Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pointers To Review in TLE 9
Uploaded by
franciscayabyab015Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pointers To Review in TLE 9
Uploaded by
franciscayabyab015Copyright:
Available Formats
Pointers to Review in TLE 9
Cookery - is a strand or specialization wherein you will gain the skills and expertise needed to
produce dishes and take a leading role in commercial kitchen environments.
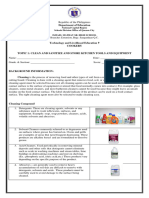
Cleaning Agents
1. Detergents. Detergents are chemicals that used to remove dirt and grease on tableware’s,
surfaces and equipment however detergent do not kill bacteria and other microorganisms.
2. Solvent Cleaners- commonly referred to as degreasers used on surfaces where grease has
burned on. Ovens and grills are examples of areas that need frequent degreasing.
3. Acid Cleaners. Used periodically in removing mineral deposits and other soils that
detergents cannot eliminate such as scale in washing machines and steam tables, lime buildup
on dishwashing machines and rust on shelving.
4. Abrasives – are generally used to remove heavy accumulations of soil that are difficult to
remove with detergents, solvents and acids. These products must be carefully used to avoid
damage to the surface being cleaned.
5. Chlorine- a halogen element that is isolated as a heavy greenish-yellow diatomic gas of
pungent odor and is used especially as a bleach, oxidizing agent, and disinfectant in water
purification.
The right cleaning agent must also be selected to make cleaning easy it is very vital to
follow manufacturer’s instruction for sanitary purposes, health and safety in preparing
chemical agents. Here are some samples of manufacturer’s instructions in using
cleaning compounds such as:
Dishwashing Liquid Manufacturer’s Instruction
• Do not add bleach.
• Not for use in automatic dishwashers.
Keep out of reach of children.
Chlorine
• Mix 2 tbsp. of chlorine and detergent per liter of water.
• Chlorine serve as disinfectant and deodorizer.
Acid Cleaner
• Always pour acid into water dilute cleaning products with water before cleaning any masonry
surface.
Steps in Washing Dishes
1.) Prepare.
2.) Scrape left over food
3.) Stack the dishes
4.) Fill the sink with water and add a considerable amount of detergent.
5.) Wash the lightest soiled items first.
6.) Wash plates, bowls, and serving dishes.
7.) Wash pots and pans last.
8.) Lay your dishes out on a rack to air-dry or wipe them clean with a towel.
9.) There should be no visible matter and no "greasy" feel.
10.) Rinse out brush, sponge and allow to dry.
11.) Wipe down the sink and your tools.
Scraped excess food should be placed in a compost bin.
Cleaning the Cutting Board
- It is important to use separate chopping boards for different kinds of food to reduce the spread
of bacteria.
- Cutting boards should be stored vertically or in an upright position. This helps to avoid
moisture from getting trapped underneath the board and the accumulation of dust or grime.
Methods of Cleaning Equipment
Foam – You use this to increase the contact time of the chemical
solutions to improve cleaning with less mechanical force.
High Pressure – used to increase mechanical force, aiding in soil removal. In
high pressure cleaning, chemical detergents are often used along with an
increase temperature to make soil removal more effective.
Clean In Place (CIP) – is a cleaning that is utilized to clean the interior surfaces of tanks
and pipelines of liquid process equipment without disassembly.
Clean Out of Place (COP) – is utilized to clean the parts of filters and parts of
other equipment. This requires disassembly for proper cleaning. Parts removed for cleaning
are placed in a circulation tank and cleaned using a heated chemical solution and agitation.
Mechanical – it normally involves the use of brush either by hand or a machine such as a floor
scrubber. Mechanical cleaning uses friction for food soil removal.
Proper storage and handling of cleaned and sanitized equipment and utensils are very
important to prevent recontamination prior to use.
Safety Measures
The following are safety measures that you should do when using cleaning agents:
1. Ensure adequate ventilation.
2. Have knowledge of basic first aid.
3. Wear cotton clothing to cover your limbs and other parts of your body that might be
exposed to thecleaning agent.
4. Wear suitable footwear–it should be closed in and have a steel toe.
5. Wear industrial strength, thick plastic or rubber gloves. Wear protective eye and face wear.
First aid procedure caused by chemical poisoning What to do?
If the person has been exposed to poisonous fumes, such as carbon monoxide, get
him or her into fresh air immediately
If the person swallowed the poison, remove anything remaining in the mouth.
