Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Media Networks - Multicast
Uploaded by
Adrian HuitCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Media Networks - Multicast
Uploaded by
Adrian HuitCopyright:
Available Formats
MEDIA NETWORKS
Multicast
Media Networks - Multicast
1
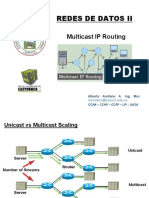
UNICAST
• content is sent from one device to another with a one-
to-one connection
• When a client is connecting to a media server using
unicast, it creates a direct relationship between the
client and the server. Each individual relationship with
the server takes up additional bandwidth
Media Networks - Multicast
2
MULTICAST
• multiple viewers are allowed to simultaneously connect to one stream or
source in a one-to-many connection
• The multicast source relies on the multicast routers to forward the
stream to all client subnets that have clients listening
• Viewers can attach to the same stream at different points during the
live stream
• delivering a single stream of information simultaneously to potentially
thousands of businesses and homes.
• video conferencing, video streaming, computer imaging, Music on hold
services, sensor updates, webcasts, Software updates, …
Media Networks - Multicast
3
MULTICAST APPLICATIONS
• One-to-Many Multicast
− Most common
• Video streaming
• Os deployment
• NTP
• Many-to-Many Multicast
− Senders also act as receivers
• Video conferencing
• Document and whiteboard sharing
• Many-to-One Multicast
− Not common, no significant improvement over unicast
• Data collection
Media Networks - Multicast
4
MULTICAST IN THE OSI MODEL
• IP Multicasting supports UDP as higher layer
Media Networks - Multicast
5
MULTICAST SOURCES
• A source is a device in the IP network that sends a
packet to a multicast group IP Address
• A source does not have to send any indication on the
network that it wants to become a source
• A router processing a multicast message creates an (S,
G) (= source comma group)entry
239.0.0.1
192.168.0.10 (S, G) = (192.168.0.10,239.0.0.1)
Media Networks - Multicast
6
MULTICAST RECEIVERS
• A receiver is a device in the IP network that has
expressed interest in a particular multicast group
or specific (S, G)
• The multicast receiver listens to all packets that arrive
with the multicast group address as the destination
address
• The subscription is managed by
− Internet Group Messaging Protocol (IGMP) - IPv4
− Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) – IPv6
Media Networks - Multicast
7
MULTICAST IPV4 ADDRESSES
• IPv4 Class D address space
• range 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
• Multicast address can only be destination address in IP
header
Media Networks - Multicast
8
RESERVED LINK-LOCAL ADDRESSES
• 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255
• Local network control
• network protocols on a local network
segment
• typically sent with a time-to-live (TTL)
value of 1 and are not forwarded by a
router
• E.g. Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
uses the IP addresses 224.0.0.5 and
224.0.0.6 to exchange link-state
information
Media Networks - Multicast
9
GLOBALLY SCOPED ADDRESSES
• 224.0.1.0 to 238.255.255.255
• send multicast data between organizations across the
Internet
• E.g. the IP address 224.0.1.1 is reserved for Network
Time Protocol (NTP)
Media Networks - Multicast
10
LIMITED SCOPE ADDRESSES
• 239.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
• administratively or limited scoped addresses for use in
private multicast domains
• local multicast applications that will not be forwarded
outside a domain
Media Networks - Multicast
11
MULTICAST IPV6 ADDRESSES
• Prefix of FF00::/8 (first octet from FF00 to FFFF)
Media Networks - Multicast
12
WELL KNOWN MULTICAST ADDRESSES
• Reserved addresses
Address Listeners
FF02::1 All nodes on subnet
FF02::2 All routers on subnet
FF02::5 OSPFv3 routers on subnet
FF02::A EIGRP routers on subnet
FF05::1:3 All DHCP servers on site
FF02::1:FFXX:XXXX Solicited-Node
Media Networks - Multicast
13
TRANSIENT MULTICAST (DYNAMIC
MULTICAST)
• FF10::/12 address range
• Used as temporary multicast addresses by applications
− Audio/Video streaming
− Video Conferencing
− OS deployment
Media Networks - Multicast
14
HARDWARE/ETHERNET MULTICASTING
• the network card is configured, via its drivers, to watch out for particular
MAC addresses: multicast MAC addresses
• Ethernet uses the low-order bit of the high-order octet to distinguish
conventional unicast addresses from multicast addresses. A unicast
would have this bit set to ZERO (0), whereas a multicast would be set
to ONE (1)
• When a normal (unicast) packet is put on the network by a computer, it
contains the Source and Destination MAC address
• a multicast packet is not directed to one host but a number of hosts, so
the destination MAC address will not match the unique MAC address of
any computer
• you will never find a source address that is a multicast MAC address, the
source address will always be a real one, to identify which computer the
packet came from.
