0% found this document useful (0 votes)
278 views9 pagesSoftware Engineering - WaterFall Model
The document describes the waterfall model of software project management. The waterfall model involves a sequential sequence of activities from top to bottom, with some limited ability for iteration. It works well for projects with defined requirements and methods, allowing for forecasting and control. The model can be expanded into a V-process model by expanding testing against each stage of the project life cycle.
Uploaded by
jegadheeshnarayanan27Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
278 views9 pagesSoftware Engineering - WaterFall Model
The document describes the waterfall model of software project management. The waterfall model involves a sequential sequence of activities from top to bottom, with some limited ability for iteration. It works well for projects with defined requirements and methods, allowing for forecasting and control. The model can be expanded into a V-process model by expanding testing against each stage of the project life cycle.
Uploaded by
jegadheeshnarayanan27Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Waterfall Model: Introduces the document's focus on the Waterfall Model as a method used in software development.
- Waterfall Model Overview: Describes the classical Waterfall Model in software development, covering its sequential operation and primary characteristics.
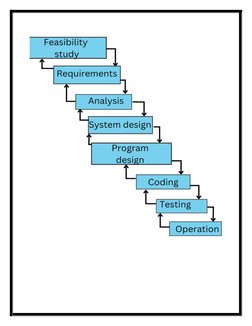
- Waterfall Process Steps: Illustrates the specific stages of the Waterfall Process from feasibility study to operation, showing the sequential progression of tasks.
- Diagram Analysis and Feedback Mechanism: Analyzes the visual representation of the Waterfall Model, highlighting potential feedback loops through arrows indicating stages of iteration or rework.
- Strengths and Scope of Iterations: Explains the limited iterative scope within the Waterfall Model as a strength for handling large projects aiming to minimize rework.
- Project Management and Stage-Gate Model: Discusses how the model creates natural milestones, potentially using a stage-gate approach for project evaluation and control.
- Effective Control in Well-defined Environments: Details advantages of the Waterfall Model in environments where requirements and development methods are well established, allowing better project control.
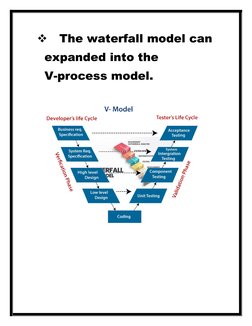
- Expansion to V-Model: Introduces the V-Model as an expansion of the Waterfall Model, focusing on the addition of testing and validation within the development lifecycle.
- Testing Process Expansion: Explores enhancements in the testing process by integrating different testing stages to verify outputs against project lifecycle activities.