0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views7 pagesSDLC V Model
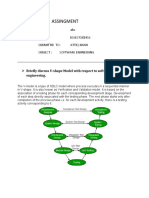
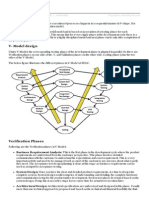
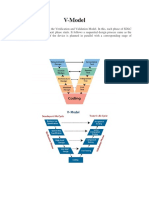
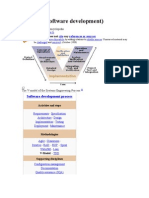
1. The V-Model is a type of software development life cycle (SDLC) model that involves a sequential development process shaped like a "V".
2. It emphasizes testing where each stage of development has a corresponding testing stage mirrored at the opposite side of the "V".
3. The V-Model is often used for safety-critical systems like aerospace due to its clear definition of steps and emphasis on thorough testing.
Uploaded by
Usman DogarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views7 pagesSDLC V Model
1. The V-Model is a type of software development life cycle (SDLC) model that involves a sequential development process shaped like a "V".
2. It emphasizes testing where each stage of development has a corresponding testing stage mirrored at the opposite side of the "V".
3. The V-Model is often used for safety-critical systems like aerospace due to its clear definition of steps and emphasis on thorough testing.
Uploaded by
Usman DogarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd