Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HA Final Exam
Uploaded by
cariazomuriahcarylle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pages1) The correct order for abdominal assessment is inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation.
2) Normal bowel sounds should be heard 5-35 times per minute in each abdominal quadrant.
3) An important part of abdominal assessment is explaining each step to the patient.
This summarizes the key information regarding the correct process and important considerations for performing an abdominal assessment according to the provided document.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The correct order for abdominal assessment is inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation.
2) Normal bowel sounds should be heard 5-35 times per minute in each abdominal quadrant.
3) An important part of abdominal assessment is explaining each step to the patient.
This summarizes the key information regarding the correct process and important considerations for performing an abdominal assessment according to the provided document.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesHA Final Exam
Uploaded by
cariazomuriahcarylle1) The correct order for abdominal assessment is inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation.
2) Normal bowel sounds should be heard 5-35 times per minute in each abdominal quadrant.
3) An important part of abdominal assessment is explaining each step to the patient.
This summarizes the key information regarding the correct process and important considerations for performing an abdominal assessment according to the provided document.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
1.
) Nurse Anthony is nurse clinical instructor -Should not detect masses
discussing about Abdomenal Assessment. -May locate the margins of the liver
What is the correct order for abdominal -All of the above
assessment?
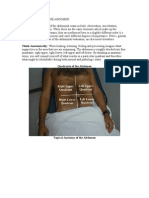
* 6.) What organs are in the RUQ of the
-Inspection, palpation, auscultation, percussion abdomen? (Select and complete all 7 correct
-Inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation answers)
-Auscultation, inspection, palpation, *
percussion -The head of the pancreas,
-Palpation, inspection, auscultation, percussion -cardiac organ
-The gallbladder,
2.) Nurse Kris is havig her assessment on the -And part of the ascending and transverse
bowel status of her patient. How often should colon.
normal bowel sounds be heard in each -The right kidney and adrenal gland,
quadrant of the abdomen? -The liver
* -cerebro spinal fluid
-5-35 times per minute -The duodenum,
-Less than 5 times per minute -The hepatic flexure of the colon
-15-20 times per minute
-20-40 times per minute 7.) What organs are in the RLQ of the
abdomen? (Select and complete all 4 correct
3.) Nurse Ben is performing his routine answers)
abdomenal assessment to Jen, the newly *
admitted patient in the ward. Which of the -scapula
following is an important part of performing -The right ureter,
an abdominal assessment? -right ovary and fallopian tube
* -The cecum
-Completing the assessment as quickly as -ciatic nerve
possible -The appendix,
-Stopping the assessment if the patient has any
tenderness 8.) When doing abdomenal assessment how do
-Explaining each step of the assessment to the you relax a patient for an abdominal exam?
patient (Select and complete the 5 correct answers)
-Having the patient breathe normally at all *
times Correct answer
-ensure that the stethoscope is warm and not
4.) Josephine is a newly hired nurse having a too cold
hard time performing her abdominal -warm and comfortable room
assessment with her patient. What should you -Patient supine with arms at side or on chest
do if a patient is ticklish when you are -Pillow under head and feet
palpating the abdomen? -Imagery/deep breathing exercises
*
-Distract the patient by talking to him or her. 9.) How would nurse Thelma assess John, a
-Do not palpate the abdomen in the upper patient for possible abdominal hernia?
quadrants. *
-Do only deep palpation of all four quadrants. -A hernia is a protrusion of the abdominal
-Place your hand over the patient's hand during viscera through an abnormal opening in the
palpation muscle wall.You would be able to tell upon
inspection.
5.)Nurse Clinical Instructor Hans is -Hernia cant be palpated and imaging test such
emphasizing his lecture to her nursing students as CT Scan or Xray must be done to the
on how to properly palpate teh abdomen. The patient.
moderate and deep palpation of the abdomen -Hernia is confirmed through laboratory test
* such as MRI.
