Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Das Perfekt
Das Perfekt
Uploaded by
packyee840 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesThe perfect tense in German is used to describe past events, such as something that happened an hour ago or yesterday. It is formed with an auxiliary verb (haben or sein) and the past participle of the main verb. For regular verbs, the past participle is formed by removing the "-en" ending and adding "ge-" and "-t". Common regular past participles include gelernt, gemacht, gekocht, gekauft, geraucht, gewohnt, gefragt, and gesagt. Weak verbs use "haben" as the auxiliary verb and can have three English translations depending on context. Examples are provided of conjugating "spielen" in
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe perfect tense in German is used to describe past events, such as something that happened an hour ago or yesterday. It is formed with an auxiliary verb (haben or sein) and the past participle of the main verb. For regular verbs, the past participle is formed by removing the "-en" ending and adding "ge-" and "-t". Common regular past participles include gelernt, gemacht, gekocht, gekauft, geraucht, gewohnt, gefragt, and gesagt. Weak verbs use "haben" as the auxiliary verb and can have three English translations depending on context. Examples are provided of conjugating "spielen" in
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesDas Perfekt
Das Perfekt
Uploaded by
packyee84The perfect tense in German is used to describe past events, such as something that happened an hour ago or yesterday. It is formed with an auxiliary verb (haben or sein) and the past participle of the main verb. For regular verbs, the past participle is formed by removing the "-en" ending and adding "ge-" and "-t". Common regular past participles include gelernt, gemacht, gekocht, gekauft, geraucht, gewohnt, gefragt, and gesagt. Weak verbs use "haben" as the auxiliary verb and can have three English translations depending on context. Examples are provided of conjugating "spielen" in
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
School of Humanities
Languages
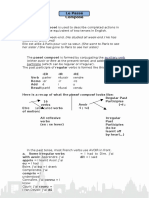
Das Perfekt - The Perfect Tense
The perfect tense is used to describe events in the past, for example, what happened
an hour ago, yesterday, last week.
To form the perfect tense you need 2 parts,
an auxiliary (or helping) verb ‘haben’ or ‘sein’
a past participle – for weak (regular) verbs follow this pattern :
1) take the infinitive e.g. spielen (to play)
2) take off the ending (-en) spiel-
3) put ge- on the front and add a ‘t’ = gespielt
Work out the past participle (p.p.) of these (weak/regular) verbs:
lernen/ machen/ kochen/ kaufen/rauchen/wohnen/fragen/sagen
Weak verbs are conjugated with the present tense of ‘haben’ in the perfect tense.
There are three possible English translations of the one German form.
For example:
spielen- to play
ich habe ….. gespielt I have played/I played/I did play
du hast ….. gespielt you have played etc.
er hat ….. gespielt he or it has played
sie hat ….. gespielt she or it has played
es hat ….. gespielt it has played
man hat …. gespielt one has played
wir haben …gespielt we have played
ihr habt … gespielt you (plural) have played
Sie haben ... gespielt you (formal) have played
sie haben … gespielt they have played
Vorsicht!
1. The past participle must go to the end of a main clause.
zum Beispiel. Ich habe Tennis gespielt.
I played tennis.
2. Normal word order rules still apply.
z.B. Gestern habe ich Tennis gespielt.
Yesterday I played tennis.
3. In a subordinate clause the auxiliary verb, e.g. ‘haben’ goes to the end.
z.B. Ich gehe nicht wandern, weil es geregnet hat.
I’m not going hiking because it has rained.
4. The past participle never changes.
5. The past participles of strong (irregular) verbs do not follow a pattern. Learn
them from a verb list.
Aufgabe: Ergänzen Sie diese Tabelle:
Infinitiv Das Perfekt (3rd p.sing.) Englisch (x1)
sprechen es hat…gesprochen it has spoken
trinken
lesen
essen
finden
vergessen
gefallen
sitzen
schreiben
sehen
tragen
waschen
schließen
helfen
singen
nehmen
haben
empfehlen
leiden
rufen
stehlen
gewinnen
brechen
backen
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- GCSE French Verbs GuideDocument13 pagesGCSE French Verbs GuidePJ0% (1)
- UntitledDocument33 pagesUntitledInsi GrouNo ratings yet
- French Basic Grammar TensesDocument1 pageFrench Basic Grammar Tensesrhianniki80% (10)
- Present PerfectDocument8 pagesPresent PerfectIvka SalopekNo ratings yet
- The Auxiliary Verbs-AvoirDocument3 pagesThe Auxiliary Verbs-AvoirganeshdhageNo ratings yet
- PerfektDocument3 pagesPerfektHülya Karhan BegunNo ratings yet
- Participles Used As Adjectives: Geben Sie Den Titel Des Dokuments EinDocument12 pagesParticiples Used As Adjectives: Geben Sie Den Titel Des Dokuments Einธรรมรัตน์ หรั่งเจริญNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Auxiliary Verbs in English and Spanish.Document4 pages2.2 Auxiliary Verbs in English and Spanish.Sole MuñizNo ratings yet
