Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 - Liabilities
Uploaded by
Patrick Jayson Villademosa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesLiabilities Valix
Original Title
Chapter 1- Liabilities
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLiabilities Valix
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesChapter 1 - Liabilities
Uploaded by
Patrick Jayson VillademosaLiabilities Valix
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Economic resource is an asset, thus, the
Chapter 1: Liabilities term share dividends payable are
considered as an accounting liability,
because the obligation is to issue an entity's
LIABILITIES
own share. Thus, dividends payable is
Liabilities are 1. Present obligations of an classified as an equity rather than
entity 2. To transfer an economic resource accounting liability.
3. As a result of past events.
1. An obligation is a responsibility that an
3. Liability only arises on past events
entity has no practical ability to avoid.
because the liability is not recognized until it
Present obligations may be legal or is incurred.
constructive.
Obligating events creates a present
A legal obligation arises because of a obligation as a result of an event that has no
binding contract or statutory requirement. alternative solution but to settle the
obligation created by the event.
Legal Example: (Statutory requirement) To
pay tax, (Binding contract) To pay the Ex. When an entity tries to secure a loan, an
entity’s accounts payable. obligating event only arises, when the cash
has already been received.
The constructive obligation arises by the
reason of conducting a normal business
practice, a desire to alleviate or maintain
Measurement of liabilities
good business relations.
Constructive Example: As the entity Initial Subsequent
promotes its sales, the entity must conduct
Short-term - FV FV
some sort of gimmick like, buy 1 take 1 or
Interest
50% off, therefore, entity’s obligated to bearing
deliver their goods or services lower than
the original price. Short-term - FV FV
Non Interest
The payee to whom the obligation is owed, Bearing
the time, and the no. of individuals that
Long-term - FV FV
entities oblige into are not necessarily
Interest
needed. bearing
2. Economic resource is the asset that Long-term - PV Amortized
represents a right with a potential to Non Interest
produce economic benefits. Bearing
Obligation must be to pay cash, non-cash,
or provide a service at some future time.
Example of Liabilities as current, it'll be classified as noncurrent.
Noncurrent liabilities include the ff:
A. Accounts payable.
A. Noncurrent portion of long-term
B. Withholding tax or incentives. debt
C. Accrued payable. B. Finance lease liability
D. Dividends payable (excluding C. Deferred tax liability
share dividends payable)
D. Long-term obligation to officers
E. Advances from the customer.
E. Long -term deferred revenue
F. Debt payable like notes,
mortgage, and bonds Long-term debt falling due within a year.
G. Income tax payable Basically, the long-term debt falling due
within a year is reclassification of a
H. Deferred or Unearned revenue long-term liability.
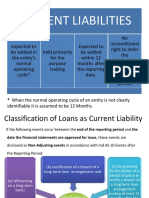
Current liabilities If the entity decides that they would
refinance, the liability that is falling within a
Current liabilities shall be classified when year, it will be classified as still non-current
one of the following arises: liability, if they decided not to, the liability will
be reclassified as current liability; still, it will
A. The entity expects to settle it
depend on the contract on who has the right
within the operating cycle.
of the power in the liability.
B. The entity holds the liability
A. Original term was for a period longer
primarily for the purpose of
than 12 months.
TRADING.
B. An agreement to refinance or to
C. The liability is due to be settled
reschedule payment on a long-term
within 12 months after the
basis is completed after the reporting
reporting period.
period and before the financial
D. The entity does not have the right statements are authorized for issue.
at the end of the reporting period
Covenants
to defer settlement of the liability
for at least 12 months after the Covenants are often attached to borrowing
reporting period. agreements which represent undertakings
by the borrower.
Noncurrent liabilities
These covenants are restrictions on the
The term noncurrent liabilities is a residual
borrower as to undertaking further
definition, meaning that if it's not classified
borrowings, paying dividends, maintaining
specified level of working capital and so Income less: Bonus = After bonus x Bonus
forth. rate
Breach of covenants
If a certain condition has been breached,
the liability becomes payable on demand.
This liability is classified as current because
at the end of the reporting period, the entity
does not have the right to defer settlement
for at least 12 months after the end of the
reporting period.
However, the liability is classified as
noncurrent if the lender agreed on or before
the end of the reporting period to provide a
grace period ending at least 12 months after
the end of the reporting period.
Grace period
Is the period within which the entity can
rectify the breach and during which the
lender cannot demand immediate payment.
Est. liabilities
Are obligations which exist at the end of the
reporting period although their amount is not
definite.
Deferred or Unearned revenue
Is an income already received but not yet
earned. It may be realizable within a year or
more than a year after the end of the
reporting period.
Bonus Computation
Before bonus and tax
Income x Bonus
After bonus but before tax
You might also like
- Learning Resource 1 Lesson 1Document11 pagesLearning Resource 1 Lesson 1Novylyn AldaveNo ratings yet
- Learning Material 1Document7 pagesLearning Material 1salduaerossjacobNo ratings yet
- ULOa. Liabilities - 1Document47 pagesULOa. Liabilities - 1pam pamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1clarizaNo ratings yet
- Understanding LiabilitiesDocument28 pagesUnderstanding LiabilitiesRacelle FlorentinNo ratings yet
- Module 001 Accounting For Liabilities-Current Part 1Document6 pagesModule 001 Accounting For Liabilities-Current Part 1Gab BautroNo ratings yet
- VALIX IA2 Chapter 1Document5 pagesVALIX IA2 Chapter 1M100% (1)
- Audit of LiabilitiesDocument13 pagesAudit of LiabilitiesJoshua Catalla MabilinNo ratings yet
- Definition Explained:: Liabilities A Liability Is ADocument26 pagesDefinition Explained:: Liabilities A Liability Is ACurtain SoenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Liabilities PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Liabilities PDFKesiah FortunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Liabilities LiabilitiesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Liabilities LiabilitiesJessica AllyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1clarizaNo ratings yet
- Present ObligationDocument6 pagesPresent ObligationArgem Jay PorioNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document7 pagesModule 1Alextrasza LouiseNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument3 pagesFinancial Accounting and ReportingEmma Mariz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ms. Sharon A. Bactat Prof. Suerte R. Dy: Sabactat@mmsu - Edu.ph Srdy@mmsu - Edu.phDocument26 pagesMs. Sharon A. Bactat Prof. Suerte R. Dy: Sabactat@mmsu - Edu.ph Srdy@mmsu - Edu.phCrisangel de LeonNo ratings yet
- Current Liab Trade and Other PayablesDocument6 pagesCurrent Liab Trade and Other PayablesRamainne Chalsea RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Module 1-LIABILITIES and PREMIUM LIABILITYDocument10 pagesModule 1-LIABILITIES and PREMIUM LIABILITYKathleen SalesNo ratings yet
- Ia 2 - ReviewerDocument3 pagesIa 2 - ReviewerCenelyn PajarillaNo ratings yet
- College of Business and Accountancy: Obligating EventDocument4 pagesCollege of Business and Accountancy: Obligating EventAnthony DyNo ratings yet
- Understanding LiabilitiesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding LiabilitiesXienaNo ratings yet
- Aks 2023 - 2024 - Far 4 - Day 1Document8 pagesAks 2023 - 2024 - Far 4 - Day 1John Carl TuazonNo ratings yet
- Account for Liabilities in AccountingDocument8 pagesAccount for Liabilities in Accountingpam pamNo ratings yet
- Intacc 2 NotesDocument25 pagesIntacc 2 Notescoco credoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LiabilitiesDocument1 pageIntroduction To LiabilitiesAJ GasparNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY For INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 2 PDFDocument20 pagesSUMMARY For INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING 2 PDFArtisan100% (1)
- Current LiabilitiesDocument3 pagesCurrent Liabilitiesreymonastrera07No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: LiabilitiesDocument1 pageChapter 1: LiabilitiesJen Bernadette CiegoNo ratings yet
- Current LiabilityDocument5 pagesCurrent LiabilityMaria AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Notes: Liabilities and Current LiabilitiesDocument8 pagesChapter 13 Notes: Liabilities and Current LiabilitiesOmar MetwaliNo ratings yet
- Intacc NotesDocument10 pagesIntacc NotesIris FenelleNo ratings yet
- Current Liabilities - ProblemsDocument15 pagesCurrent Liabilities - ProblemsJames Ryan AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Questions 14,54,81, and 114Document5 pagesQuestions 14,54,81, and 114Damian Sheila MaeNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Acctg Lecture On Liabilities 22Document3 pagesIntermediate Acctg Lecture On Liabilities 22Tracy Lyn Macasieb NavidadNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 2 LiabilitiesDocument17 pagesIntermediate Accounting 2 LiabilitiesAngel MilanNo ratings yet
- Know About LiabilitiesDocument1 pageKnow About LiabilitiesStorm ShadowNo ratings yet
- Current LiabilitiesDocument14 pagesCurrent LiabilitiesESTRADA, Angelica T.No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting - Accounting For LiabilitiesDocument5 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting - Accounting For LiabilitiesLuisitoNo ratings yet
- (Liabilities) : Lecture AidDocument20 pages(Liabilities) : Lecture Aidmabel fernandezNo ratings yet
- Current Liabilities and ContingenciesDocument6 pagesCurrent Liabilities and ContingenciesDivine CuasayNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting Volume 2 by Robles and Empleo 2017 (book) chapterDocument13 pagesIntermediate Accounting Volume 2 by Robles and Empleo 2017 (book) chapterAbraham ChinNo ratings yet
- Know About LiabilitiesDocument1 pageKnow About LiabilitiesMandapalli SatishNo ratings yet
- LiabilitiesDocument3 pagesLiabilitiesClyn CFNo ratings yet
- IA2 - Key accounting concepts and principlesDocument2 pagesIA2 - Key accounting concepts and principlesAsh imoNo ratings yet
- Tax Receivables and Payables: Understanding Debt Types and CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesTax Receivables and Payables: Understanding Debt Types and CharacteristicsEKI TEENENo ratings yet
- Chapter 26Document8 pagesChapter 26Mae Ciarie YangcoNo ratings yet
- Current Liabilities: When The Normal Operating Cycle of An Entity Is Not ClearlyDocument9 pagesCurrent Liabilities: When The Normal Operating Cycle of An Entity Is Not Clearlysispita dashNo ratings yet
- Accounting for Refundable Deposits, Premiums, and WarrantiesDocument4 pagesAccounting for Refundable Deposits, Premiums, and WarrantiesJadon MejiaNo ratings yet
- Financial Reporting CaseDocument2 pagesFinancial Reporting CaseChristian Lloyd Alquiroz VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Module 008 Week003-Finacct3 Statement of Financial PositionDocument6 pagesModule 008 Week003-Finacct3 Statement of Financial Positionman ibeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Current LiabilitiesDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Current LiabilitiesEUNICE NATASHA CABARABAN LIMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 LiabilitiesDocument7 pagesChapter 1 LiabilitiesVirgilio EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Accounting 2: Liabilities and Financial ClassificationsDocument37 pagesAccounting 2: Liabilities and Financial ClassificationsAndrei GoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Chapter 12 LiabilitiesDocument5 pagesAssignment 1: Chapter 12 LiabilitiesKarylle Ynah MalanaNo ratings yet
- LiabilitiesDocument4 pagesLiabilitiesreymonastrera07No ratings yet
- LIABILITIESDocument12 pagesLIABILITIESJOHANNANo ratings yet
- Module 1: Classifying Current LiabilitiesDocument8 pagesModule 1: Classifying Current LiabilitiesMicah Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Intermediate Accounting Vol 2 Canadian 2nd Edition Lo Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Intermediate Accounting Vol 2 Canadian 2nd Edition Lo Solutions Manual PDFvaginulegrandly.51163100% (8)