If the suspected poison is a household cleaner or other chemical, read the label and
follow instructions for accident poisoning. If the product is toxic, the label will likely
advise you to call the hospital/doctor.
Follow treatment directions given by poison centers.
If the poison is spilled on the person’s clothing, remove the clothing and pour the body with
continuous tap water.
Kitchen Tools and Equipment
The following are the tools and equipment needed in preparing appetizers:
1. Rubber Scraper – used to scrape off contents of bowls..
2. Spatula – used for manipulating foods like spreading.
3. French knife – for chopping, slicing and dicing.
4. Paring knife – used for trimming and paring fruits and vegetables.
5. Cutting board – board for cutting fruits and vegetables.
6. Kitchen shear – cutting device for ingredients like scissors.
7. Chiller – for keeping cold foods chilled for service.
8. Oven – for baking.
9. Measuring spoons – are used for measuring dry and liquid ingredients in small
quantity.
10. Measuring cups – is used to measure dry ingredients. They come in various sizes and
volumes.
11. Glass measuring cup – container which is usually transparent. It is used for
measuring liquid ingredients like water and oil.
12. Mixing bowls – these containers have smooth, rounded interior surfaces with no
creases to retain some mixture.
13. Mixing spoon - is used for mixing ingredients. It is made of wood in different sizes and
different length of the handle.
14. Refrigerator – use to for chilling and freezing food
15. Strainer/colander – use to drain spaghetti noodle
16. Funnel – it use to easily transfer liquid from one container to another.
17. Scoop – it is use to putting ice cream to cone
18. Household scale - it is a measuring tool used by sellers e.g. rice sellers
Cooking materials
Aluminium – This cooking material is mostly used in the kitchen because of its lightweight,
attractive, and less expensive.
Cast Iron - This cooking material is durable but must be kept oiled to avoid rusting
Glass - It is used in kitchen when making salad and dessert but not practical for top or surface
cooking
Classification of Appetizers
1. Cocktails- are usually juices of orange, pineapple, grapefruit or tomatoes served with
cold salad dressings. It may be in the form of a fruit or vegetable juice mixed with little
alcoholic beverage.
2. Hors D’ Oeuvres- It is small portion of highly seasoned foods.
a. Antipasto – this includes cured meat like salami, bologna and boiled ham, seafood items
like sardines, cheeses, eggs, and mushroom.
b. Bruschetta – slice of Italian bread.
c. Tapas – a small food item intended to be eaten with wine and other drinks.
d. Caviar – salted roe or eggs of the sturgeon.
e. Amuse Bouche (ah-mews-boosh) – a tiny appetizer or hors d’ oeuvres offered to guest
seated at their tables either before or after they have ordered from the menu.
3. Canapé- are made out of thin slices of bread in different shapes. The bread may be
toasted like bread cut outs, crackers, melba toast and tiny biscuits, miniature pancakes, tiny
unsweetened pastry shells, polenta cut outs.
Three Parts of Canapes
a. Base b. Spread c. Garnish
4 . Relishes/Crudités- are pickled item which are raw, crisp vegetables such as julienne
carrots, celery sticks, pickled papaya, and pickled cucumber.
5. Petite Salad- are small portions and usually display the characteristics found in most salad.
6. Chips and Dips- are popular accompaniments to potato chips and French fries.
7. Fresh Fruits and Vegetables – are the simplest appetizer. For example, chunks of avocado
or watermelon.
8. Anything, Smaller- are varieties of appetizers wherein the only requirement is that you
keep everything small enough to be picked up with the fingers and eaten with little mess.
Examples:nuts, cocktail hotdogs, dumplings and sausages.
