Professional Documents
Culture Documents
액츄얼1 첨삭완
Uploaded by
cse41361418Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
액츄얼1 첨삭완
Uploaded by
cse41361418Copyright:
Available Formats
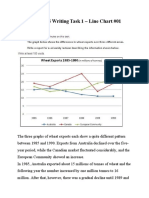
The charts below illustrate the electric energy production in Spain and China, in
terms of the energy origin in 2005 and 2015. Overall, there are some decreasing
related prevalent source coal source in both countries, over the 10 yearsbetween
2005 and 2015. Also, we can see increasing of the eco-friendly source usage.
In China, coal was the most used electricity source in 2005, with 80%. The coal
accounted for large extent in both years, recordinged high percentages ,which over
than rest sources combined. However, the extent of the coal decreased in 2015, at
70%. In the same year, using the renewables source for electricity increased by 9%.
Extent of the nuclear origin also enlarged in 2015, with 3%.
Using oil and gas for electricity generation in Spain accounted for the largest
percentage of the total in 2005, with 32%. Flowing oil and gas, the percentage of
coal recorded at 30%. Meanwhile, the using of renewables source for electricity
generation in Spain was lower than that of China. In 2015, The using percentages of
coal, oil and gas were minimized reduced, shrined, by 10%, 9% respectively. On the
other hand, the extent of renewables source increased at 37%, standing featured
스탠딩아웃 써도됨? from the rest as a large changing. An Increased using
-서론에서 석탄 사용감소 재생에너지 언급했으니까 두번째 문단에서도
석탄 감소, 재생에너지 증가 위주로 쓰는 게 좋을 듯.
-분사구문> ing 는 보통 능동, ed 는 수동.
유의어 raise, extend, boost
반의어 decrease, shrink, decrease
The pie charts below display the means used to produce electrical power in China
and Spain in 2005 and 2015. It’s immediately discernible that China relied more
heavily on coal than Spain for its energy needs, and both countries introduced more
renewable sources between 2005 and 2015.
At 80% we can see that coal made up for the vast majority of China’s sources for
electric generation in 2005, and this percentage dropped to just 70% in2015. Spain,
on the other hands, featured much more variety in its proportions. In2005, coal only
represented 30% of the sources; oil and gas led with 32%, with nuclear and
renewable sources trailing at20% and 18%, respectively.
Between 2005 and 2015, the amount of electricity generated from renewable
resources in China rose from 16% to 25%. Renewable sources also became more
prominent in Spain, with a marked increase from 18% in 2005 to 37% in 2015, which
was also the most prominent energy source for Spain that year.
You might also like
- EU China Energy Magazine 2021 Christmas Double Issue: 2021, #4From EverandEU China Energy Magazine 2021 Christmas Double Issue: 2021, #4No ratings yet
- Theme Session AT Kerney PDFDocument36 pagesTheme Session AT Kerney PDFCarl Chakravarthy100% (1)
- Body 1:: Petrol and Oil 1980: Greatest + 2 Times More Than Coal and Natural Gas: in 1980Document4 pagesBody 1:: Petrol and Oil 1980: Greatest + 2 Times More Than Coal and Natural Gas: in 1980Tuấn Hiệp NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BP Statistical Review of World Energy 2016 Full ReportDocument48 pagesBP Statistical Review of World Energy 2016 Full ReportKiranPadmanNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing Task 1 - Pie ChartDocument53 pagesIelts Writing Task 1 - Pie ChartAmy HicksNo ratings yet
- Example 1 PDFDocument14 pagesExample 1 PDFAzharuddin_kfupmNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1Document1 pageWriting Task 1Kamal deep singh SinghNo ratings yet
- Energy Consumption: Mtoe of Energy Consumed by Each CountryDocument5 pagesEnergy Consumption: Mtoe of Energy Consumed by Each CountryPrakash CherianNo ratings yet
- Pie ChartDocument6 pagesPie ChartNguyen LeNo ratings yet
- A Greener Shade of Grey: A Special Report On Renewable Energy in ChinaDocument24 pagesA Greener Shade of Grey: A Special Report On Renewable Energy in Chinaapi-147105116No ratings yet
- C D K SirDocument62 pagesC D K SirVivek SinhaNo ratings yet
- World Energy Council 2013 World Energy Resources: CoalDocument32 pagesWorld Energy Council 2013 World Energy Resources: CoalIswan ArpadiNo ratings yet
- Homework 16.1.2024Document1 pageHomework 16.1.2024trongquy.thcs.18.22No ratings yet
- Ielts EssayDocument1 pageIelts EssayHotan KheyrandishNo ratings yet
- Homework Line Chart 1Document2 pagesHomework Line Chart 1Bảo TrâmNo ratings yet
- Energy For The Future Chile's National Energy Strategy 2012 2030 EnglishDocument38 pagesEnergy For The Future Chile's National Energy Strategy 2012 2030 EnglishVincentNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentToàn ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Mie Project Report - Group 1 - Section BDocument14 pagesMie Project Report - Group 1 - Section Bashwin saiNo ratings yet
