh Pgdbm-A Roll No - 35Document69 pagesErgonomics: Name:Jibran Rarh Pgdbm-A Roll No - 35jibranrarhNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Trauma Activation FeeDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The Trauma Activation Feenlprofits100% (1)
- Kuliah 3 - Fisiologi Sistem Muskuloskeletal (Dr. Adelia Handoko)Document36 pagesKuliah 3 - Fisiologi Sistem Muskuloskeletal (Dr. Adelia Handoko)Linda ayuNo ratings yet