Fundamentals of Plating
1. Balance
2. Portion size
3. Arrangement on the plate
Sanitary Practices when storing salads and appetizers
1. Handle the food properly to prevent spoilage and contamination.
2. Wash utensils and equipment thoroughly.
3. Keep off hand to a minimum contact to ingredients and food.
4. Keep away from food when you are ill.
5. Store food and ingredients properly.
6. Safeguard the food during distribution and serving.
7. Chill to refrigerate or to reduce the temperature of food.
8. Place it to cold storage like refrigerator to preserve perishable food.
Storing Techniques
Storing foods could be done through the following techniques:
1. Refrigeration – to keep food cold or cool.
2. Cold storage – the process of preserving food by means of refrigeration.
3. Chilling – to refrigerate to reduce the temperature of food.
You might also like
- Around The World Cookbook by Katya HenryDocument49 pagesAround The World Cookbook by Katya HenryIva-Marija MatulecNo ratings yet
- Campbells Budget Friendly RecipesDocument30 pagesCampbells Budget Friendly RecipesRobert Currie100% (3)
- Lesson 1: Principles of Food Preparation What Is Preparation of Food?Document4 pagesLesson 1: Principles of Food Preparation What Is Preparation of Food?Kim So-Hyun100% (1)
- Cookery 10 Q1 LAS Week1Document16 pagesCookery 10 Q1 LAS Week1Roberto MabulacNo ratings yet
- Y2 - Module 1 - Clean and Maintain Kitchen PremisesDocument21 pagesY2 - Module 1 - Clean and Maintain Kitchen PremisesLissa Mahinay83% (18)
- Jerusalem by Yotam Ottolenghi and Sami Tamimi - Recipes and ExcerptDocument13 pagesJerusalem by Yotam Ottolenghi and Sami Tamimi - Recipes and ExcerptThe Recipe Club27% (26)
- Lesson 1 - CLEAN AND MAINTAIN KITCHEN TOOLS, AND, PREMISESDocument162 pagesLesson 1 - CLEAN AND MAINTAIN KITCHEN TOOLS, AND, PREMISESAdriano Bahian Jr.100% (7)
- Prepare Eggs, Cereals and StarchesDocument14 pagesPrepare Eggs, Cereals and StarchesLen Bulgar100% (2)
- Learner'S Packet No.1 Quarter 1: Name of Student: Learning Area/Grade Level: Tle-He-Cookery-Grade 9 Date: Activity TitleDocument10 pagesLearner'S Packet No.1 Quarter 1: Name of Student: Learning Area/Grade Level: Tle-He-Cookery-Grade 9 Date: Activity TitleSalgie MasculinoNo ratings yet
- Krcek Allen N. - Discovering Global Cuisines. Traditional Flavors and Techniques. 1st Edition - 2013Document958 pagesKrcek Allen N. - Discovering Global Cuisines. Traditional Flavors and Techniques. 1st Edition - 2013Raphaël LamotheNo ratings yet
- CBLM Food ProcessingDocument118 pagesCBLM Food ProcessingKenn Marvin Salcedo II100% (1)
- Recipes From Tyler Florence FreshDocument10 pagesRecipes From Tyler Florence FreshThe Recipe Club100% (4)
- Baking FAQsDocument3 pagesBaking FAQsRommel Barcelona57% (7)
- AFA-food ProcessingDocument50 pagesAFA-food ProcessingJenny Fausto MonrealNo ratings yet
- Clean, Sanitize Kitchen Tools 4Document4 pagesClean, Sanitize Kitchen Tools 4JaideHizoleSapulNo ratings yet
- Clean, Sanitize and Store Tools and EquipmentDocument105 pagesClean, Sanitize and Store Tools and EquipmentShailini Latonero100% (6)
- Technology and Livelihood Education (Exploratory) Grade 7: Commercial CookingDocument129 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education (Exploratory) Grade 7: Commercial CookingCharity ChangpaNo ratings yet
- Valrhona RecipesDocument70 pagesValrhona Recipessernikos86% (7)
- CookeryDocument25 pagesCookeryGlenda Jaca100% (1)
- Clean Kitchen Tools and EquipmentDocument20 pagesClean Kitchen Tools and EquipmentReyna Marke Buhawe100% (2)
- Cleaning baking tools and equipmentDocument10 pagesCleaning baking tools and equipmentIrine Irine100% (1)
- Q1 - Module4 - G7 - 8 - BPP - Mangaldan NHSDocument11 pagesQ1 - Module4 - G7 - 8 - BPP - Mangaldan NHSElaeca AbenNo ratings yet
- Cookery-Module With Activity SheetsDocument19 pagesCookery-Module With Activity SheetsHerminia Antolo100% (1)
- Q1 MODULE2 G9 Cookery BautistaNHSDocument10 pagesQ1 MODULE2 G9 Cookery BautistaNHSElaeca AbenNo ratings yet
- Module2 Part2Document68 pagesModule2 Part2jhaezhydomafergarcia2020No ratings yet
- Assessment Requirements For SITHCCC013 Prepare Seafood Dishes Modification HistoryDocument23 pagesAssessment Requirements For SITHCCC013 Prepare Seafood Dishes Modification HistoryMarijana NikoloskaNo ratings yet
- Cookery NC II competency and training guideDocument6 pagesCookery NC II competency and training guideKandi ZuenNo ratings yet
- Maintain Tools and Equipment for Food SafetyDocument56 pagesMaintain Tools and Equipment for Food SafetyJosephine Rivera100% (1)
- COOKERY NC2, Daladap Esperanza, Sultan KudaratDocument77 pagesCOOKERY NC2, Daladap Esperanza, Sultan KudaratNai ZeugirdorNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Q3 Week 1 1Document13 pagesCookery 10 Q3 Week 1 1Ivy SalazarNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 LASQ1Document6 pagesCookery 10 LASQ1Erich Niña AyoNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 9: KITCHEN TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTDocument79 pagesCOOKERY 9: KITCHEN TOOLS AND EQUIPMENTDessarie BusogNo ratings yet
- 8Document15 pages8MARCIA PATIANNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Lesson 1 Part 2Document22 pagesQuarter 3 Lesson 1 Part 2Shara Franchesca MonterubioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document21 pagesLesson 2BPISHERENo ratings yet
- Cleaning and SanitizingDocument23 pagesCleaning and SanitizingMha'ahm VheckNo ratings yet
- Cookery 9 LAS-Q2-W1Document13 pagesCookery 9 LAS-Q2-W1ChelleyOllitroNo ratings yet
- Cookery L1 L2Document19 pagesCookery L1 L2Emmanuel Louis CruzNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in TLE Cookery 7 8Document3 pagesReviewer in TLE Cookery 7 8Marc ParalesNo ratings yet
- Clean Kitchen Tools SEODocument6 pagesClean Kitchen Tools SEOCzarina GuillermoNo ratings yet
- TLE-ACTIVITY-SHEET-1-Grade-9-Cookery-CopyDocument10 pagesTLE-ACTIVITY-SHEET-1-Grade-9-Cookery-CopyKate Marie EtakNo ratings yet
- Cookery Topics 1 2Document9 pagesCookery Topics 1 2Kate Marie EtakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cookery Ncii: Cooking-The Act of Using Heat To Prepare Food For ConsumptionDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Cookery Ncii: Cooking-The Act of Using Heat To Prepare Food For Consumptionfranco jocsonNo ratings yet
- Week 1-2-AppetizerDocument4 pagesWeek 1-2-AppetizerJohn Ezra SustalNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 11, W1, Module 3Document12 pagesCOOKERY 11, W1, Module 3Lea Lee BaudingNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Kitchen Tools and EquipmentDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Kitchen Tools and EquipmentCiela TormentoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document26 pagesLesson 2marvin cayabyabNo ratings yet
- Maintain ToolsDocument6 pagesMaintain ToolsKrisha PoloanNo ratings yet
- Quarter1 Cookery 9 ModuleDocument45 pagesQuarter1 Cookery 9 ModuleKate AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Tle Grade7n8 Cookery Module 2 Week2Document11 pagesTle Grade7n8 Cookery Module 2 Week2Mhel Alvarado - PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 BPPDocument6 pagesWeek 4 BPPLeo Nino DulceNo ratings yet
- Sith Kop 001Document9 pagesSith Kop 001Abhinav GuliaNo ratings yet
- Clean and sanitize kitchen tools and equipment the right wayDocument25 pagesClean and sanitize kitchen tools and equipment the right wayThea Jeonieesa GarayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 GR. 10 PowerpointDocument61 pagesLesson 1 GR. 10 PowerpointanalynbabieraNo ratings yet
- Types and Uses of Cleaning MaterialsDocument30 pagesTypes and Uses of Cleaning MaterialsThirdy EstolanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cleaning and Clearing Food Service AreasDocument42 pagesChapter 2: Cleaning and Clearing Food Service AreasMa. Rochelle CabralesNo ratings yet