Media Networks - Multicast
15
RECOGNIZE A MULTICAST MAC ADDRESS
Unicast MAC multicast MAC
Media Networks - Multicast
16
MAPPING IP MULTICAST TO ETHERNET
MULTICAST IPV4
• place the low-order 23 bits of
the IP multicast address into the
low-order 23 bits of the special
Ethernet multicast address. The
rest of the high-order bits are
defined by the IEEE (yellow
color in the example)
• It is possible for multiple IP
Multicast addresses to have the
same MAC Multicast address
− All frames with the correct MAC
address will be de-encapsulated and
send to the upper layer, which will
drop the packets to which the device
is not subscribed
Media Networks - Multicast
17
MAPPING IP MULTICAST TO ETHERNET
MULTICAST IPV6
• the most significant 16 bits
of an IPv6 multicast MAC
address are 0x3333. The
least significant 32 bits are
mapped from the least
significant 32 bits of an IPv6
multicast address
• the problem of duplicate
IPv6-to-MAC address
mapping also arises like
IPv4-to-MAC address
mapping
Media Networks - Multicast
18
MULTICAST ON THE LINK-LOCAL NETWORK
• MAC address table is filled by storing the source MAC
addresses from incoming frames
• Multicast address is never the source MAC
• Multicast frames will be flooded to all ports
Media Networks - Multicast
19
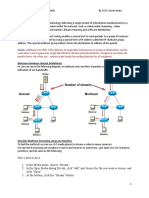
MULTICAST AND LAYER-2 SWITCHES
• When multicasting with Layer 2 switches, all
attached devices receive the packets,
whether they want them or not.
• Because a multicast header does NOT have a
destination IP address, an average network
switch (a Layer 2 switch without supported receiver
capabilities) will not know what to do with it.
So the switch sends the packet out to every
network port on all attached devices. When
the client or network interface card (NIC) source
receives the packet, it analyzes the
destination MAC address and discards it if
not wanted.
receiver
Media Networks - Multicast
20
• Switches and routers need to be aware of devices on the
network interested in a specific multicast stream
• Without this, the only option is to flood the frames on
the local network
• Host group membership is a dynamic process
− Hosts can join a multicast group
− Hosts can leave a multicast group
Media Networks - Multicast
21
MULTICAST GROUP MEMBERSHIP
DISCOVERY (MGMD) PROTOCOLS
• Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
− IPv4
• Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD)
− IPv6
• IGMPv1
• IGMPv2 = MLDv1
• IGMPv3 = MLDv2
Media Networks - Multicast
22
• receivers indicate their interest by sending an IGMP/MLD host
report to the gateway router (called the querier) per segment
• The routers use Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) to
dynamically create a multicast distribution tree
• The data stream will then be delivered only to the network
segments that are in the path between the source and the
receivers
Media Networks - Multicast
23
IGMP
• Router periodically broadcasts IGMP/MLD Query messages
onto the link.
• Hosts respond to the Query messages by sending IGMP/MLD
Report messages indicating their group memberships.
• All routers receive the Report messages and note the
memberships of hosts on the link.
• If a router doesn't receive a Report message for a particular
group for a period of time, the router assumes there are no more
members of the group on the link.
Media Networks - Multicast
24
IGMP AND PIM
• Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used
between hosts on a LAN and the routers on that LAN to
track the multicast groups of which hosts are members.
• Protocol Independent Multicast(PIM) is used between
routers so that they can track which multicast packets to
forward to each other and to their directly connected
LANs.
Media Networks - Multicast
25
IGMP V1
• IGMP v1
No mechanism to leave a group
− Queries
• Querier sends IGMP query messages to 224.0.0.1 (all hosts on the network) with
ttl = 1
• One router on LAN is designated/elected (highest IP address) to send queries =
querier
» There is no election process in IGMPv1, it depends on PIM for the election
• Query interval 60–120 seconds
− Reports
• IGMP report sent by one host suppresses sending by others
• Restrict to one report per group per LAN
• Unsolicited reports sent by host, when it first joins the group
Media Networks - Multicast
26
IGMP - JOINING A GROUP
Media Networks - Multicast
27
IGMP V2
• IGMP v2:
− Host sends leave message if it leaves the group and is the last member (reduces
leave latency and unneeded traffic in comparison to v1)
− Router sends Group-specific queries to make sure there are no members present
before stopping to forward data for the group for that subnet
− Standard querier election (no longer relies on PIM)
• Every router querier by default
• 2 queriers on one link
» Lowest ip becomes querier → Sending IGMP query reports
» Highest ip becomes Designated router → Sending PIM messages
− A query message contains a Maximum Response Time (MRT)
• Group members receiving a query start the timer at a random value, when no other host has sent a
membership report, the host will send the report → only one host on the network needs to send the report
Media Networks - Multicast
28
IGMP MEMBERSHIP QUERY
Media Networks - Multicast
29
IGMP MEMBERSHIP REPORT
Media Networks - Multicast
30
IGMP V2—LEAVING A GROUP
Media Networks - Multicast
31
IGMP LEAVE GROUP
Media Networks - Multicast
32
IGMP V3
• IGMP v3:
− packing multiple group memberships in a single Report message to reduce
the number of packets sent
− Enables to listen only to a specified subset of the hosts sending to the group
• Source Specific Multicast
Media Networks - Multicast
33
IGMP (IPV4) ROUTER CONFIGURATION
• Router(config)#ip multicast-routing
Media Networks - Multicast
34
MULTICAST LISTENER DISCOVERY (MLD)
• MLD is used by IPv6 devices to discover multicast listeners
on directly connected links
• A querier is a network device that sends query messages to
discover which network devices are members of a given
multicast group
• A host is a receiver that send report messages to inform the
querier of a host membership
• MLD reports to join and leave multicast groups
• MLD reports are ICMPv6 with link-local addresses with
hop limit of 1
Media Networks - Multicast
35
MLD LISTENER REPORT
Media Networks - Multicast
36
MLD MULTICAST LISTENER QUERY
Media Networks - Multicast
37
MLD LEAVE GROUP
Media Networks - Multicast
38
MLD ROUTER CONFIGURATION
• Router(config)#ipv6 multicast-routing
Media Networks - Multicast
39
SWITCH IGMP AND MLD SNOOPING
• Switch listens to IGMP and MLD listener reports to know
who wants to receive the multicast packet and who
doesn’t
• When a receiving device wants to tap into a multicasting
stream, it responds to the multicast broadcast with an
IGMP or MLD listener report
Media Networks - Multicast
40
CONFIGURING IGMP SNOOPING
• Switch(config)#ip igmp snooping
• Switch(config)#ip igmp snooping vlan 1
• Switch(config)#ipv6 mld snooping
• Switch(config)#ipv6 mld snooping vlan 1
• Switch#show ip igmp snooping mrouter
• Switch#show ip igmp snooping groups
Media Networks - Multicast
41
ANY SOURCE MULTICAST (ASM)
• host can use any version of IGMP or MLD to join a
multicast group (G)
• The network will deliver IP multicast packets from any
source host with the destination address G to all receiver
hosts in the network that have joined group G.
