Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Schedule Maths-1
Uploaded by
strategicsurya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views8 pagesMaths PGT Schedule
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMaths PGT Schedule
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views8 pagesTest Schedule Maths-1
Uploaded by
strategicsuryaMaths PGT Schedule
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
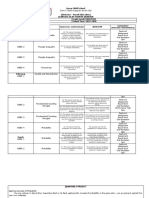
ARYAN INSTITUTE
(The Education Startup)
HPSC PGT MAINS TEST SERIES
✆ 8930347005, 7988601810
Meticulously selected questions from most probable part of syllabus that may get
weightage in final paper. That gives you edge in your preparation.
TOPIC WISE TEST SCHEDULE
Test No. & Date Section & Topics
▪ Sets:
Sets and their representation. Empty set. Finite & Infinite sets.
Equal sets. Subsets. Subsets of the set of real numbers. Power set.
Universal set. Venn diagrams. Union and Intersection ofsets.
Difference of sets. Complement of a set.3
▪ Relations & Functions:
Ordered pairs, Cartesian product of sets. Number of elements in
the cartesian product of two finite sets. Cartesian product of the
reals with itself (upto R x R x R). Definition of relation, pictorial
Test 1 diagrams, domain, co-domain and range of a relation. Function as
19-10-2023 a special kind of relation from one set to another. Pictorial
representation a function, domain, co-domain & range of a
function. Real valued function of the real variable, domain and
range of these functions, constant, identity, polynomial, rational,
modulus, signum and greatest integer functions with their graphs.
Sum, difference, product and quotients of functions. Set and their
Representations. Union, intersection and complements of sets,
and their algebraic properties. Relations, equivalence relations,
mappings, one-one, into and onto mappings, composition of
mappings.
▪ Principle of Mathematical Induction:
Processes of the proof by induction. The principle of
mathematical induction.
▪ Linear Inequalities:
Linear inequalities. Algebraic solutions of linear inequalities in
one variable and their representation on the number line.
Graphical solution of linear inequalities in two variables. Solution
of system of linear inequalities in two variables-graphically.
Absolute value. Inequality of means, Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality,
Tchebychef’s Inequality.
▪ Binomial Theorem
Statement and proof of the binomial theorem for positive integral
indices. Pascal’s triangle, general and middle term in binomial
expansion, simple applications. Binomial theorem for anyindex.
Properties of Binomial Co-efficient. Simple application for
approximations.
▪ Sequence and Series:
Sequence and Series. Arithmetic, Geometric and Harmonic
progressions (G.P.). General terms and sum to n terms of A.P.,
G.P. and H.P. Arithmetic mean (A.M.). Geometric Mean (G.M.),
and harmonic Mean (H.M.), Relation between A.M., G.M. and
H.M. Insertion of Arithmetic, Geometric and Harmonic Means
between two given numbers. Special series. Sum to n terms of the
special series. Arithmetic, Geometric Series, Exponential and
Logarithmic series.
▪ Permutations & Combination:
Fundamental principle of counting. Factorial n. Permutation and
combinations, derivation of formulae and their connections
simple applications.
▪ Elementary Number Theory:
Peano’s Axions, Principle of Induction; First Principle, Second
Principle, Third Principle, Basis Representation Theo Greatest
Integer Function Test of Divisibility, Euclid’s algorithm, The
unique Factorization Theorem. Congruence, Sum divisions of a
number. Euler’s totient function. Theorems of Fermat and Wilson.
▪ Statistics:
Test 2 Calculation of mean, median and mode of grouped and
23-10-2023 ungrouped data. Measure of dispersion; mean deviation, variable
and standard deviation of ungrouped/ grouped data. Analysis of
frequency distribution with equal means but difference variances.
▪ Probability:
Random experiments ; outcomes, sample spaces. Events:
occurrence of events, exhaustive events, mutually exclusive event
Probability of an event, probability of ‘not’, ‘and’ & ‘or’ events.,
Multiplication theorem on probability. Condition probability,
independent events.
Baye’s theorem, Random variable and its probability distribution,
Binomial and poisson distribution and their properties.
▪ Complex Numbers:
Complex numbers. Algebraic properties of complex number,
Argand plane and polar representation of complex numbers,
Statement of Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, solution of
quadratic equations in the complex number system. Modulus and
Test 3 Argument of a complex number, square root of a complex
27-10-2023 number. Cube roots of unity, triangle inequality.
▪ Quadratic Equations:
Quadratic equations in real and complex number system and their
solutions. Relations between roots and co-efficient, nature roots,
formation of quadratic equations with given roots; Symmetric
functions of roots, equations reducible to quadratic equations –
application to practical problems.
Polynomial functions, Remainder & Factor Theorems and their
convers, Relation between roots and coefficients, Symmetric
functions of the roots of an equation. Common roots.
▪ Trigonometric Functions:
Positive and negative angles. Measuring angles in radians & in
degrees and conversion fromone measure to another. Define of
trigonometric functions with the help of unit circle.
Graphs of trigonometric functions. Expressing sin (x + y) and cos
(x + y) in terms of sinx, siny, cosx & cosy. Identities relate sin2x,
cos2x, tan2x, sin3x, cos3x and tan3x. Solution of trigonometric
equations, proofs and simple applications of simple cosine
formulae. Solution of triangles. Heights and Distances.
▪ Inverse Trigonometric Functions:
Definition, range, domain principle value branches. Graphs of
inverse trigonometric functions. Elementary properties inverse
trigonometric functions.
▪ Two Dimensional Geometry:
Cartesian system of rectangular co-ordination in a plane, distance
formula, section formula, area of a triangle, condition formula
collinearity of three points, centroid and in-centre of a triangle,
locus and its equation, translation of axes, slope of a parallel and
Test 4 perpendicular lines, intercepts of a line on the coordinate axes.
31-10-2023 Various forms of equations of a line, intersection of lines, angles
between two lines, conditions for concurrence of three line
distance of a point from a line, Equations of internal and external
bisectors of angles between two lines, coordinate centroid,
orthocenter and circumcenter of a triangle, equation of family of
lines passing through the point of intersection of lines,
homogeneous equation of second degree in x and y, angle
between pair of lines through the origin, combined equation the
bisectors of the angles between a pair of lines, condition for the
general second degree equation to represent a pair of line point of
intersection and angle between two lines.
Standard form of equation of a circle, general form of the
equation of a circle, its radius and centre, equation of a circle it
parametric form, equation of a circle when the end points of a
diameter are given, points of intersection of a line and a centre
with the centre at the origin and condition for a line to be tangent
to the circle, length of the tangent, equation of the tangent
equation of a family of circles through the intersection of two
circles, condition for two intersecting circles to be orthogonal.
Section of cones, equations of conic sections (parabola, ellipse
and hyperbola) in standard forms, condition for y = mx + x be a
tangent and point(s) of tangency.
▪ Vectors:
Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector.
Direction cosines/ratios of vectors. Types of vectors (equal, zero
parallel and colinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative
of a vector, components of a vector, addition vectors,
multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point
dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Scalar product of vectors,
projection of a vector on a line. Vector (cross) product of vectors.
▪ Three Dimensional Geometry:
Coordinates of a point in space, distance between two points;
Section formula, Direction cosines/ ratios of a line joining points.
Cartesian and vector equation of a line, coplanar and skew lines,
shortest distance between two lines. Cartesian a vector equation
of a plane. angle between (i) two lines, (ii) two planes, (iii) a line
and a plane. Distance of a point from plane. Scalar and vector
triple product. Application of vectors to plane geometry. Equation
of asphere, its centre and radius Diameter form of the equation of
a sphere.
▪ Differential Calculus:
Polynomials, rational, trigonometric, logarithmic and exponential
functions, Inverse functions. Graphs of simple function Limits,
Continuity and differentiability; Derivative, Geometrical
interpretation of the derivative, Derivative of sum difference
product and quotient of functions. Derivatives of polynomial and
trigonometric functions, Derivative of composite function chain
rule, derivatives of invers trigonometric functions, derivative of
implicit function. Exponential and logarithmic function and their
derivatives. Logarithmic differentiation. Derivative of functions
expressed in parametric forms. Second derivatives. Rolle’s and
Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorems and their geometric
interpretations.
Test 5 ▪ Applications of Derivatives:
04-11-2023 Applications of derivatives: rate of change, increasing/
decreasing functions, tangents & normal, approximation maxima
and minima.
▪ Integral Calculus:
Integral and an anti-derivative. Fundamental integrals involving
algebraic, trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic function
integration by substitution, by parts and by partial fractions.
Integration using trigonometric identities. Definite integrals limit
of aum, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Basic Properties of
definite integrals and evaluation of definite integral Applications
of definite integrals in finding the area under simple curves,
especially lines, areas of circles/ Parabolas areas between the two
curves.
▪ Differential Equation:
Definition, order and degree, general and particular solution of a
differential equation. Formation of differential equation.
▪ Matrices and Determinants:
Determinants and matrices of order two and three, properties of
determinants. Evaluation of determinants. Area of triangle using
determinants. Addition and multiplication of matrices, adjoint
and inverse of matrix. Test of consistency and solution
simultaneous linear equations using determinants and matrices.
▪ Linear Algebra:
Examples of vector spaces, vector spaces and subspace,
independence in vector spaces, existence of a Basis, the row a
column spaces of a matrix, sum and intersection of subspaces.
Test 6 Linear Transformation and Matrices, Kernel, image and
08-11-2023 Isomorphism, change of bases, Similarity, Rank and Nullity,
Product spaces, orthonormal sets and the Gram-Schmidt Process,
the Method of least Square. basic theory of Eigenvector and
Eigenvalues, algebraic and geometric multiplicity of eigen value,
diagonalization of matrices, application to system linear
differential equations. Generalized Inverse of matrices, Moore-
Penrose generalized inverse. Real quadratic form reduction and
classification of quadratic forms, index and signature, triangular
reduction of a pair of forms, singular value decomposition,
extrema of quadratic forms. Jordan canonical form, vector and
matrix decomposition.
▪ Analysis:
Monotone functions and functions of bounded variation. Real
valued functions, continuous functions, Absolute continuity
functions, standard properties. uniform continuity, sequence of
functions, uniform convergence, power series and radius
convergence. Richman-Stieltjes integration, standard properties,
multiple integrals and their evaluation by repeating integration,
change of variable in multiple integration. Uniform convergence
Test 7 in improper integrals, differentiation under sign of integral –
12-11-22023 Leibnitz rule.
Dirichlet integral, Liouville’s extension. Introduction to n-
dimensional Euclidean space, open and closed intervals
(rectangular compact sets, Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem, Heine-
Borel theorem. Maxima-Minima of functions of several variable
constrained maxima-minima of functions. Analytic function,
Cauchy-Riemann equations, singularities, Statement of Cauchy
theorem and of Cauchy integral formula with applications,
Residue and contour integration. Fourier and Laplace transform
Mellin’s inversion theorem.
Test 8 Full Syllabus
16-11-22023
Test 8 Full Syllabus
20-11-22023
Test 8 Full Syllabus
24-11-22023
Note: Schedule may be changed according to exam date.
You might also like
- Wbjee MathDocument2 pagesWbjee MathPinaki BiswasNo ratings yet
- JEE Syllabus - 01 MainDocument16 pagesJEE Syllabus - 01 MainVijay PatelNo ratings yet
- Book (Calculus)Document48 pagesBook (Calculus)Rajat KaliaNo ratings yet
- SetsDocument4 pagesSetsNavneet VishnoiNo ratings yet
- Maths SyllabusDocument3 pagesMaths SyllabusManju ManuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PGTsDocument54 pagesSyllabus PGTspriyambada biswalNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) - Mathematics Syllabus: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument5 pagesJEE (Main) - Mathematics Syllabus: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsSahithReddyRegatteNo ratings yet
- Reduced Syllabus of JEE Main 2024 - MathematicsDocument3 pagesReduced Syllabus of JEE Main 2024 - Mathematicsthe.gamer.02421100% (1)
- JEE Main 2024 Mathematics SyllabusDocument3 pagesJEE Main 2024 Mathematics SyllabusGowthamNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2012 Mathematics Syllabus: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument4 pagesAIEEE 2012 Mathematics Syllabus: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsAjay Singh GurjarNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus:: Math Syllabus For Recruitment-HgDocument4 pagesPre-Calculus:: Math Syllabus For Recruitment-Hgsurajkumarjaiswal9454No ratings yet
- Joint Entrance Examination (Advanced) - 2014 Indian Institutes of TechnologyDocument3 pagesJoint Entrance Examination (Advanced) - 2014 Indian Institutes of TechnologyAvinash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Aieee MathsDocument5 pagesSyllabus of Aieee MathsBastab DeyNo ratings yet
- Maths Super 500 Questions With SolutionsDocument120 pagesMaths Super 500 Questions With Solutions30-Shaurya Shivpriya-9FNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Mathematics SyllabusDocument3 pagesJee Main Mathematics SyllabusexamfarraNo ratings yet
- RPSSC SR Teacher Exam Math SyllabusDocument6 pagesRPSSC SR Teacher Exam Math Syllabussanju kumari meenaNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2018 SyllabusDocument8 pagesWBJEE 2018 SyllabusNishit kumar100% (1)
- WBJEE 2024 SyllabusDocument10 pagesWBJEE 2024 Syllabussm3935107No ratings yet
- JEE (Advanced) 2024: Syllabus: MathematicsDocument3 pagesJEE (Advanced) 2024: Syllabus: Mathematicsrbqjm9jv4zNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Complete AnalysisDocument20 pagesJee Main Complete AnalysisARAVIND SANTHOSHNo ratings yet
- Jee Maths FormulaDocument2 pagesJee Maths FormulaHardeep Sinh ParmarNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Syllabus 2020Document26 pagesJEE Main Syllabus 2020Rabia BanoNo ratings yet
- Math Jeemain - GuruDocument120 pagesMath Jeemain - GuruAnand TripathiNo ratings yet
- Paper-I Mathematics (Maximum Marks - 300)Document2 pagesPaper-I Mathematics (Maximum Marks - 300)alokNo ratings yet
- Arihant 20 Years Chapterwise Topicwise JEE Main Solved Papers Mathematics-1Document481 pagesArihant 20 Years Chapterwise Topicwise JEE Main Solved Papers Mathematics-1Krishna K100% (2)
- Syllabus B.tech.2014 PDFDocument6 pagesSyllabus B.tech.2014 PDFSaurabh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- RPSC Lecturer Exam Syllabus for MathematicsDocument6 pagesRPSC Lecturer Exam Syllabus for MathematicsGajen BishnoiNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Entrance Exam SyllabusDocument6 pagesB.Tech. Entrance Exam SyllabusNiranjan RameshNo ratings yet
- Article Careers360 20230521075Document27 pagesArticle Careers360 20230521075Filme RosterNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMathematics: Unit 1: Sets, Relations and Functionsrchandra2473No ratings yet
- JEE Main SyllabusDocument7 pagesJEE Main SyllabusSohan ChandraNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 Maths SyllabusDocument4 pagesJEE Main 2023 Maths SyllabusTieagleNo ratings yet