- Prepare Egg, Cereal, and Starch DishesDocument14 pagesPrepare Egg, Cereal, and Starch DishesGlyza Marie CendanaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Tle 8Document16 pagesReviewer in Tle 8llyra maeNo ratings yet
- Pre Unit 1 and Unit 1 Key Terms and Study QuestionsDocument4 pagesPre Unit 1 and Unit 1 Key Terms and Study QuestionsConnor WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Tle 10 - Handout 1.3Document2 pagesTle 10 - Handout 1.3Danica PerezNo ratings yet
- Cleaning and Sanitizing Kitchen ToolsDocument2 pagesCleaning and Sanitizing Kitchen ToolsMaxicris Slower100% (1)
- Kitchen Knives: (According To Its Use)Document31 pagesKitchen Knives: (According To Its Use)Thanya Sofia De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Facts Sheet1Document3 pagesFacts Sheet1YohAnna AsakuraKyoyamaNo ratings yet
- Cookery PresentationDocument21 pagesCookery Presentationsalazarjustinmae652No ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 3: CookeryDocument16 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 3: Cookeryroderic v. perezNo ratings yet
- Cookery 7 8 Module 2Document34 pagesCookery 7 8 Module 2Tr Darren Joy LaluonNo ratings yet
- CLEANING AND SANITIZING PROCEDURESDocument33 pagesCLEANING AND SANITIZING PROCEDURESRuth Zamora Calanday DomingoNo ratings yet
- Tle LM Commercial Cooking 78Document220 pagesTle LM Commercial Cooking 78zyra rose leachonNo ratings yet
- Cooking Materials g9Document2 pagesCooking Materials g9Rodrigo SuarezNo ratings yet
- Easy Way to Can and Preserve: Simple Canning and Preserving Process for Your Food: Fermentation & Survival HacksFrom EverandEasy Way to Can and Preserve: Simple Canning and Preserving Process for Your Food: Fermentation & Survival HacksNo ratings yet
- Saint Thomas Development Academy of Bulacan Inc. Third Periodical Examination in Technology and Livelihood Education 9Document2 pagesSaint Thomas Development Academy of Bulacan Inc. Third Periodical Examination in Technology and Livelihood Education 9Ka KlasmeytNo ratings yet
- Basic Food Micro Safety TipsDocument1 pageBasic Food Micro Safety TipsJohn Nelson PiconesNo ratings yet
- Bread and Pastry Production Ncii Grade 11 Assessment Week1-2Document2 pagesBread and Pastry Production Ncii Grade 11 Assessment Week1-2Rio Krystal Reluya MolateNo ratings yet
- Dawn BreadDocument16 pagesDawn BreadMuhammad Umer Khalid100% (1)
- Tle 10Document5 pagesTle 10Kassandra Alexa GustiloNo ratings yet
- 5 Deliverables Needed For Catering Service OpeningDocument3 pages5 Deliverables Needed For Catering Service OpeningErica Williams100% (1)
- grade-9-lp-basic-vegetable-cutsDocument12 pagesgrade-9-lp-basic-vegetable-cutsJerome Tala-ocNo ratings yet
- PAS Bahasa Inggris KELAS 3Document3 pagesPAS Bahasa Inggris KELAS 3MFikriAlfadliNo ratings yet
- Italian Almond CakeDocument1 pageItalian Almond CakeantonioforteseNo ratings yet
- Balay 3eb915lpDocument28 pagesBalay 3eb915lpaaa20013547No ratings yet
- Value Addition and Processing of Poultry ProductsDocument25 pagesValue Addition and Processing of Poultry ProductsGourav Wagh0% (1)
- Basic Granola: Happy Earth Day GranolaDocument5 pagesBasic Granola: Happy Earth Day GranolaBongTizonDiaz100% (1)
- International Cuisine Revised SyllabusDocument5 pagesInternational Cuisine Revised Syllabusanon_400440224100% (3)
- Chipotle's Spicy Corn Salsa: IngredientsDocument1 pageChipotle's Spicy Corn Salsa: IngredientsbazfolarinNo ratings yet
- Honey Mustard Chicken and Vegetables RecipeDocument1 pageHoney Mustard Chicken and Vegetables RecipeVera CastroNo ratings yet
- MEss Menu Redefined WordDocument2 pagesMEss Menu Redefined WordsrivatsavNo ratings yet
- MeatDocument19 pagesMeatbhaskarNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy menu plan for first trimester Week 1Document1 pagePregnancy menu plan for first trimester Week 1Sachin JaisNo ratings yet
- The Greenwich MenuDocument1 pageThe Greenwich MenuCaleb PershanNo ratings yet