Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trade
Trade
Uploaded by
Kao SophearakOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trade
Trade
Uploaded by
Kao SophearakCopyright:
Available Formats
In a general sense, "trade" refers to the action of buying and selling goods or services.
It
involves the exchange of one item or commodity for another, often with the goal of
obtaining something of value in return. Trade can occur on various scales, from
individuals engaging in local transactions to nations participating in international trade.
In a more specific context, "trade" is often used in the financial and economic domain to
describe the buying and selling of financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds,
currencies, commodities, and other assets. Here are a couple of common contexts for
the term "trade":
1. Financial Markets: In the context of financial markets, a "trade" refers to the
buying or selling of a financial instrument. Traders engage in these transactions
to take advantage of price fluctuations, aiming to make a profit. Various types of
trading exist, including stock trading, forex (foreign exchange) trading,
commodity trading, and cryptocurrency trading.
2. International Trade: On a broader economic scale, "trade" can refer to the
exchange of goods and services between countries. Nations engage in
international trade to obtain products or services they may not produce
efficiently themselves and to benefit from comparative advantages. International
trade is a fundamental aspect of the global economy.
In both financial and economic contexts, trade involves the transfer of ownership from
one party to another in exchange for something of value, whether it be money, goods,
or services. The motivations for trade can vary, but they often include the pursuit of
economic efficiency, access to resources, and the opportunity for specialization and
growth.
You might also like
- Currencies A PrimerDocument15 pagesCurrencies A PrimerNicolae VutcariovNo ratings yet
- If Sle ContentDocument4 pagesIf Sle ContentLavesh KaushikNo ratings yet
- A New Era of Currency Derivatives Market in India: Dr. E.V.P.A.S.PallaviDocument5 pagesA New Era of Currency Derivatives Market in India: Dr. E.V.P.A.S.PallavirommelNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument2 pagesContemporary WorldKricel PereñaNo ratings yet
- Project Foregin Exchange MarketDocument9 pagesProject Foregin Exchange MarketjagrutiNo ratings yet
- FMDONEDocument6 pagesFMDONECheska TuazonNo ratings yet
- Subject Code & Name: Mf0015 International Financial ManagementDocument5 pagesSubject Code & Name: Mf0015 International Financial ManagementNIKHILPATNINo ratings yet
- Commerce - International TradeDocument2 pagesCommerce - International Tradewitness vurayayiNo ratings yet
- GigiDocument2 pagesGigiAleko tamiruNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments: Current Account Capital Account Balancing AccountDocument3 pagesBalance of Payments: Current Account Capital Account Balancing AccountMohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Tema 1 IfimDocument29 pagesTema 1 Ifimacaroie13364No ratings yet
- Financial Market SEM-3Document5 pagesFinancial Market SEM-3naomiNo ratings yet
- A Financial Instrument Is A Monetary Contract That May Be Traded and Settled Between Two PartiesDocument2 pagesA Financial Instrument Is A Monetary Contract That May Be Traded and Settled Between Two PartiesMaricon GalacioNo ratings yet
- Abstract of Financial Market 1Document8 pagesAbstract of Financial Market 1mmkrishnan94100% (1)
- International Financial MarketDocument36 pagesInternational Financial MarketSmitaNo ratings yet
- Module I INTRODUCTION TO INTERNATIONAL TRADEDocument11 pagesModule I INTRODUCTION TO INTERNATIONAL TRADEDaniela SebastianNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument48 pagesFinancial MarketAHUTI SINGHNo ratings yet
- Module I INTRODUCTION TO INTERNATIONAL TRADE-2Document11 pagesModule I INTRODUCTION TO INTERNATIONAL TRADE-2Cezarene FernandoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Contemporary WorldDocument31 pagesReviewer Contemporary WorldJon Nicole DublinNo ratings yet
- MGT107 IBT Midterm ReviewerDocument15 pagesMGT107 IBT Midterm ReviewerMary Grace AlzateNo ratings yet
- Financial AssetDocument14 pagesFinancial AssetkhushboogeetaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Financial MarketDocument49 pagesRisk Management in Financial MarketAashika ShahNo ratings yet
- Module-1: Financial MarketsDocument41 pagesModule-1: Financial MarketsPeeYush SahuNo ratings yet
- Eco1 NotesehehhehDocument14 pagesEco1 NotesehehhehDon't Mess With MeNo ratings yet
- Preamble DerivativesDocument1 pagePreamble DerivativesmichaelrtzNo ratings yet
- Classification and Functions of Financial MarketsDocument18 pagesClassification and Functions of Financial MarketsKongskieRicNo ratings yet
- MarketDocument7 pagesMarketVerlyn ElfaNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Financial InstrumentsDocument80 pagesFinancial Markets and Financial Instrumentsabhijeit86100% (2)
- MentDocument1 pageMentvandanaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Learning ResourcesDocument13 pagesDerivatives Learning ResourcesPrasadNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument8 pagesDerivativesSubrahmanyam RajuNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument2 pagesFinancial MarketsShann WickNo ratings yet
- Unit Viii STFMDocument11 pagesUnit Viii STFMmrzaa2114No ratings yet
- Unit - 4 FERMDocument12 pagesUnit - 4 FERM22mba113No ratings yet
- Inter - CH - 1 (1) (Read-Only)Document23 pagesInter - CH - 1 (1) (Read-Only)sharifhass36No ratings yet
- Stock MarketDocument24 pagesStock MarketRig Ved100% (2)
- THE FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET HandoutDocument6 pagesTHE FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET HandoutNoeline ParafinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-I Introduction of DerivativesDocument11 pagesChapter-I Introduction of DerivativesAvula Shravan YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Fi & CMDocument12 pagesChapter - 1 Fi & CMsitina.at.lunarNo ratings yet
- Hanna Hussan 1bbads Cia1 IfsDocument16 pagesHanna Hussan 1bbads Cia1 Ifslakshya lashkariNo ratings yet
- Meaning & Definition of FEDocument1 pageMeaning & Definition of FEmbapritiNo ratings yet
- Financial DerivativesDocument309 pagesFinancial DerivativessuryaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of DerivativesDocument23 pagesIntroduction of DerivativesBhavani Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Sip ReportDocument77 pagesSip ReportRosita JacobNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Slides 1.3Document5 pagesFinancial Management Slides 1.3honathapyarNo ratings yet
- Financial Market & InstrumentDocument73 pagesFinancial Market & InstrumentSoumya ShettyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Fin MarketsDocument3 pagesIntro To Fin Markets65xykwtn8rNo ratings yet
- Ass1 InternationalDocument21 pagesAss1 InternationalAbdulhafiz HajkedirNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument2 pagesFinancial Marketnysasunuwar44No ratings yet
- Ifim Units 3&4Document19 pagesIfim Units 3&4kushalNo ratings yet
- Assignment of IFSDocument3 pagesAssignment of IFSvishnu sharmaNo ratings yet
- Trichy Full PaperDocument13 pagesTrichy Full PaperSwetha Sree RajagopalNo ratings yet
- The Global EconomyDocument8 pagesThe Global EconomyRaven Evangelista CanaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Futures and Options Mba ProjectDocument92 pagesDerivatives Futures and Options Mba ProjectAboli Junagade40% (5)
- FMI NotesDocument93 pagesFMI Notesjain_ashish_19888651No ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial MarketsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Financial MarketsMuhammad Azhar SaleemNo ratings yet
- IBM Assignment DevangSSDocument11 pagesIBM Assignment DevangSSdevangshekhawat123No ratings yet
- Forex MarketDocument7 pagesForex MarketDivya ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Maths For Grade 7Document1 pageMaths For Grade 7Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 3Document1 pageMath Grade 3Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
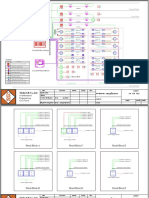
- SLD-16N704A - CSWS - Booster Pump Panel With VSDDocument1 pageSLD-16N704A - CSWS - Booster Pump Panel With VSDKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 1Document1 pageMaths Grade 1Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
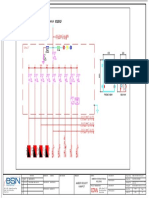
- SLD-16N704A - CSWS - Booster Pump Panel With VSD2Document1 pageSLD-16N704A - CSWS - Booster Pump Panel With VSD2Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Quotation: Phase 7 Overhead Option I MDB Panel 400ADocument1 pageQuotation: Phase 7 Overhead Option I MDB Panel 400AKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- In Second GradeDocument2 pagesIn Second GradeKao SophearakNo ratings yet
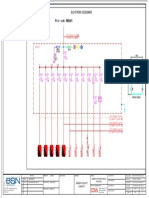
- SLD-16N704A - CSWS - Booster Pump Panel With VSD 1Document1 pageSLD-16N704A - CSWS - Booster Pump Panel With VSD 1Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- SCADA Stands For Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionDocument1 pageSCADA Stands For Supervisory Control and Data AcquisitionKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Power MetersDocument2 pagesPower MetersKao SophearakNo ratings yet
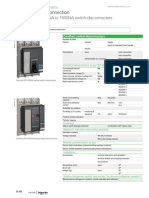
- Control and Disconnection: Compact Ns630Bna To 1600na Switch-DisconnectorsDocument2 pagesControl and Disconnection: Compact Ns630Bna To 1600na Switch-DisconnectorsKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- MV ProjectDocument8 pagesMV ProjectKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Drawing 800A OUTDOOR PANEL PDFDocument4 pagesDrawing 800A OUTDOOR PANEL PDFKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Alend Trading & Engineer Solution: NTS@A4Document1 pageAlend Trading & Engineer Solution: NTS@A4Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- LVDB 800A & CAP BANK 350KVAR & SDB 250apdf PDFDocument3 pagesLVDB 800A & CAP BANK 350KVAR & SDB 250apdf PDFKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Alend Trading & Engineer Solution: I MDB 800A Abb 1 SETDocument2 pagesAlend Trading & Engineer Solution: I MDB 800A Abb 1 SETKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Machine ListDocument7 pagesMachine ListKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Scope Freshy and MilkDocument1 pageScope Freshy and MilkKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Singsong industial Co.,Ltd: Assembled the main switch cabinet (ตู ้เมนไฟฟ้า)Document3 pagesSingsong industial Co.,Ltd: Assembled the main switch cabinet (ตู ้เมนไฟฟ้า)Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Singsong 240 TPD Tapioca Starch 1year Spareparts List (Electric Department) 2019Document2 pagesSingsong 240 TPD Tapioca Starch 1year Spareparts List (Electric Department) 2019Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- Transformer Technical Specification: Rated Voltage Ratio (Primary / Secondary)Document3 pagesTransformer Technical Specification: Rated Voltage Ratio (Primary / Secondary)Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- 78.milk &pet FA SystemDocument3 pages78.milk &pet FA SystemKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- 78.milk &pet - PaDocument2 pages78.milk &pet - PaKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- LS Bus Duct System: WWW - Lsis.bizDocument48 pagesLS Bus Duct System: WWW - Lsis.bizKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- VN1801-RHD-00-XX-DR-E-1002-P2 Main Single Line DiagramDocument1 pageVN1801-RHD-00-XX-DR-E-1002-P2 Main Single Line DiagramKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- VN1801-RHD-00-XX-DR-E-1003-P2 Main Single Line DiagramDocument1 pageVN1801-RHD-00-XX-DR-E-1003-P2 Main Single Line DiagramKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- SLD C2Document1 pageSLD C2Kao SophearakNo ratings yet
- SLD C1BDocument1 pageSLD C1BKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- SLD C1CDocument1 pageSLD C1CKao SophearakNo ratings yet
- SLD C3Document1 pageSLD C3Kao SophearakNo ratings yet