Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ISO 9001 2015 - Compressed
ISO 9001 2015 - Compressed
Uploaded by
مختار حنفى0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views38 pagesOriginal Title
ISO-9001-2015_compressed
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views38 pagesISO 9001 2015 - Compressed
ISO 9001 2015 - Compressed
Uploaded by
مختار حنفىCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 38
FINAL INTERNATIONAL — 1SO/FDIS
DRAET STANDARD 9001
ISO/TC 176/82
Secretariat: BSI Quality management systems —
i mn
Voting begins an Requirements
eee _Systdmes de monogenrent de fa quate — Exigences
‘Young terminates on:
2015-09-09
Please see the administrative notes on page
Reterence number
is0/DIS 9001:2015(E)
© 150 2015
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
CEN PARALLEL PROCESSING
“This final draft hasbeen developed within the International Organization for Standardization (180), and pro
cessed under the O-lead mode of collaboratian as defined in the Vienna Ageeement. The final draft was
asis of comments received during aa thedran.
lel enquiry.
is hereby submitted to the 150 raecnl
two-month approval vate in 150)
Positive votes shall not be accompanied by comments,
Negative votes shall be accompanied by the relevant techi
rer bodlies and to the CEN member budics for ap
1 formal vote in CEN,
A COPYRIGHT PROTECTED DOCUMENT
5. Published in Soizerland
served less otierwise specified 9 art oC this publication may be repraduced ar
ny thea, electrante OF mocha,
1 pernissia, Peruissian can be regu
the requests
150 coprrightoffice
ot #CP AOL
ied oxherwis ina form,
cacopying. oF posting on the meret of an IMC, KOU por
130 the aes ey ISO's anezber aay i the caaley af
opyriehtlsacrs,
une lsO.T
i wrs0 2 nes rosorvul
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
Contents Page
Foreword
Introduction
1 Scope
2 Normative references
3 Terms and definitions
4+ Context ofthe organization .
41 Understanding the organization and its context
42 — Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties
43 Determining the scope of the quality management system.
44 Quality managenent system and its prncesses
Leadership
5.1 Leadership and commitment
Sil
5
52 Policy
S21
522
53 Organizational roles, responsibilities and authorities
Planning.
6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities
62 — Quality objectives and planning to atbieve them. ee a
63 Planning of changes
Support
Resourves == Se ae
TAd General
MLZ People
713 Infrastructure
7.14 — Environment{for the operation of processes
TLS Monitoringand measuring resources
7.146 — Organizational knowledge
72 Competence
73° Awareness:
74 Communication
7.5 Documented information
General
Customer focus
Developing the quality policy tt i
Communicating the quality policy
We COC DOAIVYA DATA UO SeeeuuUe DONE ee De
75. General.
7.52 Creating and updating —_— z = :
7.53 Control of documented information
‘Operation
8.1 Operational planning and contrat = Beer oe
BZ Requirements for products and services 10
821 — Customer communication 10
822 Determining the requirements related to products and services 10
823 Review of requirements related to products and services 10
24 — Changes to requirements for products and services W
@3 Desig and development of products and serviews, ara u
83.1 General. i uw
3:2 Design and development planning ir
833 Design and development inputs Ww
34 — Design and development en 12
43.5 Design and development outputs. " 12
83.6 Design and development changes 12
© 1502015 All rights reserve i
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
10.
B4 Control ofexternally provided processes, products and services
@41 General
B42 —Typeand extent of control
G42 _ Information for external providers S 3
85 Production and service provision...
5.1 Control of produstion and service provision.
B52 — Identification and traceability
53 Property helonging to customers or external providers.
B54 Preservation.
G55. Posi-delivery activities
856 Control of changes
85 Release af products and services
87 — Control ofnancanforming outputs
Performance evalttation
9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysisand evaluation i s
FLL General
94.2 Cuswomersatisfaction
91.3 Analysis and evaluation,
92 Internal au
93. Management review - _
931 General
932 Management review inputs
93.3 Management review outputs
Improvement.
10:1 General
10.2 Nonconformity and corrective action
10.3
\Contiaual improvement
Annex A (informative) Clarification of new structure, terminology and concepts
Annex B (informative) Other International Standards on quality management and quali
‘ibliography
management systems developed by 180/TC 176
(© 80 2015 = Alt igh
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
Foreword
180 (the luternational Organization for Standardization) isa workdwidefederation af national standards
bodies (180 member bodies}, The work nf preparing International Standards is normally carried out
through 180 technical committees, Each mietnber body interested In a subject for whieh a technical
cammittee has been established has the right to be represented on that committee. International
‘organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
150 collahorates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of
electrotechnical standardization.
The procedures used to develop this Jacument and those intended for its further maintenance are
described in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 1. In particular the different approval criteria needed far the
dlfferent types of [80 documents should be noted, This document was drafted in accordance with the
editorial rules of the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2 (see wiwwisaorg/lirectives)
‘Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements ofthis document may be the subject of
petent rights. [$0 shall not he held responsible for identifying any orall such patent rights. Details of any
patent rights identified during the development of the document will be in the Introduction and/or on
the ISO list of patent declarations recetved (see Wwu'vilso.org/patents).
Any trade name used In this document is Information given for the coavenience of users and does wot
canstitutean endorsement.
Foran explanationonthemeaningofisOspecificterms and expressiansrelatedtoconformity assessment,
as well as information about ISO's adherence to the World Trade Organization (WTO) principles in the
‘Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) see the following URL: www. jsa.org isn /foreword hum
‘The cammittee responsible for this document is Technical Committee ISO/TC 176, Quality management
‘and quality assurance, Subcommittee SC 2, Quality systems,
‘This fifth edition cancels and replaces the fourth edition (ISO 9001;2008), which has been technically
Fevised, through the adaption of a revised clause sequence and the adaptation of the revised quality
‘management principlesand of new cancepts,
© 1502015 All rights reserve i
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
Introduction
0.1 General
‘The adoption of « quality: management system isa strategic decision for an organization that can help
to improve its averall performance and provide a sound hasis for sustainable develapment initiatives,
‘The potential benefits to an organization of implementing a quality management system based an this
International Standard are:
8) the ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and applicable
statutory and regulatory requirements;
b) facilitating opportunities to enhance customer satisfaction;
addressing risks and opportunities associated with its context and objectives;
1d) the ability to demonstrate conformity to specified quality management system requirements.
‘This International Standard can be used hy internal and external parties.
It is not the intent of this International Standard to imply the need for:
= uniformity in the structure of different quality management systems
= alignment of documentation to the clause structure of this International Standard:
— the use ofthe specific terminology afthis International Standard within the organization,
The quality management system requirements specified ia this Imernational Standard are
complementary to requirements for products and services.
‘This International Standard employs the process approach, which incorporates the Plan-Do-Check-Act
(PDCA) cycle and risk-based thinking.
‘The processappreach enables an organization to plan its processesand their interactions.
‘The PCA cycle enables an organization to ensure that its prosesses are adequately resourced and
managed, and that opportunities for improvement are determined and acted on.
‘Risk-based thinking enables an organization to determine the factors that could cause its processes and
its quality management system to deviate from the planned results, to put in place preventive controls
to minimize negative effects and to make maximum use of opportunities as they arise (see Clause A}.
Consistently meeting requirements and addressing future needs aru! expectations pases a challenge
for organizations in an increasingly dynamic and complex environment. Ta achieve this objective, the
‘organization might find it necessary tu adept various forms of improvement in addition te correction
sand coatinual improvement, such as breakthrough change, innavation and re-organization,
{n this International Standard, the following verbal forms are used:
— “shall” indicates a requirement;
— "should" indicates a recommendation;
— "may" indicatesa permission:
— ‘cant indicates a passibility or a capability.