- Far 20Document7 pagesFar 20Yusra PangandamanNo ratings yet
- Conflicts Digests and Notes Av PDFDocument189 pagesConflicts Digests and Notes Av PDFRostum AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Philbanking v. Lui She land lease caseDocument2 pagesPhilbanking v. Lui She land lease caseAljenneth Micaller100% (1)
- Hollis V Dow Corning CorporationDocument2 pagesHollis V Dow Corning CorporationAlice Jiang100% (1)
- Stodu 10Document6 pagesStodu 10Ahmad NafisNo ratings yet
- Liability of PartiesDocument16 pagesLiability of PartiesSGTNo ratings yet
- National Bank Of Lahore Ltd. vs Sohan Lal Saigal Case MemorialDocument16 pagesNational Bank Of Lahore Ltd. vs Sohan Lal Saigal Case MemorialTiger Khan0% (1)
- National Housing Authority Vs BasaDocument2 pagesNational Housing Authority Vs BasaMilagros Isabel L. VelascoNo ratings yet
- Prenuptial AgreementDocument2 pagesPrenuptial AgreementYavin FizowojNo ratings yet
- Conciliation Settlement Agreement AbhuDocument3 pagesConciliation Settlement Agreement AbhuABHINAV CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Preweek Handouts in Business Law May 2014 BatchDocument8 pagesPreweek Handouts in Business Law May 2014 BatchPhilip CastroNo ratings yet
- Escheats - Guardianship - AdoptionDocument9 pagesEscheats - Guardianship - AdoptionIrish AnnNo ratings yet
- Fletcher v. City of AberdeenDocument1 pageFletcher v. City of AberdeenMadison MonzonNo ratings yet
- DLL General-Mathematics Q2 W5Document13 pagesDLL General-Mathematics Q2 W5Princess DeramasNo ratings yet
- Critically Examine the Doctrine that by Giving Time to the Principal Debtor, the Creditor Discharges the SuretyDocument14 pagesCritically Examine the Doctrine that by Giving Time to the Principal Debtor, the Creditor Discharges the SuretyDigvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- John Floyd ContractDocument3 pagesJohn Floyd ContractRobert GouveiaNo ratings yet
- Rallos V Felix Go Chan & Sons Realty CorpDocument3 pagesRallos V Felix Go Chan & Sons Realty CorpCocoi ZapantaNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 225033 - Spouses Beltran v. Spouses CangaydaDocument6 pagesG.R. No. 225033 - Spouses Beltran v. Spouses CangaydaThalia Rose RomanovNo ratings yet
- Probate Court Determines Bank Account OwnershipDocument2 pagesProbate Court Determines Bank Account OwnershipAngela Louise SabaoanNo ratings yet
- Cruz, Chielsea - Civil LawDocument6 pagesCruz, Chielsea - Civil LawChielsea CruzNo ratings yet
- 13 Sps Santos vs. Court of AppealsDocument2 pages13 Sps Santos vs. Court of AppealsMyla RodrigoNo ratings yet
- C Syed Wajih 10kW Hybrid ESSDocument5 pagesC Syed Wajih 10kW Hybrid ESSChaudhary Muhammad Suban TasirNo ratings yet
- Opposition To Reopening Chapter 7 CaseDocument5 pagesOpposition To Reopening Chapter 7 Caserobertosantana1No ratings yet
- Jupiter International LimitedDocument6 pagesJupiter International LimitedRahul syalNo ratings yet
- Remission of Debt ExtinguishmentDocument3 pagesRemission of Debt ExtinguishmentRhos Bernadette Suico100% (2)
- CFA Level1 - Fixed Income - SS14 v2021Document154 pagesCFA Level1 - Fixed Income - SS14 v2021Carl Anthony FabicNo ratings yet
- Bank Mergers and Acquisitions Employee AgreementsDocument2 pagesBank Mergers and Acquisitions Employee AgreementsCPMMNo ratings yet
- Corpo ReviewerDocument24 pagesCorpo ReviewerJovie Hernandez-MiraplesNo ratings yet
- Deed of Absolute Sale: 45,000.00), Philippine Currency, To Me in Hand Paid ByDocument2 pagesDeed of Absolute Sale: 45,000.00), Philippine Currency, To Me in Hand Paid Bylyndon melvi sumiogNo ratings yet
- Mini-Case Study 1Document4 pagesMini-Case Study 1Ana-Maria SIMIONNo ratings yet
- Professional Liability Insurance Policy Summary For Errors and Omissions MiscellaneousDocument3 pagesProfessional Liability Insurance Policy Summary For Errors and Omissions MiscellaneousQBE European OperationsNo ratings yet