-May cause tenderness
-Hernia is not a significant finding and should *
not be included on the assessment. -Gallbladder disease
-Overuse of laxatives
10.) Patient Maritess comes into the clinic -Gastrointestinal bleeding
complaining that they have these weird marks -Localized bleeding around the anus
on their abdomen that look like silvery white
cracks but they used to look pink. What would 15.) Ascites is defines as:
you tell them? *
-A bowel obstruction
What kinds of patients would experience these -A proximal loop of the large intestine
type of marks? (Select and complete the 2 -An abnormal enlargement of the spleen
correct answers) -An abnormal accumulation of serous fluid
Correct answer: within the peritoneal cavity
-These marks are called Striae. There is
nothing to be concerned with them. They 16.) The nurse is assessing the abdomen of a
occur with excessive stretching. pregnant woman who is complaining of having
-Patients who have experienced excessive acid indigestion all the time. The nurse knows
weight gain and/or pregnancy see this as a that esophageal reflux during pregnancy can
normal finding. cause:
*
11.) A patient is suspected of having -Diarrhea
inflammation of the gallbladder, or -Pyrosis
cholecystitis. The nurse should conduct which -Dysphagia
of these techniques to assess for this -Constipation
condition?
17.) A 40-year -old man states that his
-Obturator test physician told him that he has a hernia. He
-Test for Murphy sign asks the nurse to explain what a hernia is.
-Assess for rebound tenderness Which response by the nurse is appropriate?
-Iliopsoas muscle test *
-No need to worry. Most men you age develop
12.) The nurse is percussion the seventh right hernias
intercostal space at the mid-clavicular line -A hernia is a loop bowel protruding through a
over the liver. Which sound should the nurse weak spot in the abdominal muscles.
expect to hear? -A hernia is the result of prenatal growth
abnormalities that are just causing problems
-Dullness -I’ll have to have your physicians explain this
-Tympany to you
-Resonance
-Hyperresonance 18.) Methods to enhance abdominal wall
relaxation during examination include:
13.) When palpating the abdomen of a 20- *
year-old patient, the nurse notices the presence -A cool environment
of tenderness in the left upper quadrant with -having the patient place arms above the head
deep palpation. Which of these structures is -Examining painful areas first
most likely to be involved? -Positioning the patient with the knees bent.
-Spleen 19.) Which of the following may be noted
-Sigmoid colon through inspection of the abdomen?
-Appendix *
-Gallbladder -Fluid waves, abdominal contour
-Umbilical eversion, Murphy’s sign
14.) The nurse notices that a patient has had a -Venous pattern, peristaltic waves, abdominal
black, tarry stool and recalls that a possible contour
cause would be:
-Peritoneal irritation, general tympany, 26.) An action potential:
peristaltic waves *
-Involves the outflux of negative ions to
20.) Hyperactive bowel sounds that may be depolarize the membrane
heard normally which are characteristic of -Involves the influx of negative ions to
stomach growling are: (Select all that apply). depolarize the membrane
* -Is initiated by potassium ion movements
-Loud -Is essential for nerve impulse propagation
-Soft
-Prolonged gurgles 27.) Cell bodies of the sensory neurons of the
-Tinkling spinal nerves are located in:
*
21.) The absence of bowel sounds is -The dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord
established after listening for: -The thalamus
* -The hypothalamus
-1 full minute -The ventral root ganglia of the of the spinal
-3 full minutes cord
-5 full minutes
-7 full minutes 28.) The effects of the sympathetic nervous
system are essentially opposite of the:
22.) The vital centers for the control of visceral *
activities such as heart rate, breathing blood -Motor division
pressure, swallowing and vomiting are located -Parasympathetic nervous system
in the: -Sensory division
* -Central nervous system
-Hypothalamus
-Pons 29.) Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through all
-Cerebrum of the following except:
-Medulla oblongata *
-Corpus callosum
23.) Immediately after an action potential is -Lateral ventricle
propagated, which one of the following ions -Fourth ventricle
rapidly diffuses out of the cell into the tissue -Cerebral aqueduct
fluid:
* 30.) Regulation by the nervous system
-Potassium provides:
-Sodium *
-magnesium -Relatively slow but long-lasting responses to
-calcium stimuli
-Swift, long-lasting responses to stimuli
24.) The blood-brain barrier is effective -Swift but brief responses to stimuli
against the passage of: -Relatively slow, short lives responses to
* stimuli
-Nutrients such as glucose
-Metabolic waste such as urea 31.) All the motor neurons that control skeletal
-Water muscle are:
-Anesthetics *
-Multipolar neurons
25.) The sympathetic and parasympathetic -Myelinated bipolar neurons
nervous systems are subdivisions of the: -Unipolar, unmyelinated sensory neurons
* -Proprioceptors
-Autonomic nervous system
-Voluntary nervous system
-Somatic nervous system
-Central nervous system
32.) The amorphous ground substance imparts 38.) When regard to muscle fiber arrangement
compressive forces to connective tissue and is in the pennate muscle ______.