- I-Arch: Nata Exam SyllabusDocument4 pagesI-Arch: Nata Exam Syllabusvivek vallakatiNo ratings yet
- Arihant 41 Years Maths (Crackjee - Xyz) PDFDocument625 pagesArihant 41 Years Maths (Crackjee - Xyz) PDFShushma100% (2)
- JEE (Main) Mathematics Syllabus: Crack JEE With A Program Trusted by ToppersDocument5 pagesJEE (Main) Mathematics Syllabus: Crack JEE With A Program Trusted by ToppersNo Subject SubjectNo ratings yet
- 2022Document4 pages2022rbqjm9jv4zNo ratings yet
- Nda MathDocument2 pagesNda Mathanurag bansalNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains Advanced Latest SyllabusDocument24 pagesJEE Mains Advanced Latest SyllabusViki HNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board Syllabus For Class 11 and 12 MathsDocument13 pagesMaharashtra State Board Syllabus For Class 11 and 12 MathsTanmay MandlikNo ratings yet
- Mathematics & Statistics (40) : (For Arts and Science) Std. Xi & XiiDocument9 pagesMathematics & Statistics (40) : (For Arts and Science) Std. Xi & XiiIshwar PanchariyaNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains SyllabusDocument10 pagesJEE Mains SyllabusJatain KumarNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2022 SyllabusDocument16 pagesJEE Main 2022 SyllabusShreya.M hanabemanjunathNo ratings yet
- Information Bulletin: Jee (Main) - 2022: Appendix - VIDocument13 pagesInformation Bulletin: Jee (Main) - 2022: Appendix - VIHrithik JerathNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) Mathematics Syllabus: UNIT 1: Sets, Relations and FunctionsDocument4 pagesJEE (Main) Mathematics Syllabus: UNIT 1: Sets, Relations and Functionsmajji satishNo ratings yet
- Ojee Btech 2023Document4 pagesOjee Btech 2023Jerry MishraNo ratings yet
- OJEE Syllybus For MCA 1Document9 pagesOJEE Syllybus For MCA 1Goto HellNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Math Syllabus EbookDocument4 pagesJEE Main Math Syllabus EbookVaishakh VarierNo ratings yet
- 2023Document3 pages2023rbqjm9jv4zNo ratings yet
- JEE Maths Syllabus Algebra, Trigonometry, CalculusDocument3 pagesJEE Maths Syllabus Algebra, Trigonometry, CalculusSankhaNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS For JEE (Main) - 2021 Syllabus For Paper-1Document19 pagesSYLLABUS For JEE (Main) - 2021 Syllabus For Paper-1HrishiNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS For JEE (Main) - 2021 Syllabus For Paper-1 (B.E./B.Tech.) - Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry MathematicsDocument3 pagesSYLLABUS For JEE (Main) - 2021 Syllabus For Paper-1 (B.E./B.Tech.) - Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry MathematicsTeja workNo ratings yet
- Units Topics: Remark (Completion)Document3 pagesUnits Topics: Remark (Completion)siddanshNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus 2024Document5 pagesMathematics Syllabus 2024C1B-33-AdityaNo ratings yet
- APSC Optional Paper MathematicsDocument2 pagesAPSC Optional Paper MathematicsmanashNo ratings yet
- JEE (Main) - 2021 (B.Arch) Syllabus For Paper-2Document6 pagesJEE (Main) - 2021 (B.Arch) Syllabus For Paper-2ganji.karthik.9999No ratings yet
- Elementary Analysis: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mathematics Division, Volume 1From EverandElementary Analysis: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mathematics Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesFrom EverandMathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Special Matrices and Their Applications in Numerical Mathematics: Second EditionFrom EverandSpecial Matrices and Their Applications in Numerical Mathematics: Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- STATISTICS WITH R PROGRAMMING Question Paper PDFDocument5 pagesSTATISTICS WITH R PROGRAMMING Question Paper PDFArul Kumar Venugopal100% (5)
