0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesBtech 1 Sem Basic Mathematics 1 75371 Jan 2023
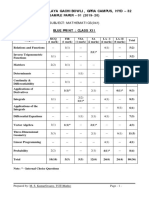
This document is the instructions for a Basic Mathematics exam consisting of 3 sections with a total of 9 questions. Section A has 10 multiple choice questions worth 2 marks each. Section B and C each have 4 questions worth 8 marks each, and students must attempt 5 questions total between these two sections selecting at least 2 from each. The document provides examples of the types of math problems that could be covered, such as solving equations, working with matrices, trigonometric identities, and statistics. It also includes standard exam instructions regarding time limits, maximum points possible, and a note about academic integrity.
Uploaded by
rahulpanjkosiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesBtech 1 Sem Basic Mathematics 1 75371 Jan 2023
This document is the instructions for a Basic Mathematics exam consisting of 3 sections with a total of 9 questions. Section A has 10 multiple choice questions worth 2 marks each. Section B and C each have 4 questions worth 8 marks each, and students must attempt 5 questions total between these two sections selecting at least 2 from each. The document provides examples of the types of math problems that could be covered, such as solving equations, working with matrices, trigonometric identities, and statistics. It also includes standard exam instructions regarding time limits, maximum points possible, and a note about academic integrity.
Uploaded by
rahulpanjkosiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- SECTION-A: Contains compulsory questions focusing on basic mathematics problems and short answers.
- SECTION-C: Features elective questions that require the use of advanced problem-solving techniques.
- SECTION-B: Includes optional questions that delve into more complex mathematical proofs and scenarios.