Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osteoporosis
Uploaded by
lisavanseterspooCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Osteoporosis
Uploaded by
lisavanseterspooCopyright:
Available Formats
Osteoporosis
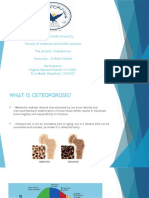
Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by low bone mass and deterioration of the
skeleton leading to bone fragility and a predisposition to fractures. Osteoporosis is a major
cause of morbidity and mortality.
Common diseases associated with osteoporosis:
o Endocrine disorders
o Gastrointestinal disorders
o Hepatic disorders
o Nutritional Disorders
o Hematological disorders
o Renal Disorders
o Autoimmune disorders
Osteoporosis can be classified into two main groups:
o Primary osteoporosis
o Secondary osteoporosis
Primary Osteoporosis Type I
It is also known as postmenopausal osteoporosis. It is caused by the deficiency of estrogen,
mainly affecting the trabecular bone; therefore, women are more susceptible to osteoporosis
than men.
Primary Osteoporosis Type II
It is also called senile osteoporosis, and it is related to bone mass lost due to the aging of
cortical and trabecular bones.
Secondary Osteoporosis
Different diseases, medications, and lifestyle changes can cause osteoporosis
Diagnosis
Bone mineral density to be below 2.5 or more below that of the mean level for a young adult
reference population
Note: Osteoporosis is often a silent disease until the patient experiences a fracture. When a
patient experiences a fracture is classified as ‘severe osteoporosis’.
Basic Treatment Recommendations
o intake of calcium and vitamin D (fundamental for any osteoporosis prevention or
treatment)
o including lifelong regular weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises
o cessation of tobacco use
o cessation of excess alcohol intake
o of risk factors for falling
Readings
Sözen, T., Özışık, L., & Başaran, N. Ç. (2017). An overview and management of
osteoporosis. European journal of rheumatology, 4(1), 46.
You might also like
- OsteoporosisDocument3 pagesOsteoporosissamtaynbNo ratings yet
- Defining OsteoporosisDocument11 pagesDefining OsteoporosisMelissa RosariNo ratings yet
- OSTEOPOROSISDocument3 pagesOSTEOPOROSISHenry KaweesaNo ratings yet
- Biology 310 Assignment OsteoporosisDocument24 pagesBiology 310 Assignment OsteoporosisMohd IzwanNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis PDFDocument15 pagesOsteoporosis PDFعبدالرحمن علىNo ratings yet
- Bone DiseaseDocument4 pagesBone DiseaseHuzaifa CHNo ratings yet
- Final Project PDFDocument75 pagesFinal Project PDFuzzal ahmedNo ratings yet
- What Is Osteopenia?: What Are Causes and Risk Factors For Osteopenia?Document2 pagesWhat Is Osteopenia?: What Are Causes and Risk Factors For Osteopenia?Jeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠٢-٢٣ في ٥.١٨.٥١ مDocument41 pagesلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠٢-٢٣ في ٥.١٨.٥١ م5rdqfr98ngNo ratings yet
- ASKEP OsteoporosisDocument41 pagesASKEP OsteoporosisMaya PinteNo ratings yet
- Referat OsteoporosisDocument32 pagesReferat OsteoporosisMarzuqi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument6 pagesOsteoporosisKarla Mariana Gallegos P�rezNo ratings yet
- THE Ultimate Guide To Osteoporos ISDocument7 pagesTHE Ultimate Guide To Osteoporos ISMohsen Sarrafan ChaharsoughiNo ratings yet
- Novartis Osteoporosis Slide KitDocument42 pagesNovartis Osteoporosis Slide KitShravanti SatyanandNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis DR SawsawDocument19 pagesOsteoporosis DR SawsawNariman SternNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument6 pagesOsteoporosisabdulghaffarsp8No ratings yet
- Chap 18 Musculoskeletal SystemDocument29 pagesChap 18 Musculoskeletal SystemAna Dominique Espia100% (1)
- OsteoperosisDocument4 pagesOsteoperosisifeoluwasubomi.adeleyeNo ratings yet
- What Is Osteoporosis?Document6 pagesWhat Is Osteoporosis?MaryamNo ratings yet
- Osteo Pros IsDocument6 pagesOsteo Pros IsMaryamNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument11 pagesOsteoporosis906 SoNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument16 pagesOsteoporosisDe Sesto Rhys CarloNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Signs and SymptomsDocument9 pagesOsteoporosis: Signs and SymptomschelseachoirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document26 pagesLecture 4tamtamtamtama0No ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument6 pagesOsteoporosiskingNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument6 pagesOsteoporosiskingNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument6 pagesOsteoporosiskingNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument6 pagesOsteoporosiskingNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument11 pagesOsteoporosisAdine Jeminah LimonNo ratings yet
- Diseases and Disorders of The Skeletal SystemDocument32 pagesDiseases and Disorders of The Skeletal SystemPatrisha Georgia AmitenNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Skeletal SystemDocument16 pagesDiseases of The Skeletal SystemNoor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- Your Paragraph TextDocument21 pagesYour Paragraph TextPrincess Aliah SolmeronNo ratings yet
- OsteoDocument2 pagesOsteoChristine Katherine LibuitNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 - Metabolic Bone DisordersDocument35 pagesUnit - 5 - Metabolic Bone Disorderskelemwork WaleNo ratings yet
- Final EbookDocument22 pagesFinal Ebookjinalgpatel11998No ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument13 pagesOsteoporosisRuaa MalekNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: Prepared By: Md. Giash Uddin Lecturer, Dept. of Pharmacy University of ChittagongDocument30 pagesOsteoporosis: Prepared By: Md. Giash Uddin Lecturer, Dept. of Pharmacy University of Chittagongsamiul bashirNo ratings yet
- Men OsteoporosisDocument5 pagesMen Osteoporosisapi-309082881No ratings yet
- Lorentz On 2015Document23 pagesLorentz On 2015Sanita AurinNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis Final AssignmentDocument7 pagesOsteoporosis Final AssignmentMaryamNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis enDocument14 pagesOsteoporosis enFOONG YI KUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Patogenesis Osteoporosis V PDFDocument15 pagesPatogenesis Osteoporosis V PDFaji pangestuNo ratings yet
- Patogenesis Osteoporosis VDocument15 pagesPatogenesis Osteoporosis Vaji pangestuNo ratings yet
- Presented by Dr. Faisal Muttaqien: 12 February 08Document40 pagesPresented by Dr. Faisal Muttaqien: 12 February 08Faisal M100% (1)
- Bio Project File 2Document19 pagesBio Project File 2jiya singhNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Presentation (Osteoporosis)Document24 pagesBiochemistry Presentation (Osteoporosis)Ahmed AlyNo ratings yet
- Bone Diseasesdisorder Adult.Document22 pagesBone Diseasesdisorder Adult.amal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument12 pagesOsteoporosisAzharul Islam ArjuNo ratings yet
- A Review On Some Physiological Studies Related To OsteoporosisDocument14 pagesA Review On Some Physiological Studies Related To OsteoporosisAndy KumarNo ratings yet
- OsteoporosisDocument15 pagesOsteoporosisapi-302473168No ratings yet
- 5 .Document28 pages5 .Dewy Shinta PagalaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 01: OsteoporosisDocument7 pagesAssignment: 01: OsteoporosisMaryamNo ratings yet
- Rad. Patho - Skeletal SystemDocument77 pagesRad. Patho - Skeletal SystemNikko L. Pescueso100% (1)
- Definisi OsteoporosisDocument3 pagesDefinisi OsteoporosisimissgnaNo ratings yet
- Mpu3313 - v2 Mohamad Shafik Bin Supaat 821022145381001Document12 pagesMpu3313 - v2 Mohamad Shafik Bin Supaat 821022145381001محمد شافق ابنو شافعتNo ratings yet
- What Is Osteoporosis?: Osteoposis Is A Disease ofDocument48 pagesWhat Is Osteoporosis?: Osteoposis Is A Disease ofTaruna GargNo ratings yet
- What Is OsteoporosisDocument4 pagesWhat Is OsteoporosisYanis Indiana YacmaNo ratings yet
- Bone Disease, Any of The Diseases or Injuries That Affect HumanDocument10 pagesBone Disease, Any of The Diseases or Injuries That Affect Humanrichelle joy reyesNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis: How To Treat Osteoporosis: How To Prevent Osteoporosis: Along With Nutrition, Diet And Exercise For OsteoporosisFrom EverandOsteoporosis: How To Treat Osteoporosis: How To Prevent Osteoporosis: Along With Nutrition, Diet And Exercise For OsteoporosisNo ratings yet