- Calculating Amounts Earned from Selling Copper WireDocument25 pagesCalculating Amounts Earned from Selling Copper WireMary Rose D. SisperezNo ratings yet
- Maths Aptitude BookDocument114 pagesMaths Aptitude BookEr Biswajit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Calculating torsion in narrow rectangular and hollow cross sectionsDocument10 pagesCalculating torsion in narrow rectangular and hollow cross sectionsbatmanbittuNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates: Department of Aerospace and Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 pagesOrthogonal Curvilinear Coordinates: Department of Aerospace and Mechanical EngineeringTushar GhoshNo ratings yet
- 08 Matlab InterpolationDocument21 pages08 Matlab InterpolationOmed GharebNo ratings yet
- Geometry Ubd Stages 1 2 3 - Edu 223 - 9 12 - Aurora TurmelleDocument7 pagesGeometry Ubd Stages 1 2 3 - Edu 223 - 9 12 - Aurora Turmelleapi-434662376No ratings yet
- 2004 Swamee, Prabhata K. Rathie, Pushpa N. - Exact Solutions For Normal Depth ProblemDocument9 pages2004 Swamee, Prabhata K. Rathie, Pushpa N. - Exact Solutions For Normal Depth Problemjosue.angelo9459No ratings yet
- Arduindoos Documentation PDFDocument777 pagesArduindoos Documentation PDFJonathan JaegerNo ratings yet
- Math-9-LAW #4-Q1-4Document8 pagesMath-9-LAW #4-Q1-4Keira cassandra delacruzNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas PDFDocument4 pagesGeometry Formulas PDFManuelAlexNo ratings yet
- 9 Ideal Truss: Force MethodDocument8 pages9 Ideal Truss: Force MethodAiman RashidNo ratings yet
- Modern Software Engineering - Doing What Works To Build Better Software FasterDocument299 pagesModern Software Engineering - Doing What Works To Build Better Software FasterOmar López PáezNo ratings yet
- 2016 Grade 10 Mid Year Exam June Math Paper 1 MemoDocument7 pages2016 Grade 10 Mid Year Exam June Math Paper 1 MemoAmaza SiswanaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Africa: World History of MathematicsDocument6 pagesMathematics in Africa: World History of MathematicsJacob ObboNo ratings yet
- Java-Interview ProgramsDocument109 pagesJava-Interview ProgramsKumar SwamyNo ratings yet
- L03 FourierDocument60 pagesL03 Fourierفراس فراس فراسNo ratings yet
- Spectral element method lecture notesDocument42 pagesSpectral element method lecture notesFaresNo ratings yet
- Shakuntala Devi 2Document68 pagesShakuntala Devi 2Nitesh HotwaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heim's Mass FormulaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Heim's Mass FormulaitootellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: GrowthDocument35 pagesChapter 4: GrowthJamaica JunioNo ratings yet
- Zone 7, Bulua Cagayan de Oro City: Merry Child SchoolDocument3 pagesZone 7, Bulua Cagayan de Oro City: Merry Child SchoolJessa Mae Neri SardanNo ratings yet
- Markov Chain Implementation in C++ Using EigenDocument9 pagesMarkov Chain Implementation in C++ Using Eigenpi194043No ratings yet
- Print 1Document16 pagesPrint 1Sudarshan PhajageNo ratings yet
- A Short To Kalman Filters: Alan WashburnDocument31 pagesA Short To Kalman Filters: Alan WashburnrfcNo ratings yet
- Geometry: 9.5 Trigonometric RatiosDocument28 pagesGeometry: 9.5 Trigonometric Ratiosbernadeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- CE 809 - Lecture 2 - Free Vibration Response of SDF SystemsDocument31 pagesCE 809 - Lecture 2 - Free Vibration Response of SDF SystemsArslan UmarNo ratings yet
- CMC 2020 12A SolutionsDocument6 pagesCMC 2020 12A SolutionsJohn WickNo ratings yet
- Functions: 2nd Quarter Unit 1 Day 5Document34 pagesFunctions: 2nd Quarter Unit 1 Day 5HULANo ratings yet
- Singapore Math Kangaroo Contest 2019: Secondary 4 / Grade 10 Contest PaperDocument12 pagesSingapore Math Kangaroo Contest 2019: Secondary 4 / Grade 10 Contest PaperMickey WongNo ratings yet