composed of all the following EXCEPT: *
* -The fascicle are short and attach obliquely to
-Water a central tendon that runs the length of a
-Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) muscle
-Hyaluronic acid -The fascicular patter is circular
-Collagen -The fascicle forms a triangle
-The fascicle are in a fusiform arrangement
33.) The muscle spindle receptor in skeletal
muscle can be silenced by one of the following 39.) What primary determines the power of
mechanisms: muscle?
* *
-Contraction f the same muscles extrafusal -The length
fibers -The shape
-Passive stretch of the whole muscle -The number if neurons innervating it
-Stimulation of the gamma motoneuron -The total number f muscle cells available for
-Contraction of the antagonist muscles contraction
extrafusal fibers
40.) A muscle that provides the major force for
34.) Which of the following injuries occurs producing a specific movement is called
from repetitive overuse and affects the _____?
common wrist extensor origin f the extensor *
carpi radialis longus and brevis, and extensor -A synergist
digitorum ad digiti minimi? -An agonist
* -A antagonist
-Lateral epicondylitis -A fixator
-Medial epicondylitis
-Medial valgus stress overload 41.) When the term biceps, triceps or
-Fracture of the distal humerus quadriceps forms part of a muscle’s name, you
can assume that ______.
35.) Scissors demonstrate which type of lever? *
* -The muscle has two, three or four origins,
-A first-class lever respectively
-A second-class lever -The muscle is able to change direction twice,
-A third-class lever three times or four times faster than other
-A fourth-class lever muscles, respectively.
-The muscle has two, three, or four functions,
36.) What muscle is responsible for keeping respectively
your toes from dragging when walking? -The muscle has two, three or four insertions,
* respectively
-Extensor digitorum
-Tibialis anterior 42.) Which of the following statements is true
-Extensor hallicus longus regarding the total number of skeletal in the
-Fibularis tertius human body?
*
37.) What is the mojor factor controlling the -There are approximately the same number of
manner in which level work? muscles as bones: 206
* -There are approximately 350 muscles in the
-The structural characteristics of the muscle of body
the person using the lever -There are over 600 muscles in the body
-The weight of the load -If one considers the very tiny, insignificant
-The direction of the load is being moved muscles, there are over 1000 muscles in the
-The difference in the positioning of the effort, body
load and fulcrum
43.) Muscle tissue, one of the four principal -Sarcomere
types of tissue, consists chiefly of muscle cells -Sarcolayer
that are highly specialized for:
* 50.) Electrical impulses (action potentials)
-Conduction travel down ____ into the muscle cells to
-Contraction efficiently trigger muscle fibre contraction.