• an ASM group should only be used by a single
application
Media Networks - Multicast
42
SOURCE SPECIFIC MULTICAST (SSM)
• IP multicast receiver host must use IGMP Version 3
(IGMPv3) or MLDv2 to subscribe to channel (S,G)
• receiver host is indicating that it wants to receive IP
multicast traffic sent by source host S to group G
• network will deliver IP multicast packets from source
host S to group G to all hosts in the network that have
subscribed to the channel (S, G)
• SSM does not require group address allocation within the
network, only within each source host
Media Networks - Multicast
43
MULTICAST ROUTING PROTOCOL
• Deliver multicast packets to their destination over a
layer-3 network = deliver the packets to all the group
members on the network
• Packets can be replicated by routers to multiple outgoing
interfaces
• Routers will need to send information about group
membership
Media Networks - Multicast
44
REVERSE PATH FORWARDING TREE
• Unicast routing build network trees based on destination
− Forwarding decisions are based on the destination address
− Routing table contains learned networks with their exit interface
• Multicast builds a reverse path forwarding tree
− Forward packets based on where the source is
− The root of the distribution tree is the router connected to the sources network
− In the network, incoming multicast packets will not be accepted/forwarded unless they
are received on an interface that is the outgoing interface for the unicast route to the
source of the packet
Media Networks - Multicast
45
PROTOCOL INDEPENDENT MULTICAST
(PIM)
• Multicast routing protocol for IPv4 and IPv6
• PIM uses unicast routing information from routing protocols (no
static routes) to perform the multicast forwarding function
• uses the unicast routing table to perform the reverse path forwarding
(RPF) check function instead of building up a completely independent
multicast routing table
• PIM does not send and receive routing updates between routers
• Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Border Gateway
Protocol (BGP)
Media Networks - Multicast
46
PIM MESSAGES
• Hello: Discovering neighbors
• Join: When a host joins a group by sending an IGMP
report, the router uses a PIM Join message to join the
group network tree
• Leave and prune: When a host leaves a group by
sending an IGMP leave, and no other hosts are a
member of the group, the router uses a PIM Prune
message to leave the group network tree
Media Networks - Multicast
47
JOIN/PRUNE MESSAGE
Media Networks - Multicast
48
PIM DENSE MODE
• Multicast packets are flooded throughout the network
• Routers that have upstream devices listening to the
multicast send a PIM Leave message to stop the
upstream router from sending the multicast packets
• Every 3 minutes, the network is flooded and pruned again
• Push model for building trees
• A router can send a PIM join message to receive a
multicast
• Each router maintains its own trees
• Easy to configure
• For small networks with fast links
Media Networks - Multicast
49
PIM SPARSE MODE
• Uses the IP routing table to build the tree to
the source of a multicast
• Each group has a Rendezvois point
• Routers send periodic join/prune messages
to the RP for each group it has members
• The RP acts as the meeting place for the 1: Multicast to RP
sources and receivers
• Sources send their traffic to the RP, the RP
forwards it to the receivers 3: Multicast from RP
• By default, when the last router in the tree
receives the multicast packet, it will check if 5: Multicast to receiver
the source is in the routers unicast routing 2: join
table. If so, it will send a join message
directly to the source, creating a shorter 4: join
path
