100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views8 pagesPhysics XII CH 10 Physics Assertion Reasoning Wave Optics
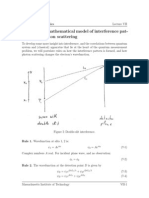
1. The document discusses wave optics and contains multiple choice questions regarding assertions and reasons about concepts in wave optics and the Young's double slit experiment.
2. The questions test understanding of principles like Huygens' principle, diffraction, interference patterns, the relationship between fringe width and wavelength or slit separation, and how properties of light change when passing through different media.
3. The document examines several statements of assertion followed by reasons and asks the reader to evaluate whether the assertion and reason are both true, or if one is true and one is false.
Uploaded by
Njan KL16么PorottaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views8 pagesPhysics XII CH 10 Physics Assertion Reasoning Wave Optics
1. The document discusses wave optics and contains multiple choice questions regarding assertions and reasons about concepts in wave optics and the Young's double slit experiment.
2. The questions test understanding of principles like Huygens' principle, diffraction, interference patterns, the relationship between fringe width and wavelength or slit separation, and how properties of light change when passing through different media.
3. The document examines several statements of assertion followed by reasons and asks the reader to evaluate whether the assertion and reason are both true, or if one is true and one is false.
Uploaded by
Njan KL16么PorottaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Assertion and Reason Questions
- Answer Key