-Shortening *
-Lifting -Myoblastic tubules
-Transverse tubules
44.) Which of the following is NOT a type of -Longitudinal tubules
muscle tissue? -Contractile tubules
*
-Smooth
-Cardiac
-Skeletal
-Vascular
45.) Skeletal muscle tissue forms skeletal
muscles, organs that also contain each of the
following, EXCEPT:
*
-Connective tissues
-Bones
-Nerves
-Blood vessels
46.) Each cell in skeletal muscle tissue is a :
*
-single muscle fiber
-Motor unit
-Myofibril
-Pun Kinji fiber
47.) Skeletal muscles performs each pf the
following functions, EXCEPT:
*
-Maintain postures and body position
-Guards entrances and exits
-Moves contents of the digestive tract
-Support soft tissue
48.) During development, groups of _____
fuse together to form individual skeletal
muscle fibers:
*
-Myoblasts
-Myelinocytes
-Myoglobins
-Myotrophs
49.) What is another name for the cell
membrane of a muscle fibre?
*
-Sarcolemma
-Sarcoplasm
You might also like
- Lessons in Artistic Deep Breathing for Strengthening the VoiceFrom EverandLessons in Artistic Deep Breathing for Strengthening the VoiceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument59 pagesAbdominal AssessmentSIR ONE100% (1)
- AbdomenDocument3 pagesAbdomenDale Ros CollamatNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment - Yuli PutriDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment - Yuli PutriIkadek AgustianaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Physical Examination of AbdomenDocument6 pagesNotes On Physical Examination of AbdomenMarwa Al-AzzawiNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Abdomen: Prepared By: Mary Ann F. Rubio, RN, MNDocument54 pagesAssessing The Abdomen: Prepared By: Mary Ann F. Rubio, RN, MNWilma Acorin OrillinedaNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan AbdomenDocument46 pagesPemeriksaan AbdomenPrystia_RNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument4 pagesAbdominal Assessmentmarianneladislao07No ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument2 pagesAbdomenRhea Rose Turno - N1ENo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument4 pagesAbdominal Assessmentmarianneladislao07No ratings yet
- Assessing AbdomenDocument1 pageAssessing AbdomenKeesha Mae Urgelles TimogNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Script v3Document7 pagesGastrointestinal Script v3Ray ChangNo ratings yet
- Examination of The AbdomenDocument4 pagesExamination of The Abdomenjamie_rubinNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination For PSIII Edited-1Document33 pagesAbdominal Examination For PSIII Edited-1myarjddbzNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Abdomen: Psik Fikes UmmDocument12 pagesPemeriksaan Abdomen: Psik Fikes UmmAbd RahmanNo ratings yet
- SGD AppendicitisDocument11 pagesSGD Appendicitisนีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Hernia: DR - Surender Singh DhankharDocument36 pagesHernia: DR - Surender Singh DhankharBharat BhushanNo ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument9 pagesAbdomenMDNICNo ratings yet
- DR MULDocument25 pagesDR MULDesak PratiwiNo ratings yet
- NursingDocument49 pagesNursingMarieNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicitisDocument22 pagesAcute AppendicitisJOY LIMBONGNo ratings yet
- PE of The Abdomen Guide 2020Document8 pagesPE of The Abdomen Guide 2020salfopsi gaming100% (1)
- AssesssingDocument20 pagesAssesssingKRISTIAN DRAZEN MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Surg Osce SummaryDocument7 pagesSurg Osce SummaryShatha AlgahtaniNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal PainDocument5 pagesAcute Abdominal PainLM Mys100% (1)
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument6 pagesAbdominal AssessmentRhelina MinNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Exam 2020Document6 pagesAbdominal Exam 2020InhoNo ratings yet
