Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Equilibrium Notes
Uploaded by
seema sahni0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageChemical Equilibrium Notes
Uploaded by
seema sahniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
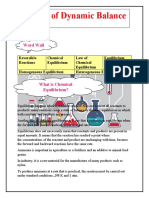
Chemical Equilibrium Notes
Equilibrium is the state of a process in which the properties like temperature,
pressure, and concentration etc of the system do not show any change with passage
of time.
In all processes which attain equilibrium, two opposing processes are involved.
Equilibrium is attained when the rates of the two opposing processes become equal.
If the opposing processes involve only physical changes, the equilibrium is
called Physical Equilibrium.
If the opposing processes are chemical reactions, the equilibrium is called Chemical
Equilibrium.
Solid – liquid Equilibrium: H 2 O(s) H 2 O(l)
Liquid – Gas Equilibrium: H 2 O(l) H 2 O(g)
Solid – Solution Equilibrium: Salt(Solid) Salt(in solution)
Gas –Solution equilibrium: CO 2 (g) CO 2 (in solution)
Equilibrium in Chemical Process
Reversible reaction: A reaction in which not only the reactants react to form the
products under certain conditions but also the products react to form reactants
under the same conditions
Examples: 3Fe(s) + 4H 2 O(g) Fe3 O 4 (s) + 4H 2 (g)
Irreversible reaction: A reaction cannot take place in the reverse direction, i.e. the
products formed do not react to give back the reactants under the same condition.
Example: AgNO 3 (aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO 3 (g)
Generally, a chemical equilibrium is represented as
Where A, B are reactants and C, D are products.
The equilibrium state is dynamic and not static in nature. A reaction is said to have
attained equilibrium when the rate of forward reaction equals that of backward
reaction
You might also like
- Chemical EquillibriumDocument31 pagesChemical Equillibriumsiddhartha2862No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Equilibrium PartDocument17 pagesChemical Equilibrium PartSubhasish SauNo ratings yet
- EquilibriaDocument47 pagesEquilibriarajiv shahNo ratings yet
- Equillibrium RevisionDocument6 pagesEquillibrium RevisionMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium - Lecture NotesDocument46 pagesChemical Equilibrium - Lecture NotespokeyballNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionOP IMPERIALNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria NotesDocument7 pagesChemical Equilibria NotesImranMalikNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument3 pagesEquilibrium NotesAnilkumarsanctumNo ratings yet
- Physical, Chemical Equilibrium, Equilibrium Constant .Document7 pagesPhysical, Chemical Equilibrium, Equilibrium Constant .Rajesh Kumar ParidaNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument1 pageChemical EquilibriumShaheen RajNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Equilibrium Law of Mass ActionDocument20 pagesChemical Equilibrium: Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Equilibrium Law of Mass ActionVíctor RuedaNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument8 pagesEquilibriumLionel Munya ChigwidaNo ratings yet
- L13 PDFDocument26 pagesL13 PDFJoshua RomeaNo ratings yet
- JB CI 7.1 Chemical EquilibriumDocument9 pagesJB CI 7.1 Chemical EquilibriumOCRChemistrySaltersNo ratings yet
- A State of Dynamic Balance - FactsDocument15 pagesA State of Dynamic Balance - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Chm012Document17 pagesChemical Equilibrium Chm012Elaiza Angelene NacarioNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument30 pagesChemical EquilibriumSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument31 pagesChemical EquilibriumRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- CLASS 11 Equilibrium - 221029 - 221055Document24 pagesCLASS 11 Equilibrium - 221029 - 2210552007jahanviNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Equilibrium - AglaSem SchoolsDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Equilibrium - AglaSem SchoolsAJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument31 pagesChemical EquilibriumPrince DigvijayNo ratings yet
- Handout No. 9 in General Chemistry 2: Co Qah + Melc LWDocument10 pagesHandout No. 9 in General Chemistry 2: Co Qah + Melc LWPortgas D. AceNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquillibriumDocument66 pagesChemical EquillibriumBalakrishna ArpulaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7-17 NotesDocument76 pagesTopic 7-17 NotesHamzaNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument36 pagesEquilibriumkamininmishraNo ratings yet
- Homework - 8chemical Equilibrium FINALDocument20 pagesHomework - 8chemical Equilibrium FINALNwachukwu ObiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Physical IIDocument31 pagesChemistry Physical IIAyush Ranjan OjhaNo ratings yet
- Army Public School Gopalpur: EquilibriumDocument11 pagesArmy Public School Gopalpur: EquilibriumAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- 7.equilibrium FDocument43 pages7.equilibrium Fshrutianand8915No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: Module - 5Document29 pagesChemical Equilibrium: Module - 5TeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium (Part I)Document8 pagesEquilibrium (Part I)Arpan SenNo ratings yet
- Conditions For Attainment of Chemical EquilibriumDocument2 pagesConditions For Attainment of Chemical Equilibriumnahil ahmedNo ratings yet
- EquilibriaDocument7 pagesEquilibriashivakafle039No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes PDFDocument7 pagesChemistry Notes PDFEngwa Clintine NdumbiNo ratings yet
- Simple Physical Phenomena at EquilibriumDocument9 pagesSimple Physical Phenomena at Equilibriumtifanny gamboaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes EquilibriumDocument14 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes EquilibriumSwastika DasNo ratings yet
- ANAchem Module9Document6 pagesANAchem Module9Marie Antonette BaligodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 52B VILORIA, Kristine Joyce D.No ratings yet
- 10.4 EquilibriumDocument35 pages10.4 EquilibriumAnsh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Chemical EquilibriumDocument9 pagesLecture Note On Chemical EquilibriumRee ClaireNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI CH 6 Chemistry Notes by AkDocument11 pagesHsslive XI CH 6 Chemistry Notes by AkkundrapupNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument5 pagesEquilibriumnanaNo ratings yet
- Garcia - Chemical Kinetics and EquilibriumDocument10 pagesGarcia - Chemical Kinetics and EquilibriumPrince SanjiNo ratings yet
- EQUILIBRIUMDocument13 pagesEQUILIBRIUMFarhan Al ZayedNo ratings yet
- GC2 Week11 Lesson ProperDocument6 pagesGC2 Week11 Lesson ProperReyNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Equilibrium ConceptsDocument21 pagesFundamental Equilibrium Conceptsnxumalopat2No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium .PresentationDocument17 pagesChemical Equilibrium .PresentationtalhawasimNo ratings yet
- Equilibria (Equilibrium) : Physical Equilibrium Chemical EquilibriumDocument5 pagesEquilibria (Equilibrium) : Physical Equilibrium Chemical EquilibriumPrashant BhandariNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument51 pagesChemical EquilibriumP NigadeNo ratings yet
- Uzair ChemistryDocument6 pagesUzair ChemistryTalbia SyedNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument12 pagesEquilibrium Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions:) Is Exceptionally High, Then ThisDocument5 pagesReversible Reactions:) Is Exceptionally High, Then ThisUsman Shaukat - 70642/TCHR/BGJTNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes EquilibriumDocument10 pages11 Chemistry Notes Equilibriumgansan105No ratings yet
- NEO JEE 11 P1 CHE E Equilibrium S14 209Document386 pagesNEO JEE 11 P1 CHE E Equilibrium S14 209cskksc17No ratings yet
- Unit 6Document53 pagesUnit 6Muktaar HassenNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument10 pagesEquilibrium NotesAlana SebyNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium NotesDocument10 pagesEquilibrium NotesAlana SebyNo ratings yet