Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PCD - 10
Uploaded by
deshpande.pxresh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesPCD - 10
Uploaded by
deshpande.pxreshCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
DEMYSTIFYING LR
PARSER: A
COMPREHENSIVE
ANALYSIS WITH
ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLES
Name : Paresh Deshpande
Roll no : 10
Subject : PCD
Class : Btech CSE
INTRODUCTION
Welcome to the presentation on
Demystifying LR Parser. In this
comprehensive analysis, we will explore the
inner workings of LR parsing algorithms,
including LR(), SLR(1), LR(1), and LALR(1).
Through illustrative examples, we aim to
provide a clear understanding of LR parsing
techniques.
LR PARSING BASICS
Before diving into LR parsing algorithms,
let's establish the foundation. LR parsing is a
bottom-up parsing technique used to
analyze the syntactic structure of a
programming language. It employs a
deterministic finite automaton known as a
LR parser to recognize valid sentences in a
language. Understanding the basic
concepts will help us grasp the intricacies of
LR parsing algorithms.
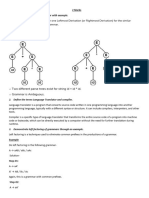
LR() PARSING
The LR() parsing algorithm is the simplest form
of LR parsing. It uses a zero-lookahead LR
parser to build an LR() canonical collection and
construct a LR() parse table. By analyzing the
LR() items and performing shift and reduce
actions, the parser can determine the validity of
the input string. Let's explore this algorithm with
an example.
SLR(1) PARSING
The SLR(1) parsing algorithm improves upon
LR() parsing by incorporating lookaheads. It
uses a lookahead LR() parser to construct an
SLR(1) parse table. By considering the follow
sets of non-terminals, the parser can resolve
conflicts and make more accurate parsing
decisions. Let's examine the SLR(1) algorithm in
action with an example.
LR(1) PARSING
The LR(1) parsing algorithm further enhances
the parsing power by utilizing item sets with
lookaheads. It constructs an LR(1) parse table
by considering the lookaheads of LR(1) items.
This allows for more precise parsing decisions
and resolves more conflicts than SLR(1) parsing.
Let's explore the LR(1) algorithm through an
example.
LALR(1) PARSING
The LALR(1) parsing algorithm aims to strike
a balance between power and efficiency. It
combines the compactness of SLR(1) parse
tables with the parsing power of LR(1) items.
By merging similar LR(1) item sets, it reduces
the size of the parse table while maintaining
the parsing capabilities. Let's delve into the
LALR(1) algorithm using an example.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, we have explored the LR parsing techniques, including LR(),
SLR(1), LR(1), and LALR(1). By understanding the inner workings of these
algorithms, we can better comprehend the parsing process and handle
various language grammars effectively. Remember, LR parsing is a
valuable tool for compiler design and language processing. Thank you for
your attention!
You might also like
- Termpaper OF System Software Topic Lalr Parser GeneratorDocument15 pagesTermpaper OF System Software Topic Lalr Parser GeneratorAman WaliaNo ratings yet
- Lalr TechniqueDocument4 pagesLalr TechniqueGabriel ChukwuemerieNo ratings yet
- Practical Arbitrary Lookahead LR Parsing: University Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32611Document21 pagesPractical Arbitrary Lookahead LR Parsing: University Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32611asfadsadasNo ratings yet
- Practical Full LR(1) Parser GenerationDocument9 pagesPractical Full LR(1) Parser GenerationManthan JadhavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Compiler DesignDocument42 pagesChapter 3 Compiler Designmishamoamanuel574No ratings yet
- Compiler Design Problem SetDocument10 pagesCompiler Design Problem SetAparup BeheraNo ratings yet
- LALRPDocument8 pagesLALRPਰਜਨੀ ਖਜੂਰਿਆNo ratings yet
- LR Parser-Part-IDocument16 pagesLR Parser-Part-IGladwin TirkeyNo ratings yet
- Semantics and Complexity of SPARQLDocument14 pagesSemantics and Complexity of SPARQLMayuri RegeNo ratings yet
- A Practical Parser With Combined Parsing TechniquesDocument10 pagesA Practical Parser With Combined Parsing TechniquesAnonymous rVWvjCRLGNo ratings yet
- LR Parsing MethodsDocument50 pagesLR Parsing MethodsBhabatosh SinhaNo ratings yet
- 2010 LR ParserDocument21 pages2010 LR Parserdanut89newNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesCompiler Design Course Syllabusmega LinkNo ratings yet
- Assembly language basics and parsing conceptsDocument8 pagesAssembly language basics and parsing conceptsABHISHEK KUMAR SAHNo ratings yet
- Faster Generalized LR Parsing PDFDocument15 pagesFaster Generalized LR Parsing PDFPRAFULKUMAR PARMARNo ratings yet
- Comp Review: Compilers: Fall 1996 Textbook: "Compilers" by Aho, Sethi & UllmanDocument10 pagesComp Review: Compilers: Fall 1996 Textbook: "Compilers" by Aho, Sethi & UllmanIc 555No ratings yet
- LR (1) & Lalr Parser: Prepared By: Nitin Goyal - 04Cs1026 Jitendra Bindal - 04Cs1027Document24 pagesLR (1) & Lalr Parser: Prepared By: Nitin Goyal - 04Cs1026 Jitendra Bindal - 04Cs1027Mera Pura NaamNo ratings yet
- Bottom-Up Parsing: Goal of Parser: Build A DerivationDocument31 pagesBottom-Up Parsing: Goal of Parser: Build A DerivationBacha HundeNo ratings yet
- A Tool For Visualization of Parsers Jflap 2u4qtn29y2Document5 pagesA Tool For Visualization of Parsers Jflap 2u4qtn29y2gopayer01No ratings yet
- Lisp AIDocument5 pagesLisp AIAbhishek Anand100% (1)
- Lecture 16nDocument23 pagesLecture 16nsharjeelNo ratings yet
- LR and SLR ParsingDocument10 pagesLR and SLR ParsingPrashast SahayNo ratings yet
- DLP VIVA Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesDLP VIVA Questions and AnswersD19DCS143 PRIYAM VAGHASIANo ratings yet
- A Faster Earley Parser: AbstractDocument13 pagesA Faster Earley Parser: AbstractbacondroppedNo ratings yet
- Written Set 2: Parsing: CS143 Handout 17 Summer 2012 July 11, 2011Document9 pagesWritten Set 2: Parsing: CS143 Handout 17 Summer 2012 July 11, 2011asfadsadasNo ratings yet
- Overview of the CL LanguageDocument37 pagesOverview of the CL LanguageWinifer HcoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Compiler DesignDocument36 pagesUnit - 1 Compiler DesignMandeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Compilers 5Document1 pageUnit I Introduction To Compilers 5RangitaRajkumarNo ratings yet
- Compiler Construction Unit 3 Part-5 LL (1), LR (0) - SLR (1) CSEDocument8 pagesCompiler Construction Unit 3 Part-5 LL (1), LR (0) - SLR (1) CSEPankaj KumawatNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design Course OverviewDocument1 pageCompiler Design Course Overviewgur_mann2k3No ratings yet
- Barve 2014Document5 pagesBarve 2014miciaaudrenNo ratings yet
- Compiler AnswersDocument18 pagesCompiler AnswersAnupam VatsNo ratings yet
- CD Unit 1Document35 pagesCD Unit 1Gomathi Aashika GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Module3 PPTDocument78 pagesModule3 PPTParth SyandanNo ratings yet
- unit-2,3 Question bank (Part-A,B,C)Document7 pagesunit-2,3 Question bank (Part-A,B,C)sd8837No ratings yet
- SPCC Case Study ParserDocument4 pagesSPCC Case Study ParserSohail SayyedNo ratings yet
- Sri Vidya College of Engineering and Technology Question BankDocument5 pagesSri Vidya College of Engineering and Technology Question BankThiyagarajan JayasankarNo ratings yet
- 2 Top Down 22.02.2022Document15 pages2 Top Down 22.02.202287Saaraansh MishraITNo ratings yet
- CS-352_Spring 2024_Lec2Document35 pagesCS-352_Spring 2024_Lec2jouf00008No ratings yet
- Tools to Teach Parsing ConceptsDocument5 pagesTools to Teach Parsing ConceptsPranav SinghNo ratings yet
- Lec23 LogicprogrammingDocument4 pagesLec23 LogicprogrammingmikeNo ratings yet
- Compiler Lab VivaDocument6 pagesCompiler Lab VivaGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Learn Computer Programming and CS606 ConceptsDocument27 pagesLearn Computer Programming and CS606 ConceptsAli AnwarNo ratings yet
- Functional Database Query Languages As Typed Lambda Calculi of Fixed OrderDocument40 pagesFunctional Database Query Languages As Typed Lambda Calculi of Fixed OrderWildo GómezNo ratings yet
- Cs1352 Principles of Compiler DesignDocument33 pagesCs1352 Principles of Compiler DesignSathishDon01No ratings yet
- PCD 2 MarksDocument23 pagesPCD 2 MarksVignesh VickyNo ratings yet
- Cs 431 CH 2 RVWDocument13 pagesCs 431 CH 2 RVWsihag_deepakNo ratings yet
- SBG Study NLP Notes From Unit 3Document14 pagesSBG Study NLP Notes From Unit 3KILLSHOT SKJNo ratings yet
- Suffix Arrays: Justin Zhang 24 May 2017Document5 pagesSuffix Arrays: Justin Zhang 24 May 2017Kartick GuptaNo ratings yet
- Querying Semantic Data On The Web: (Seq:2378690, Seq:length, "118") (Seq:2378690, Seq:taxonomy, Tax:36178)Document12 pagesQuerying Semantic Data On The Web: (Seq:2378690, Seq:length, "118") (Seq:2378690, Seq:taxonomy, Tax:36178)upper666No ratings yet
- Computer Science Notes: Principles of ProgrammingDocument10 pagesComputer Science Notes: Principles of ProgrammingMuhammedNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Common Lisp and AI Classical SystemsDocument32 pagesIntroduction to Common Lisp and AI Classical SystemsUzmanNo ratings yet
- Reference Counting As A Computational Interpretation of Linear LogicDocument54 pagesReference Counting As A Computational Interpretation of Linear LogicbromlantNo ratings yet
- The Sesame Lucenesail: RDF Queries With Full-Text Search: Nepomuk Technical Report 2008-1Document14 pagesThe Sesame Lucenesail: RDF Queries With Full-Text Search: Nepomuk Technical Report 2008-1Shobhit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusexam examNo ratings yet
- Compiler Construction Phases and TechniquesDocument3 pagesCompiler Construction Phases and TechniquesSeiar SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Ruby Programming For Beginners: The Simple Guide to Learning Ruby Programming Language Fast!From EverandRuby Programming For Beginners: The Simple Guide to Learning Ruby Programming Language Fast!Rating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Dhwani Sheth: Education Professional SkillsDocument1 pageDhwani Sheth: Education Professional SkillsDhwani ShethNo ratings yet
- Display GuidelinesDocument12 pagesDisplay GuidelinesAtul BangalNo ratings yet