- Assess The AbdomenDocument24 pagesAssess The AbdomenuybenesheartNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical ReviewerDocument6 pagesMedical Surgical ReviewerCatherine Kaye PerezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of The AbdomenDocument13 pagesClinical Examination of The AbdomenNur Miladiyah100% (1)
- Examination of The AbdomenDocument19 pagesExamination of The AbdomenAllen AykayNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Exam 4 Study GuideDocument31 pagesHealth Assessment Exam 4 Study GuideCeciliaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination ProcedureDocument5 pagesAbdominal Examination ProcedureAnamul hossainNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Physical Examination Skills Lab Handout Abdominal Exam IDocument4 pagesSemester 1 Physical Examination Skills Lab Handout Abdominal Exam IFlowerNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument2 pagesAbdominal Assessmentmarianneladislao07No ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination GuideDocument4 pagesAbdominal Examination GuidePhysician AssociateNo ratings yet
- HerniaDocument48 pagesHerniaAb BabyNo ratings yet
- 02 The Abdominal Exam Lab - CopDocument6 pages02 The Abdominal Exam Lab - CopBhumiShahNo ratings yet
- NCM 116Document19 pagesNCM 116Gail Leslie HernandezNo ratings yet
- 16-Checklist For Abdominal AssessmentDocument2 pages16-Checklist For Abdominal Assessmentgladz2575% (4)
- Abdominal Assessment 1Document39 pagesAbdominal Assessment 1Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Focused Abdominal Sonography in Trauma (FAST)Document56 pagesFocused Abdominal Sonography in Trauma (FAST)RannyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument16 pagesAbdominal ExaminationLana IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Seminar Topic On AppendicitisDocument17 pagesSeminar Topic On AppendicitisMohit GaurNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan AbdomenDocument91 pagesPemeriksaan AbdomenEndah Cahaya SufianyNo ratings yet
- Part 2 AbdoexamDocument36 pagesPart 2 Abdoexamapi-19641337No ratings yet
- HerniaDocument46 pagesHerniaZubairkhan SuraniNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Health AssessmentDocument11 pagesAbdominal Health Assessmentcrisel costalesNo ratings yet
- Hernia ExaminationDocument3 pagesHernia Examinationjackfruit5887No ratings yet
- 1 - Abdomen 1Document23 pages1 - Abdomen 1noushad aminNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastrointestinal SeriesDocument3 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal SeriesJanelle Ann CasuyonNo ratings yet
- Week 12 ASSESSMENT-OF-ABDOMEN-2020 PDFDocument104 pagesWeek 12 ASSESSMENT-OF-ABDOMEN-2020 PDFG4 - TURCO, SHERVIE HEART E.No ratings yet
- Abdomen Exam DetailsDocument5 pagesAbdomen Exam Detailsdidutza91No ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination-1Document88 pagesAbdominal Examination-1naveen kumar kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination Jan 23Document36 pagesAbdominal Examination Jan 23Adel hassounNo ratings yet
- Comment On Dressing or Bandages and Take Them Down, Comment On ScarsDocument4 pagesComment On Dressing or Bandages and Take Them Down, Comment On ScarsGNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination ChecklistDocument6 pagesAbdominal Examination ChecklistPalwasha MalikNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular (CVS) Examination: Procedure StepsDocument15 pagesCardiovascular (CVS) Examination: Procedure StepsGeorich NarcisoNo ratings yet
- CABITAC Histology (Digestive) FinalDocument9 pagesCABITAC Histology (Digestive) FinalZhon CabitacNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PainDocument16 pagesAbdominal PainSumit KhetarpalNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument13 pagesASSESSMENTarissa razaliNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Chapter 3 With Complete Solutions 100 23 2024Document17 pagesMedical Terminology Chapter 3 With Complete Solutions 100 23 2024Gregg ProducerNo ratings yet
- Pr1 Fullido Euphorbia Hirta FinalDocument87 pagesPr1 Fullido Euphorbia Hirta FinalCathy FullidoNo ratings yet
