Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiac
Cardiac
Uploaded by
Nguyên HoàngOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiac
Cardiac
Uploaded by
Nguyên HoàngCopyright:
Available Formats
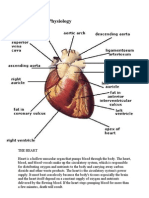
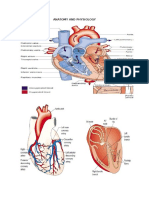
Cardiac muscle, in vertebrates, one of three major muscle types, found only in the heart.
Cardiac
muscle is similar to skeletal muscle, another major muscle type, in that it possesses contractile units
known as sarcomeres; this feature, however, also distinguishes it from smooth muscle, the third
muscle type. Cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and
is not under voluntary control. The rhythmic contraction of cardiac muscle is regulated by the
sinoatrial node of the heart, which serves as the heart’s pacemaker
The heart is made up of three layers
+pericardium : The pericardium is a fibrous sac surrounding the heart, consisting of the epicardium,
pericardial space, parietal pericardium, and fibrous pericardium.
+ myocardium: The cardiac muscle is responsible for the contractility of the heart and, therefore, the
pumping action. The cardiac muscle must contract with enough force and enough blood to supply the
metabolic demands of the entire body. This concept is termed cardiac output and is defined as heart
rate x stroke volume, which is determined by the contractile forces of the cardiac muscle and the
frequency at which they are activated
+ endocardium: The endocardium is not cardiac muscle and is comprised of simple squamous
epithelial cells and forms the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves.
You might also like
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (3)
- Cardiovascular System - Transportation 1Document28 pagesCardiovascular System - Transportation 1Louise Mica Lee100% (1)
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Heartvanessaresullar100% (1)
- Chapter 19 The Circulatory System - The HeartDocument14 pagesChapter 19 The Circulatory System - The HeartGary Bowen100% (1)
- Anatomy of HeartDocument35 pagesAnatomy of HeartIstaleih Puerto100% (1)
- Physiology of ExerciseDocument25 pagesPhysiology of ExerciseTedy Friyadi100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDocument69 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of HeartRitu Arun Kaushik100% (1)
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes NCM 102: Union Christian College College of NursingDocument77 pagesLecture Notes NCM 102: Union Christian College College of Nursingnarswiponshistoryan100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology ASCVDDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ASCVDAlvheen JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardio Vascular SystemguptaasitNo ratings yet
- The Heart: Overview and PositionDocument11 pagesThe Heart: Overview and PositionLil_QuinceNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemABDUL HANANNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemYna MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartjeffcaselNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Human HeartDocument17 pagesBiology Project Human HeartdeepmanisharmaNo ratings yet
- Human Heart AssignmentDocument12 pagesHuman Heart AssignmentMonica SreeNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Muscular System IncludeDocument8 pagesFunctions of The Muscular System IncludeDanesh CamachoNo ratings yet
- Heart Structure and FunctionsDocument3 pagesHeart Structure and FunctionsChristella KateNo ratings yet
- احلام 1 PDFDocument7 pagesاحلام 1 PDFEhab Alaa Abd Al-AmeerNo ratings yet
- ArteriesDocument3 pagesArteriesShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument29 pagesCardiovascular Systemethel roseNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesMarie ParksNo ratings yet
- Heart and BrainDocument29 pagesHeart and BrainDIPANJAN MAJUMDAR100% (6)
- Cardiovascular System Semis ReviewerDocument18 pagesCardiovascular System Semis ReviewerReggie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument9 pagesScienceMARCELINO REYESNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument19 pagesHeart Anatomydeepika kushwahNo ratings yet
- Unit Seven: Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesUnit Seven: Cardiovascular SystemKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemDhea BugnaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartJoan Devera100% (1)
- Anaphy CardioDocument10 pagesAnaphy Cardiojonel lorenzoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemSaadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The HeartJanice ScatesNo ratings yet
- The HearthDocument1 pageThe HearthRaffaela CerroneNo ratings yet
- Our Heart BeatsDocument7 pagesOur Heart BeatsferyNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 The Cardiovascular System: Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesUnit 6 The Cardiovascular System: Learning OutcomesDeolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy of The Heart: Featured Snippet From The WebDocument4 pagesBasic Anatomy of The Heart: Featured Snippet From The WebMay Larkspur TadeoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Cardiovascular Systemtewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument14 pagesCardiovascular SystemArun Kumar DhupamNo ratings yet
- Heart by Aritra SahaDocument15 pagesHeart by Aritra SahaAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Loreto, Bien BMG3FX/MWF/3:00-04:00 Lugo, Mariel Cabigao, JeanDocument4 pagesLoreto, Bien BMG3FX/MWF/3:00-04:00 Lugo, Mariel Cabigao, JeanJean CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o oDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o okayaldrNo ratings yet
- Circulation and Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesCirculation and Cardiovascular SystemSatria MandalaNo ratings yet
- Heart: Layers of The Heart WallDocument3 pagesHeart: Layers of The Heart WallAdaNo ratings yet
- Human Heart ScienceDocument7 pagesHuman Heart ScienceJewel Kathryn MorenoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Circulatory Systemolivia majcherNo ratings yet
- CPT CH 3 10-11-04 PDFDocument24 pagesCPT CH 3 10-11-04 PDFghindaruNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory Systempriyamail0525No ratings yet
- Circulation Vocabulary HandoutDocument2 pagesCirculation Vocabulary HandoutGPearce204No ratings yet
- Circulatory System Q&A.Document77 pagesCirculatory System Q&A.Alyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Project BioDocument18 pagesProject Bioyanshu falduNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Cardiovascular System EsparciaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To The Cardiovascular System EsparciaJohnferson S. BornalesNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels WorksheetDocument2 pagesBlood Vessels WorksheetNakeisha JosephNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument2 pagesCardiac CycleShaqueena DanversNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology SLEDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology SLEMoti Pagador100% (4)
- 6 - The Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pages6 - The Cardiovascular SystemKolea 2003No ratings yet