Media Networks - Multicast
50
CONFIGURING PIM DENSE MODE
• Router(config)#ip multicast-routing igmp
• Router(config-if)#ip pim dense-mode
Media Networks - Multicast
51
• Router(config-if)#ip pim sparse-mode
• Router(config)#ip pim rp-address <ipv4-address>
• Router(config)#ipv6 multicast-routing
• →enables MLD and PIM on router
• Router(config)#ipv6 pim rp-address <ipv6-address>
Media Networks - Multicast
52
SHOW COMMANDS
• Show ip mroute
• Show ip pim interface
• Show ip pim neighbors
• Show ip igmp groups
Media Networks - Multicast
53
You might also like
- Eric Johnson's Chord Lesson-Spread Triads-Volume 1 - Full Score PDFDocument2 pagesEric Johnson's Chord Lesson-Spread Triads-Volume 1 - Full Score PDFautomaçao1No ratings yet
- Erotic Arcana New NewDocument64 pagesErotic Arcana New NewunsanferNo ratings yet
- PUERTO RICO PresentationDocument24 pagesPUERTO RICO PresentationPeta-Gaye Williams0% (1)
- Multimedia Networking: #6 IP Multicast Semester Ganjil 2012 PTIIK Universitas BrawijayaDocument45 pagesMultimedia Networking: #6 IP Multicast Semester Ganjil 2012 PTIIK Universitas BrawijayaFurqon DasantoNo ratings yet
- Clase 7. Multticast-IPv4Document76 pagesClase 7. Multticast-IPv4Andrés MenaNo ratings yet
- MulicastDocument46 pagesMulicastSurekha SundarrNo ratings yet
- Scalable Network Multicast OverviewDocument34 pagesScalable Network Multicast OverviewJosh 14No ratings yet
- Tema 7. Multicast-IDocument54 pagesTema 7. Multicast-IluiscolchagNo ratings yet
- Multicast and Quality of Service: Internet Technologies and ApplicationsDocument27 pagesMulticast and Quality of Service: Internet Technologies and ApplicationsLivija JovanovićNo ratings yet
- Module21 McastDocument46 pagesModule21 Mcastomarkhanfar2No ratings yet
- CS4254 Computer Network Architecture and Programming: Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-HamidDocument32 pagesCS4254 Computer Network Architecture and Programming: Dr. Ayman A. Abdel-HamidVikram ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Multicast IntroDocument22 pagesMulticast Introapi-3761983100% (2)
- IP Multicast Tutorial PDFDocument175 pagesIP Multicast Tutorial PDFmcclaink06100% (1)
- Computer Networks: An Introduction To IP AddressingDocument28 pagesComputer Networks: An Introduction To IP AddressingChetan KuntaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems Distributed Systems: Multicast Communication Multicast CommunicationDocument22 pagesDistributed Systems Distributed Systems: Multicast Communication Multicast CommunicationArjuna KrishNo ratings yet
- Advanced RoutingDocument49 pagesAdvanced RoutinghvillafuertebNo ratings yet
- University University: MulticastingDocument18 pagesUniversity University: MulticastingsaqibNo ratings yet
- Java Ip MulticastingDocument19 pagesJava Ip MulticastingSiam AnsaryNo ratings yet
- 04 - MulticastDocument46 pages04 - MulticastbelivranNo ratings yet
- IT Infrastructure ArchitectureDocument45 pagesIT Infrastructure ArchitectureAnaheim BatoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document64 pagesChapter 4Razan GaihreNo ratings yet
- Network Fundamentals and Protocols Terms ExplainedDocument61 pagesNetwork Fundamentals and Protocols Terms ExplainedVim SamNo ratings yet
- Network Training - VITECDocument30 pagesNetwork Training - VITECRobert MautinoNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems: Paul Krzyzanowski Pxk@cs - Rutgers.eduDocument44 pagesDistributed Systems: Paul Krzyzanowski Pxk@cs - Rutgers.eduSrinath GudurNo ratings yet
- Multicast: OutlineDocument38 pagesMulticast: OutlineBùi Thế AnhNo ratings yet
- BGP and Multicasting ProtocolsDocument54 pagesBGP and Multicasting ProtocolsSoubhagya Ranjan MohantyNo ratings yet
- Unit III Multicast Address & RoutingDocument37 pagesUnit III Multicast Address & RoutingSowmiya MurugananthamNo ratings yet
- 19 InternetworkingOperationDocument77 pages19 InternetworkingOperationapi-19500872No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document39 pagesUnit 4Saurabh SachdevaNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument48 pagesNetworkinghosbadawi.hbNo ratings yet
- Multicast Routing Protocols: TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1Document114 pagesMulticast Routing Protocols: TCP/IP Protocol Suite 1mkmanojdevilNo ratings yet
- ELE3214-Handout10-CCNGuest-Network LayerV2Document80 pagesELE3214-Handout10-CCNGuest-Network LayerV2Ambrose OnapaNo ratings yet
- Multicasting: UnicastDocument20 pagesMulticasting: UnicastAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- MTCNA VPTS DobojDocument425 pagesMTCNA VPTS DobojAdnan SulejmanovicNo ratings yet
- Protocol perils “Hacking the stack”"This title summarizes the key aspects of the document by including the main topic "Protocol perils" and quoting the subtitle "“Hacking the stackDocument77 pagesProtocol perils “Hacking the stack”"This title summarizes the key aspects of the document by including the main topic "Protocol perils" and quoting the subtitle "“Hacking the stackJoey GeraciNo ratings yet
- Network Fundamentals - CCNA Exploration Companion Guide - Chapter 6 NotesDocument3 pagesNetwork Fundamentals - CCNA Exploration Companion Guide - Chapter 6 NotessnowwolfyNo ratings yet
- Building Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI)Document17 pagesBuilding Scalable Cisco Internetworks (BSCI)Hebert MolinaNo ratings yet
- InternetDocument60 pagesInternetoureducation.inNo ratings yet
- What Is MulticastDocument6 pagesWhat Is MulticastHakim QaradaghiNo ratings yet
- Addressing & SubnettingDocument80 pagesAddressing & SubnettingboybkaNo ratings yet
- Wiki Internet Protocol MulticastDocument19 pagesWiki Internet Protocol MulticastErmenegildo ZegnaNo ratings yet
- ICMP, IP, PIM, Routing ProtocolDocument26 pagesICMP, IP, PIM, Routing ProtocolQuantom McsNo ratings yet
- Ars-Msr 1 Mcast 2014Document44 pagesArs-Msr 1 Mcast 2014Sorina ElenaNo ratings yet
- Network and Transport LayersDocument54 pagesNetwork and Transport LayerstopherskiNo ratings yet
- RailnetDocument55 pagesRailnetHarshit DhakadNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol MulticastDocument17 pagesInternet Protocol MulticastPatricio QueglesNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 AddressesDocument23 pagesIpv4 AddressesNimmi DeviNo ratings yet
- Network+ Guide To Networks 5 Edition: In-Depth TCP/IP NetworkingDocument63 pagesNetwork+ Guide To Networks 5 Edition: In-Depth TCP/IP NetworkingRyan OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Ccna1 m9 TCP Ip and Ip Addressing PDFDocument25 pagesCcna1 m9 TCP Ip and Ip Addressing PDFTurkishExplorer AhmetNo ratings yet
- Multicast Routing ShortDocument43 pagesMulticast Routing ShortKhawla ElfilaliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IP Multicast PDFDocument121 pagesIntroduction To IP Multicast PDFHieuNBNo ratings yet
- Advanced Computer Networks - CS716 Power Point Slides Lecture 27Document28 pagesAdvanced Computer Networks - CS716 Power Point Slides Lecture 27Taran AulakhNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument391 pagesUnit Iiijyotsna dwivedi100% (1)
- IP Routing ProtocolsDocument31 pagesIP Routing Protocolshellboyz421No ratings yet
- Multi CastingDocument24 pagesMulti Castingkayani299636No ratings yet
- Yasser Auda CCIEv5 IPv4 Multicast Study Guide PDFDocument50 pagesYasser Auda CCIEv5 IPv4 Multicast Study Guide PDFsheraz35No ratings yet
