Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 5 - 4
Uploaded by
Josh Minaj0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesweek 5_4 jejejdhs. Ebsjsnsn d dsjjddd
Original Title
week 5_4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentweek 5_4 jejejdhs. Ebsjsnsn d dsjjddd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesWeek 5 - 4
Uploaded by
Josh Minajweek 5_4 jejejdhs. Ebsjsnsn d dsjjddd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
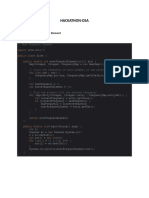
Write a Java code that takes as input a positive number (length of an array here),
and two arrays of that length - one of integers and another of strings. The code
must also take an integer and a String as input, and print the number of
occurrences of the integer and the string in the integer array and the string
array, respectively.
Format of input:
Length of the arrays
Elements in the integer array (in separate lines)
Element to count in the integer array
Elements in the string array (in separate lines)
Element to count in the string array
Variables used in the code:
len - represents length of array
s1 - represents an element to be counted for in Integer array
s2 - represents an element to be counted for in String array
import java.util.*;
class ArrayExample <T>{
T[] a;
public ArrayExample(T[] arr){
a = arr;
}
public void display(){
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public int elementCount(T x){
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){
if(a[i].equals(x)){
count = count + 1;
}
}
return count;
}
}
public class ArrayObject{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int len = sc.nextInt(); //Taking input for length of array
Integer[] x = new Integer[len];
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
x[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
ArrayExample<Integer> obj = new ArrayExample<Integer>(x);
int s1 = sc.nextInt();
String[] y = new String[len];
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
y[i] = sc.next(); //Taking input for String array
}
ArrayExample<String> obj1 = new ArrayExample<String>(y);
String s2 = sc.next(); //Taking input for the value to be counted
obj.display();
System.out.println(obj.elementCount(s1));
obj1.display();
System.out.println(obj1.elementCount(s2));
}
}
You might also like
- Virtusa Coding QuestionsDocument6 pagesVirtusa Coding QuestionsSa Dik100% (9)
- QB Method Program AnswersDocument21 pagesQB Method Program AnswersPriyeshNo ratings yet
- JAVA ExamplesDocument50 pagesJAVA ExamplesHemant KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Array, String and VectorDocument39 pagesArray, String and Vectorkaminisarode1507No ratings yet
- Zoho Level1Document118 pagesZoho Level1anitha E100% (1)
- Q. Enter A String and Print Number of Vowels and Consonants Present in It Using A ConstructorDocument6 pagesQ. Enter A String and Print Number of Vowels and Consonants Present in It Using A ConstructorArihant KumarNo ratings yet
- New CTS Sample Questions With SolutionsDocument71 pagesNew CTS Sample Questions With Solutionsகார்த்திகேயன் பழனிச்சாமி67% (3)
- CTS Sample Questions With SolutionsDocument62 pagesCTS Sample Questions With Solutionsகார்த்திகேயன் பழனிச்சாமிNo ratings yet
- CSE-1007 (Java Programming) Digital Assignment-1Document50 pagesCSE-1007 (Java Programming) Digital Assignment-1Ayush RoyNo ratings yet
- Array SolutionDocument5 pagesArray SolutionVinod ChamoliNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument9 pagesSolutionsDivyanshi BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Code To Solve Set of ProblemsDocument17 pagesCode To Solve Set of ProblemsMamta DoliyaNo ratings yet
- Linear SearchDocument1 pageLinear SearchRishika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- CH 07 Arrays, String and VectorDocument33 pagesCH 07 Arrays, String and VectorTabassum MaktumNo ratings yet
- Java Interview Programs 2Document10 pagesJava Interview Programs 2prathap7475No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document30 pagesAssignment 2Nishant Sharma100% (1)
- Computer Project - FinalDocument98 pagesComputer Project - FinalJasmine BhattNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document20 pagesAssignment 2Aayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Java CoimbatoreDocument628 pagesJava Coimbatorenithish reddyNo ratings yet
- ADI End TermDocument13 pagesADI End TermSahil DubeyNo ratings yet
- Java Assignments (1&2) : Assignment 1Document46 pagesJava Assignments (1&2) : Assignment 1Nil DasNo ratings yet
- Java Programming Lab Assignment 1: Basic ProgramsDocument27 pagesJava Programming Lab Assignment 1: Basic ProgramsSanjana chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - JAVA BY HARSH SINGHDocument13 pagesLab 2 - JAVA BY HARSH SINGHHarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- JAVA Programs Practical FileDocument86 pagesJAVA Programs Practical FileRoyAjit0% (1)
- Week 3: Import Java - Util.scanner Public Class Sum - Avg - Array (Public Static Void Main (String Args ) (Document23 pagesWeek 3: Import Java - Util.scanner Public Class Sum - Avg - Array (Public Static Void Main (String Args ) (Bikram DeNo ratings yet
- Assessment - 1: 16bit0326 Surya VamshiDocument26 pagesAssessment - 1: 16bit0326 Surya VamshiVamshi Bhamidi100% (1)
- Computer JavaDocument19 pagesComputer Javatanvi kamaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Project Work 2Document19 pagesComputer Project Work 2Soma DeyNo ratings yet
- Java ProgrammingDocument26 pagesJava Programmingsupriya100% (2)
- Java Lab 2Document8 pagesJava Lab 2Akriti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Arrays Theory & SortingDocument11 pagesArrays Theory & SortingMcDonald TrumpenNo ratings yet
- OOP Unit 4 NotesDocument10 pagesOOP Unit 4 Notesharshlaptop001No ratings yet
- Java Strings, Eh, Generics, ThreadsDocument15 pagesJava Strings, Eh, Generics, Threadsrajashekar reddyNo ratings yet
- For Finding Length of Array.: Java Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesFor Finding Length of Array.: Java Cheat Sheetrajdeep3srivastavaNo ratings yet
- 20mia1104 Psoop Ips10Document22 pages20mia1104 Psoop Ips10Sricharan SridharNo ratings yet
- Java - Introduction To ProgrammingDocument5 pagesJava - Introduction To ProgrammingSamar singhNo ratings yet
- Name: Patel Charmy Tarunkumar Course: MSC - It Subject: Java Programming Roll No.: 11 Faculty Name Assignment: Priti PatelDocument20 pagesName: Patel Charmy Tarunkumar Course: MSC - It Subject: Java Programming Roll No.: 11 Faculty Name Assignment: Priti PatelCharmy PatelNo ratings yet
- Core Java Logical QuestionsDocument37 pagesCore Java Logical Questionsvenkatesh100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentpurna mummaniNo ratings yet
- HACKATHONDocument10 pagesHACKATHONDharam SekhonNo ratings yet
- Java QuestionsDocument18 pagesJava QuestionsAditya Tiwari100% (1)
- Jan 1 To 11 CodesDocument16 pagesJan 1 To 11 Codesbhavankumarp.mech2021No ratings yet
- Radix Sort in JavaDocument7 pagesRadix Sort in JavarafiulalhasanNo ratings yet
- Class XI Sample Practical File ComputerDocument91 pagesClass XI Sample Practical File ComputerAnish BarmanNo ratings yet
- Array & Pattern Q&A 238942Document5 pagesArray & Pattern Q&A 238942chinthakindi hemanthNo ratings yet
- 19bcd7246 Assignment3 L27+L28+L31+L32Document4 pages19bcd7246 Assignment3 L27+L28+L31+L32Sriharshitha DeepalaNo ratings yet
- HCLDocument12 pagesHCLshenbagaraman cseNo ratings yet
- Arrays in CDocument13 pagesArrays in CMonti SainiNo ratings yet
- Cssexp 4Document9 pagesCssexp 4Madhura BartakkeNo ratings yet
- Accenture Test 6 HackerrankDocument4 pagesAccenture Test 6 HackerrankRavi VadayarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 AnswerDocument6 pagesUnit 3 AnswerxavierNo ratings yet
- ArrayDocument41 pagesArraynurul aqilah fauzanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document12 pagesAssignment 2DÈrríçk Thê RåcérNo ratings yet
- AIM: Write A Program in Java To Analyze Time Complexity of RecursiveDocument29 pagesAIM: Write A Program in Java To Analyze Time Complexity of RecursiveVarshiniNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional ArrayDocument8 pagesOne Dimensional ArrayEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Array in JavaDocument11 pagesArray in JavaRavikiran KadamNo ratings yet
- Arrays in JavaDocument13 pagesArrays in Javalaxmi bagadeNo ratings yet
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionFrom EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)