The GCSE Maths introductory Skills booklet
In this booklet:
Topic list for the GCSE maths assessment
Revision for the GCSE maths assessment
Initial Assessment Style questions
pg. 1
� Topic list for the GCSE maths assessment
1. Add, subtract, multiply and divide whole numbers.
2. Fraction of an amount.
3. Percentage of an amount.
4. Add, subtract, multiply and divide fractions.
5. Convert between fractions, decimals and percentages.
6. Solve problems involving fractions and percentages.
7. Reverse percentages.
8. Divide an amount in a given ratio.
9. Powers and roots.
[Link] algebraic expressions.
[Link] one-step linear equations.
[Link] inequalities.
[Link] single brackets.
[Link] values into a formula.
[Link] a formula.
[Link] of a formula.
[Link] of indices.
[Link] double brackets.
[Link] quadratics.
[Link] quadratic equations by factorising.
[Link] algebraic fractions.
[Link] linear and quadratic graphs.
[Link] simultaneous equations.
[Link] volume problems.
[Link] problems involving area and perimeter of 2D shapes.
[Link] in parallel lines.
[Link].
Online resources:
[Link]
[Link]
[Link]
pg. 1
� Revision for the GCSE maths assessment
1- Add, subtract, multiply and divide whole numbers.
• BIDMAS is the order in which operations need to be carried out.
• Brackets, indices, division, multiplication, addition, subtraction.
1) Work out 523 × 37
2) Work out 219.8 7
3) Work out 7152 + 876 – 139
4) Here is a calculation 6 + 3 × 4 – 2. James says the answer is 34. He is
wrong. Work out the correct answer.
5) Work out 7 + 8 ÷ 4 – 3
2- Fraction of an amount.
• To find a fraction of an amount, divide the amount by the denominator,
then multiply by the numerator.
3
1) Work out 7 × £28
2) The attendance at Frome United versus Trowbridge Rovers was 8,701.
Of this crowd, five-sevenths were male.
Calculate how many people were female.
1 1
3) What fraction of 1 is ? Circle your answer.
4 8
3- Percentage of an amount.
• “Per cent” means “out of 100”;
• To find a percentage of an amount, convert it to a fraction, and divide the
amount by the denominator, then multiply by the numerator.
1) Work out 22% of 250.
pg. 1
� 2) Work out 252% of 120.
4- Calculate with fractions.
• If you have a mixed number, start by converting it to an improper fraction.
• Multiply fractions is easy – just multiply the numerators and multiply the
denominators.
• To divide fractions, flip the second fraction upside-down and multiply
instead.
• If you need to add or subtract fractions, you will need to start by finding
equivalent fractions with a common denominator.
• Make sure you leave your answer in its simplest form.
• To convert a recurring decimal to a fraction you will need to multiply by
10n, where n is the number of recurring digits. Then subtract the original
number from the new one. Rearrange to find the fraction.
3 1
1) Work out 1 +3
4 2
1 2
2) Work out 3 ×4
3 5
3) Work out 31⁄3 ÷ 4¾
5- Convert between fractions, decimals and percentages.
pg. 1
� 1) Complete the table
Fraction Decimal Percentage
0.1
7/10
30
3/4
0.85
8
2) Circle the calculation that increases 50 by 200%
6- Solve problems involving fractions and percentages.
1) Last season a football club sold 8000 season tickets at £250 each.
This season the season ticket price is reduced by 20% to £200.
If the club sell 20% more tickets will the amount of money they receive
increase, decrease or stay the same?
You must show your working.
2) Two-thirds of a number is 60. What is 50% of the same number?
3) A ball is dropped from a height of 50 metres.
After each bounce, the ball reaches 20% of its previous height.
How high does it reach after the second bounce?
pg. 1
� 3
4) A raffle has three prizes. First prize is £40. Second prize is 4 of the first
1
prize. Third prize is 2 of the second prize. Raffle tickets are 50 p each.
How many tickets need to be sold to make a profit of £70?
5) Ellie bought a scarf and a dress. The scarf cost £4.
She sold both items for a total of £26.
She made 100% profit on the cost of the scarf and 30% profit on the
total cost.
Work out her percentage profit on the cost of the dress.
7- Reverse percentages.
• Work out what the multiplier would have been
1) Lauren is given a 12% pay rise.
Her new salary is £24,080
What was Lauren’s salary before the pay rise?
2) In a sale, the original price of a TV was reduced by 20%.
The sale price of the TV is £360.
Work out the original price.
3) In a sale, normal prices are reduced by 25%.
Freddie bought a car in the sale.
The sale price of the car was £7500.
Work out the normal price of the car.
8- Divide an amount in a given ratio.
• Find the total number of parts of the whole amount;
pg. 1
�• Divide the whole amount by the number of parts to find the value of one
part;
• Finally, multiply each number of parts by the value of one part.
1) Sean and Patrick share £400 in the ratio 3 : 7. How much money do they
each receive?
2) Divide 369 kg in the ratio 7 : 2.
3) Divide £36 in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3.
9- Powers and roots.
• The square root of a given number is a number that when multiplied by
itself equals the given number, ex: √ 9 = 3, because 3² = 9;
• The cube root of a given number is a number that when multiplied by itself
and then multiplied by itself again equals the given number, ex: √3 8 = 2,
because 2³ = 8;
• Powers of the same base number can be multiplied and divided;
• When multiplying, you add the indices, ex: 53× 54 = 53 +4 = 57;
• When dividing, you add the indices, ex: 35 ÷ 32 = 35−2 = 33;
• To raise to a power, you multiply the indices, ex. (9²)³ = 92 × 3.
1) Circle the number that is an integer power of 4.
2 8 16 32
2) Work out the value of 24
3) Work out the value of √ 196
pg. 1
� 4) Work out 512 ÷ 53 × 52 as a power of 5. Circle your answer.
56 58 59 511
5) Work out √3 8 × 5−2. Give your answer as a decimal.
6) x² = 3² + 4². Work out the value of x. You must show your working.
7) The sum of two square numbers is 180. What are the two square
numbers?
8) Kim says “The sum of any two different square numbers is always even.”
Is she correct? Write down a calculation to support your answer.
10- Simplify algebraic expressions.
• 2a means a + a or 2 lots of a
• a² means a × a
• The sign (+ or -) belongs to the term following it. You may find it easier to
identify like terms using two different highlighters.
1) Simplify 3m – m
2) Simplify x + x + x + y
3) Simplify y² + y² + y²
4) Simplify 7h + 5k + h - 3k
5) Simplify 2 × a × b × 5
11- Solve one-step linear equations.
• “Solve” means to find the value of the variable (what number the letter
represents).
• The inverse of + is – and the inverse of x is ÷
• Work one step at a time, keeping you = signs in line on each new row of
working.
pg. 1
� 1) Solve x − 6 = 11
2) Solve x + 7 = 56
3) Solve 4x = 48
30
4) Solve x
=6
5) Solve 4x - 5 = 17
12- Solve inequalities.
• < means less than
• > means greater than
• ≤ means less than or equal to
• ≥ means greater than or equal to
• An integer is a whole number
• On a number line, use a full circle to show a value can be equal, and an
empty circle to show it cannot.
1) List all the possible integer values of n such that
–2 ≤ n < 3
2) Circle the solution of 2x + 8 > 4
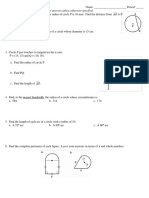
3) Circle the inequality shown by the diagram.
pg. 1
� 4) List the integers that satisfy both these inequalities.
2x + 7 < 0 and x > -10
13- Expand and factorise single brackets.
• Expand brackets means to multiply what is outside the bracket with
everything inside the bracket.
• Factorising is the opposite of expanding – put the HCF outside the
brackets to factorise fully.
1) Expand 5(m + 2)
2) Expand and simplify 2(w + 3) + 4(w −1)
3) Expand and simplify 3(2x - 5) + 4(2x + 1)
4) Work out the values of 𝑎 and 𝑏 in the identity 4𝑥+5−2𝑎𝑥−7≡𝑏−2𝑥
5) Write 2(7x + 4) – 4(x + 6) + 1 in the form a(bx + c),where a, b and c are
integers and a > 1
6) Factorise y² + 3y
7) Factorise fully 5x² − 10xy
8) Factorise 15x + 35y – 40z
14- Substitute values into a formula.
• There is always 1 mark just for writing down the numbers you have had to
put into the expression.
• Your answer must be a number – don’t forget to finish the sum
pg. 1
�• The question will always use the words “Work out the value of”
1) P = x² - 7x
Work out the value of P when x = -5
2) T, x and y are connected by the formula T = 5x + 2y
(a) Work out the value of T when x = -3 and y = 4
(b) Work out the value of y when T = 16 and x = 7
15- Rearrange a formula.
• Firstly decide what needs to be on its own.
• Secondly move all terms that contain that letter to one side. Remember
to move all terms if it appears in more than one.
• Thirdly separate out the required letter on its own.
1) Make w the subject of the formula
y = 3w – a
2) Make u the subject of the formula
D = ut + kt2
16- Use of a formula.
1) A shopkeeper uses this formula to work out the cost of bags of oranges.
pg. 1
� C = 1.8n
C is the cost in £
n is the number of bags
(a) Work out the cost of 7 bags.
(b) There are four oranges in each bag. Work out the average cost of an
orange. Give your answer in pence.
2) A plumber uses this formula for working out how much to charge for a
job.
Charge (£) = 25 + 30 × number of hours
How much will she charge for a job that lasts 3 hours?
17- Laws of indices.
• The exam question will use the word “simplify”
• When multiplying, add the indices
• When dividing, subtract the indices
• With brackets, multiply the indices
• If the exam question has the words “work out the value of”, or
“evaluate” it means the answer is a number.
• Anything to the power zero is 1
• Anything to the power one is itself
• Anything to a negative power becomes a reciprocal
pg. 1
� 1) Simplify a ×a
5 4
2) Simplify m ÷m
5 3
−1
3) Work out the value of 9 2
18- Expand double brackets.
• Use FOIL (first, outside, inside, last) or the grid method (for multiplication)
to expand brackets.
1) Expand and simplify (x + 5)(x + 9)
2) Expand and simplify (w − 3)(w − 8)
3) Expand and simplify (2x + 5)(2x − 5)(3x + 7)
4) (3x + 1)(x − 2) + ax + b ≡ 3x2 + 8x – 5. Work out the values of a and b.
19- Factorise quadratics.
• For any quadratic ax² + bx + c = 0, find a pair of numbers with a sum of b
and a product of ac to factorise.
1) Factorise x² + 5x + 4
2) Factorise x² + 2x – 24
3) Factorise x² − 64
20- Solve quadratic equations by factorising.
• A quadratic equation is an equation of degree two
• To solve a quadratic equation by factorising you need to:
Arrange so that all terms are on one side, so the equation is in the form
2
a x +bx +c=0
Factorise
Make the expression inside each bracket ¿ 0
Solve both to give two possible values for x
pg. 1
� Example:
Solve x ²+7 x+ 6=0
( x +6 ) ( x+ 1 )=0
x +6=0∨x +1=0
x=−6∨x=−1
1) Factorise and solve 𝑥²−11𝑥 + 24=0
2) Factorise and solve 𝑥²+ 2𝑥−24=0
21- Simplify algebraic fractions.
• Factorise the numerator and denominator;
• Cancel common factors;
• Then add/subtract/multiply divide if necessary.
2
6 x +3 x
1) Simplify fully 2
4 x −1
1 2
2) Write +
x+ 4 x−4
as a single fraction in its simplest form.
2 x +1 5 x−2 19 x−4
3) Show that 3
+ 2
simplifies to 6
22- Draw linear and quadratic graphs.
pg. 1
�• Draw a table of values with x and y.
• Work out the value of y when x = 0, x = 1, x = 2, then use the pattern to
work out the rest.
• Connect the coordinates with a straight line to draw a linear graph.
• Connect the coordinates with a straight line to draw a linear graph.