- Past Simple: Form (Forma)Document16 pagesPast Simple: Form (Forma)SandyTatianaNo ratings yet
- Passe ComposeDocument5 pagesPasse ComposeAnjel EnriquezNo ratings yet
- PerfektDocument18 pagesPerfektGovind MilaniNo ratings yet
- B1Document19 pagesB1prathibaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Infinitive Mit ZuDocument32 pagesChapter 1 - Infinitive Mit ZuRashmi RaoNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument24 pagesSimple Present TenseAda PérezNo ratings yet
- English 10 HandoutsDocument4 pagesEnglish 10 HandoutsChristver CabucosNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Sem 4Document1 pageModule 1 Sem 4Prafulla TekriwalNo ratings yet
- Le Passé Composé: Studied All Week-End) Her Sister / She Has Gone To Paris To See Her Sister)Document7 pagesLe Passé Composé: Studied All Week-End) Her Sister / She Has Gone To Paris To See Her Sister)FäNiÿ ŸüleÏmï Ä. RüGërÿioNo ratings yet
- Verbs PresentPerfect OverviewDocument4 pagesVerbs PresentPerfect OverviewNyake OliveNo ratings yet
- German Unit 3Document47 pagesGerman Unit 3ellahughes2206No ratings yet
- Le Film Anatomie D'une Chute Nommé Aux OscarsDocument7 pagesLe Film Anatomie D'une Chute Nommé Aux Oscarsvalar.natesan87No ratings yet
- 1.1 Present Sim-WPS Office ManuelDocument7 pages1.1 Present Sim-WPS Office ManuelEliseu Júlio MendesNo ratings yet
- Rules To Change Active To Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesRules To Change Active To Passive VoiceMaicol JR MartínezNo ratings yet
- Past Simple vs. Past ContinuousDocument3 pagesPast Simple vs. Past ContinuousCaTa LiNaNo ratings yet
- PMR English Language ModulesDocument86 pagesPMR English Language Modulespain_rinneganNo ratings yet
- Verbos Regulares e Irregulares InglesPresentation TranscriptDocument6 pagesVerbos Regulares e Irregulares InglesPresentation TranscriptAlhyGuzmanNo ratings yet
- 1 Note de GramaticaDocument15 pages1 Note de GramaticaMircea BarbuNo ratings yet
- German Tense and AspectDocument28 pagesGerman Tense and AspectRaul PaulNo ratings yet
- French Verbs HandoutDocument2 pagesFrench Verbs Handout3leni100% (2)
- 19 Im Parfait NoteDocument4 pages19 Im Parfait NoteJaphy's BreathNo ratings yet
- Present, Past, and Sometimes Perfect ParticiplesDocument3 pagesPresent, Past, and Sometimes Perfect ParticiplesOsorio AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice and Active VoiceDocument12 pagesPassive Voice and Active VoiceAbdesselam BettaharNo ratings yet
- AnglaisDocument119 pagesAnglaisKouassi Martinese ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Grammar PracticeDocument29 pagesGrammar PracticeTcer OdahNo ratings yet
- German Tutorials IIIDocument19 pagesGerman Tutorials IIIheartswarmNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesPast Continuous TensedkhekovaNo ratings yet
- Deutsch 101 Handout: The Perfekt TenseDocument4 pagesDeutsch 101 Handout: The Perfekt TenseDebbie Tschirch100% (1)
- Present and Past Participles: Ms. YasiDocument11 pagesPresent and Past Participles: Ms. Yasikh6wdstkssNo ratings yet
- Weak, Strong and Mix VerbsDocument4 pagesWeak, Strong and Mix VerbsLion KingNo ratings yet
- L'imparfaitDocument2 pagesL'imparfaitMthulisiNo ratings yet
- Oblique Moods in Koine GreekDocument3 pagesOblique Moods in Koine Greekbobmacbob5No ratings yet
- Auxilliary Verbs: A Verb Used in Forming The Tenses, Moods, and Voices of OtherDocument4 pagesAuxilliary Verbs: A Verb Used in Forming The Tenses, Moods, and Voices of OtherRuby AsadNo ratings yet
- The Imparfait: NotesDocument3 pagesThe Imparfait: NotesAnish Kantheti100% (1)
- Present PerfectDocument23 pagesPresent PerfectNam Van Do100% (2)
- ELTE 305 ActivitiesDocument7 pagesELTE 305 ActivitiesErgun TurktanNo ratings yet
- German - To Grammar WorksheetsDocument5 pagesGerman - To Grammar WorksheetsRaghav BhallaNo ratings yet
- TOIEC Grammar - ParticipleDocument3 pagesTOIEC Grammar - Participlesilly witchNo ratings yet
- Grammar Summary Passive Voice: Present Simple: For ExampleDocument8 pagesGrammar Summary Passive Voice: Present Simple: For ExampleYlenia BaldiviezoNo ratings yet
- Gramatica Ingles Nivel ElementalDocument8 pagesGramatica Ingles Nivel ElementalmmuelasgNo ratings yet
- English Class Part OneDocument19 pagesEnglish Class Part Onechristina ndong nkogheNo ratings yet
- Tenses - Grad 11 2Document17 pagesTenses - Grad 11 2farida.kargarNo ratings yet
- Italian 200 Grammar Outline by Adeel AnwarDocument8 pagesItalian 200 Grammar Outline by Adeel Anwarapi-401805073No ratings yet
- Prezentul Simplu (Present Simple) : If They ComeDocument6 pagesPrezentul Simplu (Present Simple) : If They ComemariarrNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous PresentationDocument4 pagesPast Continuous PresentationSteven PossoNo ratings yet
- Simple and Past TenseDocument4 pagesSimple and Past TenseGAME ISLANDNo ratings yet
- قواعد 3 محاضرة 6Document9 pagesقواعد 3 محاضرة 6Rand YounesNo ratings yet
- What Is The Present ParticipleDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Present ParticipleAeo FikNo ratings yet
- Passe ComposseDocument8 pagesPasse ComposseKimberly A. S. SmithNo ratings yet