- Prophylactic Antibiotics For HemorrhoidectomyDocument5 pagesProphylactic Antibiotics For HemorrhoidectomyThắng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Abstract, Introduction and Statement of The Problem 1.1 AbstractDocument39 pagesAbstract, Introduction and Statement of The Problem 1.1 AbstractIrish Mae JovitaNo ratings yet
- Rafa - Patient AssesmentDocument8 pagesRafa - Patient AssesmentRafa HassanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Community Oral Health Practice For The Dental Hygienist 3rd Edition GeurinkDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Community Oral Health Practice For The Dental Hygienist 3rd Edition Geurinkchiragramallfsk7100% (43)
- Week 6 Bone Case StudyDocument7 pagesWeek 6 Bone Case StudyAndriNo ratings yet
- B.SC Nursing-2018-Question Papers-First Year-Microbiology FR PDFDocument1 pageB.SC Nursing-2018-Question Papers-First Year-Microbiology FR PDFSwapnil satputeNo ratings yet
- Plasma CutterDocument22 pagesPlasma CutterDale Beshara100% (2)
- Bacan Stone Is A Kind of Precious StonesDocument3 pagesBacan Stone Is A Kind of Precious StonesRikson TandelilinNo ratings yet
- Green Purple Playful Illustration Class Syllabus PresentationDocument21 pagesGreen Purple Playful Illustration Class Syllabus PresentationAlmira WijayaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis in Animals An African Perspective PDFDocument448 pagesTuberculosis in Animals An African Perspective PDFjjgtNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryMinerva BertumenNo ratings yet
- Petunjuk Praktikum Lung Function Test B.1Document13 pagesPetunjuk Praktikum Lung Function Test B.1Inas Nabila AlhariNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Thorax and Lung PDFDocument9 pagesAssessing The Thorax and Lung PDFYudi TrigunaNo ratings yet
- 1 Semester: Anti-Migraine Agents Are Used To Treat Migraine HeadachesDocument26 pages1 Semester: Anti-Migraine Agents Are Used To Treat Migraine HeadachesMARY BERNADETTE EGANANo ratings yet
- GED102 Module 3 Project: Group Members: Raynard Yu John Luis Arce Miguel Agustin Galang Paul Cauman Renz Eugene GurionDocument6 pagesGED102 Module 3 Project: Group Members: Raynard Yu John Luis Arce Miguel Agustin Galang Paul Cauman Renz Eugene GurionqwertasdfgNo ratings yet
- April 4Document12 pagesApril 4HeheheytNo ratings yet
- Source For Oral FacialDocument168 pagesSource For Oral FacialNatasha Rivera100% (10)
- IMEDICS AKT Errors FINALDocument24 pagesIMEDICS AKT Errors FINALUmer AnwarNo ratings yet
- ENDOMETRIOSIS 1, Age at Menarche Does Not Correlate With The Endometriosis PhenotypeDocument12 pagesENDOMETRIOSIS 1, Age at Menarche Does Not Correlate With The Endometriosis PhenotypeBill RajagukgukNo ratings yet
- Self Study Handout - Medical Terminology - 2022Document14 pagesSelf Study Handout - Medical Terminology - 2022rhn 5b1coolNo ratings yet
- Nonin Vantage Pulse Oximeter Accuracy BrochureDocument6 pagesNonin Vantage Pulse Oximeter Accuracy Brochuresamer battatNo ratings yet
- ESTRELLA D.S. BAÑEZ, Petitioner Social Security System and de LA SALLE UNIVERSITY, RespondentsDocument15 pagesESTRELLA D.S. BAÑEZ, Petitioner Social Security System and de LA SALLE UNIVERSITY, RespondentsMa. Cristina BautistaNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 3 030 26044 6Document545 pages10.1007@978 3 030 26044 6Magda CabralesNo ratings yet
- Ajbsr MS Id 001564Document3 pagesAjbsr MS Id 001564Rodrigo AlpizarNo ratings yet
- Quiz Bee QuestionsDocument15 pagesQuiz Bee QuestionsMartin AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Jacqueline Jones-Np Resume 1Document3 pagesJacqueline Jones-Np Resume 1api-708057552No ratings yet
- (Herbal Reference Library) Kapoor, L. D - Handbook of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants-CRC Press (2001)Document425 pages(Herbal Reference Library) Kapoor, L. D - Handbook of Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants-CRC Press (2001)MadhanNo ratings yet