- Homework 22.12.2023Document4 pagesHomework 22.12.2023trongquy.thcs.18.22No ratings yet
- 03 Pa Po 3 3 PDFDocument8 pages03 Pa Po 3 3 PDFMarcelo Varejão CasarinNo ratings yet
- Energy Innovation Nov 30 2015Document9 pagesEnergy Innovation Nov 30 2015Poncho76No ratings yet
- BioethanolDocument5 pagesBioethanolTANSIEWYENNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Sample - Task 1Document31 pagesIELTS Writing Sample - Task 1Natalie TaoNo ratings yet
- 15-4 Writing 9Document94 pages15-4 Writing 9Trung tâm ngoại ngữ English Zone An ĐồngNo ratings yet
- Wri - Line GrapDocument1 pageWri - Line Grapanhkiwwi2310No ratings yet
- Limits To Growth IiDocument2 pagesLimits To Growth IiTamash MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Coal Outlook February 2014 Observations IEEFADocument3 pagesThermal Coal Outlook February 2014 Observations IEEFAdonnypsNo ratings yet
- Market Opportunities For Coal Gasi Cation in ChinaDocument7 pagesMarket Opportunities For Coal Gasi Cation in ChinaAsri GaniNo ratings yet
- Chart Energy ConsumptionDocument2 pagesChart Energy ConsumptionNguyễn Thiện DũngNo ratings yet
- World Energy Out Look 2016 Executive Summary EnglishDocument13 pagesWorld Energy Out Look 2016 Executive Summary EnglishFred Lamert100% (1)
- Kejun Energy ChinaDocument22 pagesKejun Energy ChinaKonul AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Sankey DiagramDocument4 pagesSankey Diagramlalap72411No ratings yet
- IELTS 6 - Line Graph - Electricity Ver2Document1 pageIELTS 6 - Line Graph - Electricity Ver2việt anh anNo ratings yet
- The Line Chart of Electricity Production in France From 1980 To 2012Document1 pageThe Line Chart of Electricity Production in France From 1980 To 2012Dolphy ThaiNo ratings yet
- Electricity, Global MagnitudesDocument5 pagesElectricity, Global MagnitudesThavamNo ratings yet
- Bài mẫu IELTS Writing Task 1Document4 pagesBài mẫu IELTS Writing Task 1朝陽出暮色No ratings yet
- A Report On An Overview of Renewable Energy Scenario and Its Share To The Total Energy Demand in NepalDocument45 pagesA Report On An Overview of Renewable Energy Scenario and Its Share To The Total Energy Demand in NepalIndra Kumar Maharjan67% (3)
- Line Graph wt1Document2 pagesLine Graph wt1Gia BảoNo ratings yet
- Describe Pie ChartDocument11 pagesDescribe Pie ChartAnonymous 7Vl0XCBvNo ratings yet
- Uk Energy CrisisDocument9 pagesUk Energy CrisisAnonymous nqgDQZwxNo ratings yet
- EURACOAL Coal Industry Across Europe 2013Document80 pagesEURACOAL Coal Industry Across Europe 2013euracoalNo ratings yet
- Writing PieDocument20 pagesWriting PieBishal PunksNo ratings yet
- Domestic Energy FactsheetDocument10 pagesDomestic Energy Factsheetdcc1973No ratings yet
- LTS Writing Task 1: Bài mẫu pie charts "Energy production"Document2 pagesLTS Writing Task 1: Bài mẫu pie charts "Energy production"map6878No ratings yet
- Long-Term Trends and Outlook For Global Coal Supply and DemandDocument28 pagesLong-Term Trends and Outlook For Global Coal Supply and DemandRdy SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Toward Energy Security in Chile: New YorkDocument22 pagesToward Energy Security in Chile: New YorkkamdemonnNo ratings yet
- Assig 1Document13 pagesAssig 1SriNo ratings yet
- IELTS READING TEST June 1Document16 pagesIELTS READING TEST June 1Mai LâmNo ratings yet
- Key Findings 2018: Global Energy and CO2 Status Report 2018 Energy DemandDocument27 pagesKey Findings 2018: Global Energy and CO2 Status Report 2018 Energy DemandLaura Sofía VélezNo ratings yet
- PieDocument1 pagePiehoanganhthu1305No ratings yet
- Expository Essay: Energy Crisis in The World and Philippine ContextDocument24 pagesExpository Essay: Energy Crisis in The World and Philippine ContextDensel MacalintalNo ratings yet
- Eco CommentaryDocument4 pagesEco CommentaryMarcosDeLaPintaNo ratings yet
- ReadingDocument69 pagesReadinglangocqueanhNo ratings yet
- Gas Projections and Supply Capacity AnalysisDocument19 pagesGas Projections and Supply Capacity AnalysisMengcheng LiuNo ratings yet
- Writing Task 1Document41 pagesWriting Task 1Ariful Islam Arif100% (1)
- How Turkey Can Ensure A Successful Energy Transition: by Deger Saygin, Max Hoffman, and Philipp Godron July 2018Document33 pagesHow Turkey Can Ensure A Successful Energy Transition: by Deger Saygin, Max Hoffman, and Philipp Godron July 2018HakanNo ratings yet
- EU-China Energy Magazine 2020 Christmas Double Issue: 2020, #4From EverandEU-China Energy Magazine 2020 Christmas Double Issue: 2020, #4No ratings yet
- EU-China Energy Magazine 2021 Summer Issue: 2021, #2From EverandEU-China Energy Magazine 2021 Summer Issue: 2021, #2No ratings yet
- EU China Energy Magazine 2021 Autumn Issue: 2021, #3From EverandEU China Energy Magazine 2021 Autumn Issue: 2021, #3No ratings yet