0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views6 pagesAssignment6 Tranngoctu
The document contains two Verilog modules:
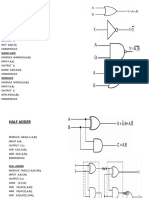
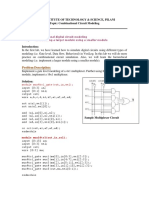
1. A 4-to-1 multiplexer module that uses assign statements to select one of 4 input bits (a[3:0]) based on the 2-bit selection input (s[1:0]) and output the result.
2. A 4-bit carry lookahead adder module that uses assign statements and logic operators to calculate the propagate, generate and intermediate carry signals to implement carry lookahead addition of two 4-bit inputs (a, b) and a carry in (cin) and output the 5-bit sum.
Testbenches are provided to simulate and verify the functionality of both modules.
Uploaded by
Tú Trần NgọcCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views6 pagesAssignment6 Tranngoctu
The document contains two Verilog modules:
1. A 4-to-1 multiplexer module that uses assign statements to select one of 4 input bits (a[3:0]) based on the 2-bit selection input (s[1:0]) and output the result.
2. A 4-bit carry lookahead adder module that uses assign statements and logic operators to calculate the propagate, generate and intermediate carry signals to implement carry lookahead addition of two 4-bit inputs (a, b) and a carry in (cin) and output the 5-bit sum.
Testbenches are provided to simulate and verify the functionality of both modules.
Uploaded by
Tú Trần NgọcCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd