Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UpToDate Approach To The Eval of Chronic Diarrhea in Adults
UpToDate Approach To The Eval of Chronic Diarrhea in Adults
Uploaded by
Atif Hussain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThis document provides guidance on evaluating chronic diarrhea in adult patients. It recommends first evaluating thyroid function, inflammation markers, and electrolytes. If comorbidities limit diagnosis, empiric therapy for conditions like lactose intolerance may be appropriate. Further lab tests and imaging of the abdomen should be considered if abdominal pain, systemic symptoms, or inflammatory bowel disease are suspected. The evaluation aims to identify potential causes of chronic diarrhea through testing and guide further diagnostic steps or treatment.
Original Description:
Approach to the evaluation of chronic diarrhea in adults
Original Title
UpToDate Approach to the eval of chronic diarrhea in adults
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides guidance on evaluating chronic diarrhea in adult patients. It recommends first evaluating thyroid function, inflammation markers, and electrolytes. If comorbidities limit diagnosis, empiric therapy for conditions like lactose intolerance may be appropriate. Further lab tests and imaging of the abdomen should be considered if abdominal pain, systemic symptoms, or inflammatory bowel disease are suspected. The evaluation aims to identify potential causes of chronic diarrhea through testing and guide further diagnostic steps or treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesUpToDate Approach To The Eval of Chronic Diarrhea in Adults
UpToDate Approach To The Eval of Chronic Diarrhea in Adults
Uploaded by
Atif HussainThis document provides guidance on evaluating chronic diarrhea in adult patients. It recommends first evaluating thyroid function, inflammation markers, and electrolytes. If comorbidities limit diagnosis, empiric therapy for conditions like lactose intolerance may be appropriate. Further lab tests and imaging of the abdomen should be considered if abdominal pain, systemic symptoms, or inflammatory bowel disease are suspected. The evaluation aims to identify potential causes of chronic diarrhea through testing and guide further diagnostic steps or treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Suggested approach to the evaluation of chronic diarrhea in
adult patients in resource-rich settings
TSH: thyroid-stimulating hormone; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-
reactive protein; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; IBS: irritable bowel
syndrome; HIAA: hydroxy indole acetic acid.
* Serum electrolytes should be evaluated in patients with severe diarrhea, or
when there is concern for dehydration or electrolyte abnormalities.
¶ Refer to appropriate UpToDate topic on chronic diarrhea.
Δ Empiric therapy may be appropriate when comorbidities limit diagnostic
evaluation or when a diagnosis is strongly suspected (eg, lactose restriction for
suspected lactose intolerance, bile acid binding resin for post-cholecystectomy
diarrhea).
◊ Additional laboratory studies to assess for malabsorption include albumin, red
cell folate, serum iron, total iron binding capacity, vitamin B12, calcium,
magnesium, carotene, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D.
§ In patients with abdominal pain as a major symptom, systemic symptoms (eg,
fever, weight loss), or suspected Crohn or pancreatic disease we perform
additional abdominal imaging with an abdominal computed tomography or
magnetic resonance imaging.
Graphic 120910 Version 2.0
© 2023 UpToDate, Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Nursing Cheat LabValuesDocument4 pagesNursing Cheat LabValuessasukenoneko100% (5)
- Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansDocument17 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Nursing Care Plansmarsan12No ratings yet
- IDEXX CBC Chem ExplainedDocument38 pagesIDEXX CBC Chem Explainedmmatthew74No ratings yet
- Approach To Jaundice (1) .PPT ALAWAJIDocument28 pagesApproach To Jaundice (1) .PPT ALAWAJIayuNo ratings yet
- Dr. Herbert Situmorang, SpOG - (K) FER - Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument16 pagesDr. Herbert Situmorang, SpOG - (K) FER - Hyperemesis GravidarumDonutz RiNo ratings yet
- Adult Health Nursing Phase I Thursday 6:00-9:00 PM: Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument18 pagesAdult Health Nursing Phase I Thursday 6:00-9:00 PM: Irritable Bowel SyndromeLavinia Malazarte CaballeroNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument3 pagesJaundiceNyaoNyao MarcellanaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3Document2 pagesCase Study 3api-305352286No ratings yet
- Abnormal Liver Function Test LGHDocument35 pagesAbnormal Liver Function Test LGHElaineNo ratings yet
- Test #24 Q.Id 863 Question 1 of 39 Item Review Division: HepatologyDocument47 pagesTest #24 Q.Id 863 Question 1 of 39 Item Review Division: HepatologyJahangir AlamNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Metabolic and GastrointestinalDocument3 pagesAssessment of Metabolic and GastrointestinalClark SavageNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With JaundiceDocument33 pagesApproach To A Patient With JaundiceManish AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Med Surge Test5Document5 pagesStudy Guide For Med Surge Test5S01164503No ratings yet
- Liver MineDocument20 pagesLiver MineAhmed Al DesoukiNo ratings yet
- Liver TestsDocument20 pagesLiver Testsnudu.candlesNo ratings yet
- Renal EmergenciesDocument93 pagesRenal EmergenciesShubham gaurNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Vomiting: R. Shaoul N.L. JonesDocument2 pagesNeonatal Vomiting: R. Shaoul N.L. JonesTriponiaNo ratings yet
- Approach of A Patient With JaundiceDocument41 pagesApproach of A Patient With JaundiceDr. 001No ratings yet
- Liver Function TestsDocument14 pagesLiver Function Testsshihochan100% (2)
- ACG Abnormal Liver Chemistries Guideline SummaryDocument16 pagesACG Abnormal Liver Chemistries Guideline SummaryDanuNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)Document51 pagesPemeriksaan Fungsi Hati .: Prof. Dr. Adi Koesoema Aman SPPK (KH)kiki rawitriNo ratings yet
- Curs-5-Mai 2015 - Ficat Si Pancreas - Final de Prezentat-Recovered)Document1,110 pagesCurs-5-Mai 2015 - Ficat Si Pancreas - Final de Prezentat-Recovered)Badea Andreea CristinaNo ratings yet
- SpironolactoneDocument3 pagesSpironolactoneapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Med/Surg Nursing: Endocrine System-2009Document127 pagesMed/Surg Nursing: Endocrine System-2009arbyjamesNo ratings yet
- Acute Fatty Liver With PregnancyDocument50 pagesAcute Fatty Liver With PregnancyDr. mohammed100% (1)
- Vomiting and Diarrhea (Dogs)Document13 pagesVomiting and Diarrhea (Dogs)patjar jamalNo ratings yet
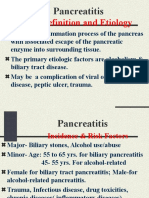
- Definition and Etiology: PancreatitisDocument24 pagesDefinition and Etiology: PancreatitisAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
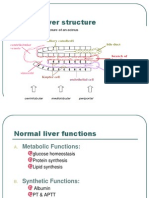
- Management of Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesManagement of Liver Cirrhosispet_trinNo ratings yet
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: DR Asmaa Fathy Lecturer of Family MedicineDocument17 pagesNonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: DR Asmaa Fathy Lecturer of Family MedicineAbdulla1999 AshrafNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument7 pagesIrritable Bowel SyndromeLavinia Malazarte CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Jaundice MasterDocument76 pagesJaundice MasterSuresh Kubavat100% (3)
- Liver Function TestDocument5 pagesLiver Function TestAnne Sison100% (1)
- Liver Function Tests and EnzymesDocument90 pagesLiver Function Tests and EnzymesNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- PANCREATITISDocument16 pagesPANCREATITISJake MillerNo ratings yet
- ALP and GGTDocument9 pagesALP and GGTRazeen RiyasatNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For Pts With Liver DiseaseDocument45 pagesAnesthesia For Pts With Liver DiseaserijjorajooNo ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument8 pagesLiver CirrhosisgoyaNo ratings yet
- AcuteHepatic Failure (Autosaved)Document32 pagesAcuteHepatic Failure (Autosaved)Lakshmi prasad minnelaNo ratings yet
- Nephrology by Prof NegoDocument9 pagesNephrology by Prof NegoAbedinego MalukaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Cholestasis 2Document28 pagesNeonatal Cholestasis 2HafsaJabbarNo ratings yet
- Dipstick UrinalysisDocument9 pagesDipstick UrinalysisAbdul Ghaffar AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Most Common Presenting Symptoms in CD Are Fatigue and Abdominal Pain While in UC Bloody BM and Diarrhea Are Most CommonDocument3 pagesThe Most Common Presenting Symptoms in CD Are Fatigue and Abdominal Pain While in UC Bloody BM and Diarrhea Are Most CommonElle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chole NotesDocument11 pagesChole NotesKeyien RadonesNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Cirrhosis of LiverDocument34 pagesPresentation On Cirrhosis of LiverAnshu kumariNo ratings yet
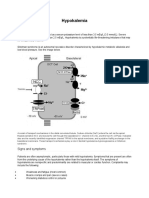
- HypokalemiaDocument10 pagesHypokalemiaAgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Reporter: FM R1 余明謙 Supervisor: Dr 陳信儒Document50 pagesAnemia: Reporter: FM R1 余明謙 Supervisor: Dr 陳信儒余明謙No ratings yet
- Test LFTsDocument2 pagesTest LFTsostarburstoNo ratings yet
- Clinical 4 PacesDocument202 pagesClinical 4 PacesMohammadAbdurRahmanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in CirrhosisDocument40 pagesNutrition in CirrhosisAuliangi TamayoNo ratings yet
- Abordaje de PX Con Enf RenalDocument12 pagesAbordaje de PX Con Enf Renalcleooatra mairenaNo ratings yet
- Acute Care - Adrenal Crisis ChecklistDocument6 pagesAcute Care - Adrenal Crisis ChecklistHanouf BakriNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument22 pagesCase PresentationVikaNo ratings yet
- Hepatotoxic DrugsDocument17 pagesHepatotoxic Drugsani bandasoNo ratings yet
- New ALT Reference Intervals For Children and AdultsDocument2 pagesNew ALT Reference Intervals For Children and AdultsYang YuNo ratings yet
- Chronic DiarhhoeaDocument34 pagesChronic DiarhhoeaJohn DorNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Alanine AminotransferaseDocument3 pagesPurpose: Alanine AminotransferaseRona PieNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case On JaundiceDocument43 pagesClinical Case On JaundicePro fatherNo ratings yet
- Complementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 6: Liver and GallbladderFrom EverandComplementary and Alternative Medical Lab Testing Part 6: Liver and GallbladderNo ratings yet