- Failure Mode Effect Analysis-APR132K7Document4 pagesFailure Mode Effect Analysis-APR132K7MuhammadAns100% (4)
- lbp5300 5360-smDocument150 pageslbp5300 5360-smciphardNo ratings yet
- Control System and Solutions - Global Case Study Collection - JIV1901 PDFDocument11 pagesControl System and Solutions - Global Case Study Collection - JIV1901 PDFcodefinderNo ratings yet
- S G Brown: Meridian Data Repeater User ManualDocument24 pagesS G Brown: Meridian Data Repeater User Manual'Egemen KayaNo ratings yet
- Database Management System ExplainedDocument6 pagesDatabase Management System ExplainedAnil ShresthaNo ratings yet
- AsiaSat's Cost Effective V61 Maritime VSAT TerminalDocument1 pageAsiaSat's Cost Effective V61 Maritime VSAT TerminalJUST AWIENo ratings yet
- Draft Resolution For MUNDocument5 pagesDraft Resolution For MUNHùng ĐihNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5-Keyword-Research-Boost-Your-Website-VisibilityDocument8 pagesLesson 5-Keyword-Research-Boost-Your-Website-Visibilityfocusinstitute84No ratings yet
- Gaussian Frequency-Shift Keying With GNU RadioDocument5 pagesGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying With GNU RadioRakesh S K60% (5)
- IEC 61937-5-2006 Digital AudioDocument22 pagesIEC 61937-5-2006 Digital AudioBenjie CallantaNo ratings yet
- Target For ArcgisDocument148 pagesTarget For Arcgisrenzoquim100% (2)
- 3.7 AI - DS Assignment2-1Document4 pages3.7 AI - DS Assignment2-1Anurag SinghNo ratings yet
- BMW Wiring Symbols & ColorsDocument2 pagesBMW Wiring Symbols & ColorsProfCBSjr86% (7)
- Sample Questions For Practical ExamDocument2 pagesSample Questions For Practical Examsamridhiverma0701No ratings yet
- CEN ISO TR 12489 (2016) (E) CodifiedDocument7 pagesCEN ISO TR 12489 (2016) (E) CodifiedJHNo ratings yet
- LBNL Software Tools March 2002Document44 pagesLBNL Software Tools March 2002Francisco José MoralejoNo ratings yet
- Solution: K K: Terms Related To Graph Theory: For K, e N (n-1) and For N 2, The Degree Is Equal To N - 1. ExampleDocument1 pageSolution: K K: Terms Related To Graph Theory: For K, e N (n-1) and For N 2, The Degree Is Equal To N - 1. ExampleAthena LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Leap Data Sheet GatewayDocument3 pagesLeap Data Sheet GatewayRafael JuncoNo ratings yet
- MCQ Programming Problem SolvingDocument8 pagesMCQ Programming Problem SolvingMAHESHWAR M R (RA2111004010136)No ratings yet
- Unsupervised Anomaly-Based Malware Detection Using Hardware FeaturesDocument12 pagesUnsupervised Anomaly-Based Malware Detection Using Hardware FeaturesSandro MeloNo ratings yet
- Moog DS2000XP GUI Manual PDFDocument47 pagesMoog DS2000XP GUI Manual PDFใบบอนสิชล100% (1)
- Quantitative Finance: 1 Probability and StatisticsDocument2 pagesQuantitative Finance: 1 Probability and StatisticsVidaup40No ratings yet
- Coatron A6Document3 pagesCoatron A6Joelito Yaringaño GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Data Visualization PresentationDocument36 pagesOptimizing Data Visualization PresentationJamicah Nicole SolisNo ratings yet
- Laptop Price Prediction in Machine Learning Using Random Forest Classifier TechniqueDocument5 pagesLaptop Price Prediction in Machine Learning Using Random Forest Classifier TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Development of Finance Management System For Mwenge Catholic UniversityDocument55 pagesDevelopment of Finance Management System For Mwenge Catholic UniversityJames mollelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Geometric TransformationsDocument2 pagesAssignment 4 Geometric TransformationsKrish100% (1)
- Soft Skills Project PlanDocument9 pagesSoft Skills Project Planapi-601533359No ratings yet