1
1) On the grid, draw the graph of y = 2 x + 1 for x values from -4 to 4.
pg. 1
� 2) (a) Complete the table of values for 𝑦=𝑥²+2𝑥−5.
pg. 1
� (b) On the gird, draw the graph of 𝑦=𝑥²+2𝑥−5.
(c) Circle the coordinates of the turning point of the curve.
(0,−5) (−1,−6) (1.4,0) (−6,−1)
23- Solve simultaneous equations.
1. Scale up (if necessary)
2. Add or subtract (to eliminate)
3. Solve (to find x)
pg. 1
�4. Substitute (to find y) (or the other way around)
1) Solve the simultaneous equations
2x + 4y = 26
3x − y = 4
2) Solve the simultaneous equations
5x + 2y = 4
x – 3y = –23
24- Solve volume problems.
• Volume of a prism = area of cross section x length
• The surface area is the area of the surface (calculate the area of each
face then add together)
1) Shown below is a trapezoid prism.
Find the volume of the prism.
2) The diagram shows an empty water container.
The container is going to be filled using a hose pipe.
The water will flow into the container at a rate of 2 litres per second.
How long will it take for the container to be filled completely?
pg. 1
� …..........................seconds
25- Solve problems involving area and perimeter of 2D shapes.
• Area of a rectangle = base x height
• Area of a triangle = ½ x base x height
• Area of a parallelogram = base x height
• Area of a trapezium = ½ (a + b) h, where a and b are the parallel sides
and h is the height
• The perimeter is the distance around the edge of the shape
1) The diagram shows a rectangle. The sides are measured in centimetres.
Explain why 5x + 3 = 3x + 9
Solve 5x + 3 = 3x + 9
Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle.
2) The diagram shows a square.
pg. 1
� Work out the length of one side of the square.
26- Angles in polygons and parallel lines.
• Angles in a triangle sum to 180°
• Angles on a straight line sum to 180°
• Angles around a point sum to 360°
• Vertically opposite angles are equal
• Alternate angles are equal
• Corresponding angles are equal
• Supplementary angles sum to 180°
• An exterior and an interior angle of a polygon sum to 180°
• An exterior angle = 360° ÷ number of sides
1) Find the size of the angle marked x.
pg. 1
� 2) Shown below is a parallelogram.
Find x
Find y
Find z
3) AB is parallel to CD.
Work out the size of the angle marked x. Give a reason for
your answer.
Work out the size of the angle marked y.
pg. 1
� 27- Averages.
Mode is most – the number that occurs the most frequently.
Median is middle – put the numbers in order then identify the middle
number.
Mean is mean to work out – add all the numbers together and divide by
the quantity in the list.
Range is the difference from the biggest to the smallest.
1) Mrs Smith asked each student in her class to record the numbers of
times they used their mobile phone last Saturday.
Here are the results for the boys.
Boys 8 10 8 9 7 9 8 13 14
(a) Work out the median.
(b) Work out the mode.
(c) Work out the mean.
(d) Work out the range.
Here are the results for the girls.
Girls 6 8 9 9 10 14 14
(e) Compare the numbers of times the boys used their mobile phones
with the numbers of times the girls used their mobile phones.
2) Here are four number cards.
One of the cards is turned over so you cannot see the number on it.
The mean of the four numbers is 6
Work out the number you cannot see.
pg. 1
�Averages from Tables.
The mode is the one with the highest frequency.
To calculate the median, find where the middle value is located by using
n+1
.
2
Σfx
The mean is given by Σf , ie. the total frequency x midpoint divided by
the total frequency.
Always look back at the data to check your answer looks realistic.
1) 30 adults took part in a survey. They were each asked how much money
they spent on lottery tickets last week. The table shows the results of
the survey.
Money (£) Frequency
0 5
2 16
4 6
20 2
30 1
Work out the mode, median and mean amount of money the 30 adults
spent on lottery tickets.
2) The table gives some information about the time taken by a group of
100 students to complete an IQ test.
Time (t seconds) Frequency
60 < t < 70 12
70 < t < 80 22
80 < t < 90 23
90 < t < 100 24
100 < t < 110 19
(a) Write down the modal class interval.
pg. 1
� (b) Calculate an estimate for the mean time taken by the students.
pg. 1