0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views42 pagesUnderstanding Plant Cell Walls
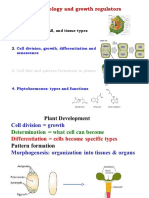
The cell wall is a defining structure of plant cells that determines the shape and limits the expansion of cells. It is composed mainly of cellulose microfibrils embedded in a matrix of hemicellulose and pectin. The primary cell wall is thin and flexible, while the secondary cell wall is thicker and strengthened with lignin. The cell wall plays crucial mechanical and metabolic roles in plant cells.
Uploaded by
Saziya QuadriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views42 pagesUnderstanding Plant Cell Walls
The cell wall is a defining structure of plant cells that determines the shape and limits the expansion of cells. It is composed mainly of cellulose microfibrils embedded in a matrix of hemicellulose and pectin. The primary cell wall is thin and flexible, while the secondary cell wall is thicker and strengthened with lignin. The cell wall plays crucial mechanical and metabolic roles in plant cells.
Uploaded by
Saziya QuadriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd