Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FIG - II.1.13-EGS Guidelines2020
FIG - II.1.13-EGS Guidelines2020
Uploaded by
MS AK0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageThe cup to disc ratio (CDR) has been used as a sign of glaucoma, but it depends mainly on disc size. A large CDR may be considered glaucomatous in a normal large disc, and a small CDR may be considered normal in a glaucomatous small disc. The document recommends not using CDR to classify patients and instead focusing on the neuroretinal rim. It also provides a table of measured optic disc sizes using different lenses to examine the disc.
Original Description:
Original Title
FIG.II.1.13-EGS_Guidelines2020
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe cup to disc ratio (CDR) has been used as a sign of glaucoma, but it depends mainly on disc size. A large CDR may be considered glaucomatous in a normal large disc, and a small CDR may be considered normal in a glaucomatous small disc. The document recommends not using CDR to classify patients and instead focusing on the neuroretinal rim. It also provides a table of measured optic disc sizes using different lenses to examine the disc.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageFIG - II.1.13-EGS Guidelines2020
FIG - II.1.13-EGS Guidelines2020
Uploaded by
MS AKThe cup to disc ratio (CDR) has been used as a sign of glaucoma, but it depends mainly on disc size. A large CDR may be considered glaucomatous in a normal large disc, and a small CDR may be considered normal in a glaucomatous small disc. The document recommends not using CDR to classify patients and instead focusing on the neuroretinal rim. It also provides a table of measured optic disc sizes using different lenses to examine the disc.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Patient Examination
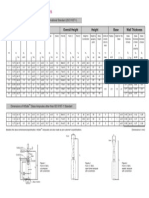
II.1.3.1.7 Rim width and cup to disc ratio (CDR) (see “Things to avoid - choosing
wisely” I.4)
A large CDR has been used as a sign of glaucoma damage. However, the CDR
depends mainly on the disc size, and a large CDR in normal large discs may be erro-
neously considered glaucomatous and a small CDR in glaucomatous small discs may
be erroneously considered as normal (Fig. II.1.13). The use of CDR to classify patients
is not recommended and the attention should be focused on the neuroretinal rim.
scale
+60D +78D +90D Superfield
lens
Volk | Nikon Volk Volk | Nikon NC Volk
© European Glaucoma Society
correction
0.94 | 1.03 1.13 1.36 | 1.59 1.50
factor
Measured uncorrected vertical diameter of optic disc
Disc area Small (<1.6 mm2) Medium (1.6 to 2.8 mm2) Large (>2.8 mm2)
Volk 60 D <1.65 mm 1.65 to 2.2 mm >2.2 mm
Volk 78 D <1.3 mm 1.3 to 1.75 mm >1.75 mm
Volk 90 D <1.1 mm 1.1 to 1.45 mm >1.45 mm
Superfield <1.15 mm 1.15 to 1.50 mm >1.5 mm
Digital 1.0x <1.5 mm 1.5 to 1.95 mm >1.95 mm
Super 66 <1.45 mm 1.45 to 1.9 mm >1.9 mm
Nikon 60 D <1.45 mm 1.45 to 1.9 mm >1.9 mm
Nikon 90 D <0.95 mm 0.95 to 1.25 mm >1.25 mm
Haag-Streit Goldmann <1.3 mm 1.3 to 1.7 mm >1.7 mm
Figure II.1.13 Optic disc size assessed at the slit lamp with handheld high power convex lens.
76
You might also like
- Accupower® Ri Escope: Instruction ManualDocument46 pagesAccupower® Ri Escope: Instruction ManualChadNo ratings yet
- ISO Ampoules 9187Document1 pageISO Ampoules 9187ravindra67% (3)
- Camhkv3090-1 Ficha Tecnica CamaraDocument3 pagesCamhkv3090-1 Ficha Tecnica CamaraIrve15No ratings yet
- 11322 Dsupport常用文档官网资料上传HiLookSpecAnalogCameraDatasheetofTHCB110P20170803Document3 pages11322 Dsupport常用文档官网资料上传HiLookSpecAnalogCameraDatasheetofTHCB110P20170803luis cabreraNo ratings yet
- Barotiwala MFG ScorecardDocument3 pagesBarotiwala MFG ScorecardAshish MishraNo ratings yet
- THC-T110-M 1 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-T110-M 1 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- Vernier Caliper and Screw Gauge ReportDocument8 pagesVernier Caliper and Screw Gauge ReportMinSugar1015No ratings yet
- Especificaciones THC-B223-MDocument3 pagesEspecificaciones THC-B223-MYale ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- Auto Anticap ENDocument2 pagesAuto Anticap ENvgciasenNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE16C0T-VFIR3F HD720p IR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesDS-2CE16C0T-VFIR3F HD720p IR Bullet Camera: Key Featuresgonzalo2205No ratings yet
- DS-2CE57D3T-VPITF 2 MP EXIR Dome Camera: Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesDS-2CE57D3T-VPITF 2 MP EXIR Dome Camera: Key FeaturesChiluvuri VarmaNo ratings yet
- What Is Robust Design or Taguchi's Method?Document29 pagesWhat Is Robust Design or Taguchi's Method?ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Grain Size AnalysisDocument13 pagesGrain Size AnalysisSATYAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE16H0T - (A) IT3ZF 5 MP Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesDS-2CE16H0T - (A) IT3ZF 5 MP Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesRoberto QuindNo ratings yet
- Latex, Online Powder Free Gloves, Palm Textured, 240MM C2Document2 pagesLatex, Online Powder Free Gloves, Palm Textured, 240MM C2William CheongNo ratings yet
- THC-B323-Z 2 MP EXIR VF Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-B323-Z 2 MP EXIR VF Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- Latex, Online Powder Free Gloves, Textured, 240MM PLM PDFDocument2 pagesLatex, Online Powder Free Gloves, Textured, 240MM PLM PDFWilliam CheongNo ratings yet
- Class Presentation M FG 318999 Sidney Shaol ADocument28 pagesClass Presentation M FG 318999 Sidney Shaol AFitra VertikalNo ratings yet
- Camara Ds-2ce16h5t-It3zeDocument3 pagesCamara Ds-2ce16h5t-It3zeLans M-ZNo ratings yet
- 63-9378 - Rev D - ULTRA Puck - VLP-32C - Datasheet - WebDocument2 pages63-9378 - Rev D - ULTRA Puck - VLP-32C - Datasheet - WebCristi ValentinNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE56H0T-ITMF 5 MP Turret Camera: Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesDS-2CE56H0T-ITMF 5 MP Turret Camera: Key FeaturesBisma Cipta SolusiNo ratings yet
- Quality ControlDocument35 pagesQuality ControlvijayNo ratings yet
- Lenses English SpecDocument1 pageLenses English SpecerazorafaelNo ratings yet
- Johnson Elite Wall Collection 30 X45 Rajasthan Feb 21Document36 pagesJohnson Elite Wall Collection 30 X45 Rajasthan Feb 21ABCNo ratings yet
- THC-B320-VF 2 MP EXIR VF Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-B320-VF 2 MP EXIR VF Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE56C0T-IRMMF HD 720p Indoor IR Dome Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesDS-2CE56C0T-IRMMF HD 720p Indoor IR Dome Camera: Key FeaturesawadalmekawyNo ratings yet
- THC-T110-P 1 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-T110-P 1 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- THC-T120-M 2 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-T120-M 2 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesIsraelAlejandroZuñigaHernandezNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE19U1T-AIT3ZF: 8 MP Outdoor Varifocal Bullet CameraDocument2 pagesDS-2CE19U1T-AIT3ZF: 8 MP Outdoor Varifocal Bullet Camerab01eru84No ratings yet
- DS-2CE56H0T-ITPF 5 MP Turret Camera: Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesDS-2CE56H0T-ITPF 5 MP Turret Camera: Key FeaturesCarlos TrianaNo ratings yet
- THC-B340-VF 4 MP EXIR VF Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-B340-VF 4 MP EXIR VF Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- Std. O-Ring TolerancesDocument5 pagesStd. O-Ring TolerancesBharatNo ratings yet
- THC-T110 1 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-T110 1 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesJavier SánchezNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE16D0T-VFIR3F HD 1080p IR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesDS-2CE16D0T-VFIR3F HD 1080p IR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesJaime PosadaNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE16D0T-VFIR3F HD 1080p IR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesDS-2CE16D0T-VFIR3F HD 1080p IR Bullet Camera: Key Featuresleonardo conchaNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE16D0T-VFIR3F HD 1080p IR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesDS-2CE16D0T-VFIR3F HD 1080p IR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesJaime PosadaNo ratings yet
- 63-9665 Rev-A Puck 32MR Datasheet WebDocument2 pages63-9665 Rev-A Puck 32MR Datasheet WebAndrew PasqualeNo ratings yet
- Ds 2ce16d0t Vfir3fDocument3 pagesDs 2ce16d0t Vfir3firvin caceresNo ratings yet
- WV LZ61 15Document1 pageWV LZ61 15Eugene LimNo ratings yet
- Johnson Tiles Floor 60x60cm (New Collection) Catalogue VJWD Mar 23Document12 pagesJohnson Tiles Floor 60x60cm (New Collection) Catalogue VJWD Mar 23sudhakarvenkatesan31No ratings yet
- 2.particle Size DistributionsDocument30 pages2.particle Size DistributionsN K KhoslaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13B CaseDocument5 pagesChapter 13B CaseAtaii Ckaa Ü Lolz100% (1)
- D 2 H 2 oDocument1 pageD 2 H 2 oStere StereNo ratings yet
- CIREX - Casting Tolerancies VDG P690Document4 pagesCIREX - Casting Tolerancies VDG P690sean jukesNo ratings yet
- B40-TURBO 4 MP EXIR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesB40-TURBO 4 MP EXIR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesalfonsoNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE56C0T-VPIR HD720P Vandal Proof Dome Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesDS-2CE56C0T-VPIR HD720P Vandal Proof Dome Camera: Key FeaturescasinaroNo ratings yet
- 2 MP Audio Camera E8-TURBO-G2/ADocument3 pages2 MP Audio Camera E8-TURBO-G2/ARicardo Reyes jimarezNo ratings yet
- THC-B240-M 4 MP EXIR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-B240-M 4 MP EXIR Bullet Camera: Key FeaturesAli AldosNo ratings yet
- Glass Specifications ClicktouchDocument7 pagesGlass Specifications ClicktouchAldrian BarbasanNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Hikvision Ds 2ce56d0t Irmf28mmDocument4 pagesData Sheet Hikvision Ds 2ce56d0t Irmf28mmJuan LauNo ratings yet
- HHMD - 1001Document1 pageHHMD - 1001Dinesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- THC-T140-M 4 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesTHC-T140-M 4 MP EXIR Turret Camera: Key FeaturesMega VoltNo ratings yet
- DX760 Service ManualDocument105 pagesDX760 Service ManualGabriel de Jesus SouzaNo ratings yet
- Physics HomeworkDocument3 pagesPhysics HomeworkAJaxNo ratings yet
- DS-2CE56D0T-IRPF 2 MP CameraDocument4 pagesDS-2CE56D0T-IRPF 2 MP CameraririsihNo ratings yet
- Ecotec 710 19mm BB Reff MTCDocument1 pageEcotec 710 19mm BB Reff MTCcarville33eownerswcNo ratings yet
- Separation Process Fundamentals Laboratory ReportDocument9 pagesSeparation Process Fundamentals Laboratory ReportfjasfNo ratings yet
- Cam5000d 022Document4 pagesCam5000d 022nikos kafaloukosNo ratings yet
- Ordinary People, Extraordinary Profits: How to Make a Living as an Independent Stock, Options, and Futures TraderFrom EverandOrdinary People, Extraordinary Profits: How to Make a Living as an Independent Stock, Options, and Futures TraderNo ratings yet