- 08.MAC and IP FundamentalsDocument37 pages08.MAC and IP Fundamentalsksav yadavNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol MulticastDocument19 pagesInternet Protocol MulticastAbhijit ThakurNo ratings yet
- BSCI30S08 IPv6Document73 pagesBSCI30S08 IPv6Amine TellibiNo ratings yet
- Forbidden Island Quick Reference GuideDocument1 pageForbidden Island Quick Reference GuideRobert John EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Safari Arms 1911 Enforcer Match Master PistolDocument42 pagesSafari Arms 1911 Enforcer Match Master PistolTactic Otd ArgNo ratings yet
- Community CPL27 SPECDocument2 pagesCommunity CPL27 SPECNoah WestonNo ratings yet
- 01 January 1989Document108 pages01 January 1989Monitoring TimesNo ratings yet
- Yangon (New Trend)Document12 pagesYangon (New Trend)Nguyễn Hương LiênNo ratings yet
- Milwaukee Avenue Improvement Plan - Logan Boulevard To Belmont AvenueDocument10 pagesMilwaukee Avenue Improvement Plan - Logan Boulevard To Belmont AvenueMina BloomNo ratings yet
- Reflection - Mini Maker FaireDocument2 pagesReflection - Mini Maker Faireapi-454530158No ratings yet
- FrankensteinDocument2 pagesFrankensteinDiego LorussoNo ratings yet
- SJ-20160119164028-002-ZXR10 5960 Series All 10-Gigabit Data Center Switch Hardware ManualDocument70 pagesSJ-20160119164028-002-ZXR10 5960 Series All 10-Gigabit Data Center Switch Hardware Manualleandro de sousaNo ratings yet
- Ge-Power: Substation Monitoring and Management SoftwareDocument28 pagesGe-Power: Substation Monitoring and Management SoftwareaMOR BENGOURICHNo ratings yet
- Past Simple: İsa Arslan 3231190027 Ömer Faruk Canpolat 3231190025 Ali Vehbi Yalınç 3231190014Document31 pagesPast Simple: İsa Arslan 3231190027 Ömer Faruk Canpolat 3231190025 Ali Vehbi Yalınç 3231190014İsa ArslanNo ratings yet
- Germany Wins World Cup With Big Data and Its Side: Case StudyDocument3 pagesGermany Wins World Cup With Big Data and Its Side: Case StudyTahsin MuntasirNo ratings yet
- Sports and HobbiesDocument11 pagesSports and HobbiesThái Huyền TrangNo ratings yet
- Puzzle 1 (Hard, Difficulty Rating 0.64) Puzzle 2 (Hard, Difficulty Rating 0.70)Document10 pagesPuzzle 1 (Hard, Difficulty Rating 0.64) Puzzle 2 (Hard, Difficulty Rating 0.70)rudolf_laszlokNo ratings yet
- Epic Fail Live Chat TranscriptDocument20 pagesEpic Fail Live Chat TranscriptinkpopNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Cdh-Le24fd04 CH 8m35s SvcmnlsDocument39 pagesHitachi Cdh-Le24fd04 CH 8m35s SvcmnlsCarlosClarosNo ratings yet
- Shojo Fashion Manga Art School Year PDFDocument18 pagesShojo Fashion Manga Art School Year PDFTaffarel Micaloski100% (1)
- Assessment of Shatkriyakaal in Ref Erence To Diagnosis of DiseasesDocument45 pagesAssessment of Shatkriyakaal in Ref Erence To Diagnosis of DiseasesBalkrishan SevatkarNo ratings yet
- Repaso Examen 2 TrimestreDocument10 pagesRepaso Examen 2 TrimestreevgarcNo ratings yet
- Claudine Vico So ResumeDocument4 pagesClaudine Vico So ResumeArun YadavNo ratings yet
- Origins of First 'Restaurant' Challenged After 200 YearsDocument15 pagesOrigins of First 'Restaurant' Challenged After 200 YearsNiharika KotwalNo ratings yet
- The Legend of Balugo Tree Marks Famous Family's HomeDocument18 pagesThe Legend of Balugo Tree Marks Famous Family's HomeDafer M. EnrijoNo ratings yet
- CCS-UC-200: Crestron RL 2 Group Collaboration System For Lync, Integrator KitDocument3 pagesCCS-UC-200: Crestron RL 2 Group Collaboration System For Lync, Integrator KitEmily MagrishNo ratings yet
- Tyb DB OnlyDocument46 pagesTyb DB OnlyAlize ChNo ratings yet
- ElementsofFiction6 4 10Document21 pagesElementsofFiction6 4 10Adina CalugaruNo ratings yet
- Cortex Diagnose ReportDocument18 pagesCortex Diagnose ReportRamesh NathanNo ratings yet