Informationmarkedas "NOTE" isforguldance in understandingorclarifyingtheassoriated requirement,
vw (© 80 2005 = Alt rghgerosoevod
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
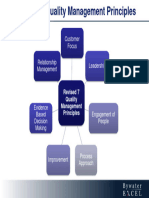
0.2. Quality management principles
This International Standard is based on the quatity management principles described in iSO 9000, The
descriptions include a statement of each principle, a rationale of why the principle is important far the
organization, some examples of benefits associated with the principle andexamples of ty plcalactians to
iprove the organization's performance when applying the principle,
‘The quality management principles are
= customer focus:
= leaderstep:
= engagement of people;
= processappraach;
= improvement;
— evidence-based decision making:
— relationship management.
0.3. Process approach
0.3.1 General
‘This International Standard promotes the adoption ofapracessepproach when developing, implementing
and improving the effectiveness af a quality management system, to enhance customer satisfaction by
‘meeting customer requirements. Specific requirements considered essential to the adaption ofa process
approach are inchueled in 4.4
Understanding and mansging interrelated processes as a system contributes fo the organization's
coffoctivonoss and officiency in achieving its intended results. This appraach enables the organization
toccantrol the interrelationsh ps and interdependencies among the processes of the system, so that the
‘overall perfarmance of the organization can be enhanced.
‘The process approach involves the systematic definition and management of processes, and their
interactions, so as to achieve the intended results in accordance with the quality policy and strategic
direction of the organization, Management of the processes and the system as.a whale cas be achieved
tusing the PDGA cycle (see 0.3.2) with an overall focus on risk-based thinking (see 0.3.3) aimed at taking
advantage of opportunities and preventing undestrable results,
The ap
tion of the process approach in a quality management system enables
a) understanding and consistency in meeting requirements,
b) the consideration of processes in terms of added value;
©) theachlevement of effective process performance:
d) improvement of processes based on evaluation of data and information,
Eigune 1 gives a schematic representation of any process and shows the interaction af its elements. The
monitoring end measuring checkpoints, which are necessary for control, are specific ta earh process
and will vary depending on the retated risks,
© 1502015 All rights reser vil
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
|
|Seapecee |
| iomaeretrat |
Senarant
| en pa
=
Fore censor
eek pats rs
SSinaewa ree
Figure 1— Schematic representation of the elements of a single process
0.3.2 Plan-Do-Check-Acteycle
‘The PDGA cycle can be applied to all processes and to the quality management system as a whole,
igure illustrates how Clauses 4 to 10-ean be grouped in relation to the PDCA cyele,
fe (uty Management Sytem 6) oe
epariztion
and its conte
Figure 2— Representation of the structure of this International Standard in the PDCA cycle
150 2015 - Al rignteresorvod
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
The PDCA cycle can be briefly described as follows:
— Plan: establish the objectives of the system and its provesses, and the resources needed to deliver
results in accordance with customers’ requirements and the organization's policies;
— Do: implement what was planned;
— Check: monitor and {where applicable} measure processes and the resulting productsand services
against policies, objectives and requirements and report the results:
— Act: take actions ta improve performance, as necessary.
0.3.3. Risk-based thinking
Risk-based thinking (See Clause A.4) is essential for achieving an effective quality management system,
‘The concept af risk-based thinking has been implicit in previous editions of this International Standard
including, for example, carrying out preventive action to eliminate potential nonconformities, analysing,
‘any nonconformities that do occur, and taking action to prevent recurrence that is appropriate far the
fects af the nonconfarmity,
‘To conform to the requirements of this International Standard, an organization needs te plan and
plement actions to address risks and opportunities. Addressing both risks and opportunities
establishes a basis for increasing the effectiveness of the quality management system, achieving
improved results and preventing negative effects,
‘Opportunities canariseas a result ofa situation favourable to achieving an intended result, fer example,
a set of circumstances that allow the organization to attract customers, develop new products and
services, reduce waste or improve productivity. Actions to address opportunities can also include
ccansideration af associated risks. Risk is the effect of uncertainty and any such uncertainty can have
positive or negative effects. A positive deviation arising froma risk can pravidean opportunity, but not
all positive effects of risk result in opportunities.
0.4 Relationship with other management system standards.
This International Standard applies the framework developed by ISD to improve alignment among its
International Standards for management systems (see Clause A.1),
‘This International Standard enables an organization to use the pracess approach, coupled with the
POCA cycle and risk-based thinking, to align or integrate its quality management system with the
requirements of other management system standards,
‘This International Standard relates to ISO 9G00 and ISO 9004 as follows:
— 180 9000 quality management systems — Fundamentals and vocabulary provides essential
background for the proper understanding and implementation of this International Standard;
— 150 9004 Managing for the sustained success of an arganization — A quality management approach
provides guidance for organizations that choose to progress beyond the requirements of this
International Standard,
Annex B pravides details af other International Standards on quality management and quality
management systems that have heen develaped by ISO/TC 176,
This International Standard does not include requirements specific to other management systems, such as
‘hose for environmentalmanagement, occupational health and safety management, or financialmanagement,
Sector-specifie quality management system standards based on the requirements of this International
Standard have been developed fora number of sectors, Some of thes standards specifyadsiittonal quality
‘management system requirements, while others are limited to providing guidance to the application of
this International Standard within the particular sector,
© 1502015 All rights reser ix
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
‘A matrix showing the correlation between the clauses ofthis edition ofthis International Stanclard and
the previous edition (ISO 9001:2008) can be found on the IS/TC 176/SC 2 open access web site at:
swwon.iso.org ftcl?6/sc02/public.
x (© 180 2015 lt gee reserved
FINAL DRAFT INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. 180/FDES 9001:2015(E)
Quality management systems — Requirements
1 Scope
This International Standard specifies requirements for a quality management system when an
organization:
si) needstodemonstrate its ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer
and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements, and
b) aims to enhance customer satisfaction through the effective application of the system, including
processes for improvernent ofthesystem and theassurance of conformity tocustomerand applicable
statutory and regulatory requirements.
All the requirements of this International Standard are generic and are intended to be applicable to any
organization, regardless of its type or size, or the products and servires it provides.
NOTE1 In this International Standard, the terms “praduct* or "service" only apply to pruducts and services
Intended for, oF required by, a customnee.
NOTE2 Statutory andreguistory requirements can be expressed as legal requirements.
2 Normative references
The following dacuments, in whole or in part, are normatively referenced in this document and are
ipensable for its application. Far dated references, oily the edition cited applies. For undated
references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
150 9000-2015, Quality management systems — Fundamentals and vacabulary
3° Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this docuttent, the terms and definitions given in 1$0.9000:2015 apply.
4 Context of the organization
4.1 Understanding the organization and its context
‘The organization shall determineenternalandinternal issues thatare relevantteitspurposeandl its strategie
direction and thataffect itsability to achieve the intended result(s) offts quality management system.
‘The orgonization shall monitor and review information about these external and internal issues.
NOTE — Issues can include positive and negative factorsor conditions for consideration.
NOTE2 Understanding the external context can be facilitated by considering issues arlsing from le
technolonial.competitivs, market, cultural, sacial and economic environments, whether intsrnational, nation
regional er local,
NOTE3 Understanding che internal context can be facilitated by considering issues related to values, culture,
knowledge and performance of the organization,
© 1502015 All rights reserve 1
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties
Due totheir effect or potential effect on the organization's ability te cansistantly provide products and
services that meet customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements, the organization
shall determine:
8) the interested parties thatare refevant to the quality management system;
b)_ the requirements of these interested parties that are relevant to the qualfly management system,
‘The organization shall moniker and review informationabout these interested partiesand their relevant
requirements,
43. Determining the scope of the quality management system
‘The organization shall determine the bounties an appicabiliy oft quality mmanegernen system
ru establish ite scape.
‘When determining this scope, the organization shall consider:
8) the external and internal issues referred twin 4.1;
b)_ the requirements of retevant interested parties referred to in-4.2;
©). the products and services af the organization,
‘The organization shall apply all the requirements of this International Standard if they are applicable
within the determined scope of its quality management system.
‘The scope of the organization's quality management system shall be available and be maintained as
documented information. The scope shall state the types of products and services covered, and provide
justification for any requirement of this International Standard that the organization determines is not
applicable to the scope of its quality management system.
Conformity to this International Standard may only be claimed if the requirements determined as not
being applicable do not affect the organization's ability or responsibility to ensure the conformity ofits
products and services and the enhancement of customer satisfaction
4.4 Quality management system and its processes
44.1 The organization shall establish, implemient, maintain and continually improve a quality
management system, Including the processes needed and their interactions, in accardance with the
requirements of this International Standard.
‘The organization shall determine the processes needed for the quality management system and their
application throughaut the organization, and shal
a) determine the inputs required and the outputs expected from these processes;
b) determine the sequence and interaction ofthese pracessas;
1) determine and apply the criteria and methods (including monitoring, measurements and related
performance indicators) needed to ensure the effective operation and control of these processes;
1) determine the resources needed for these processesand entsure their availability;
1) assign the responsibilities and authorities for these processes;
f)_ address the risks and opportunities as determined in.accordance with the requirements of 61:
fg) evaluate these processes and implement any changes needed te erisure that these processes achieve
their intended results;
2 (© 80 2015 = Alt igh
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
h) improve the processes and the quality management system.
44.2 Tothe extentnecessary, the organization shall:
a) thalntain documented information to support the operation of its processes:
b)_retaindocumented information to have con fidence thatthe processesarebeing carried outas planned.
5 Leadership
5.1 Leadership and commitment
S.L1 General
‘Top management shall demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect to the quality
management system hy:
a) taking aecountability for the effectiveness of the quality management system;
b) ensuring that the quality policy and quality objectives are established for the quatity management
system and are compatible with the coatext and strategic direction af the organization;
©) ensuring the integratian of the qu:
business procesces;
management system requirements into the arganization’s
d) promoting the use of the proces approach and risk-based thinking;
©) ensuring that the resources needed fur the quality managementsystem are available;
1) communicating the importance of effective quality management and of conforming to the quality
‘management system requirements;
B) ensuring that the quality management system achieves its intended resul
bh) engaging, directing and supporting persons to contribute to the effectiveness of the quality
management system;
4) Promoting improvement;
1) supporting other relevant management roles to demonstrate their leadership as it applies to their
areas of responsibility.
NOTE Reference to “husinoss” in this International Standard can he interpreted broadly to mean thoue
activities that are core tathe purposes of the organization's existence. whethor the argankzation |s public, private,
for profit or nat farprafit.
5.1.2 Customer focus
‘Top management shall demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect ta customer focus by
ensuring that:
a) customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements are determined, understoad and
consistently met
b) the risks and opportunities that can affect conformity of products and services and the ability to
enhance customer satisfaction are determined and addressed:
©) thefocus on enhancing customer satisfaction is maintained.
© 1502015 All rights reser 3
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
5.2 Policy
52.1 Developing the quality policy
‘Top management shall establish, implement and maintain a quality policy that:
8) tsappropriate tothe purpose and context of the organization and supports its strategie direction;
b) provides.a framework for setting quality objectives;
1) includes'a commitment to satisfy applicable requirements;
4) Includes a commitment ta continual impeovernent ofthe quality management system,
52.2. Communicating the quality policy.
‘The quality policy shall
a) beavailable and be maintalned as documented information;
b) be carmmunicated, understoad and applied within the organization;
©. beavailable to relevant interested parties. asappropriate.
5.3. Organizational roles, responsibilities and authorities
‘Top management shall ensure that the responsibilities and authorities for relevant roles are assigned,
‘communicated and understoad within the organization,
‘Top management shall assign the responsibility and authority for
8) ensuring that the quality management system conforms to the requirements of this Internatienal
Standard;
b)__ ensuring that the processes are delivering their intended outputs;
reporting on the performance of the quality management system and on opportunities for
impravement (see 10.1), in particular to top management;
¢) ensuring the promotion of customer focus throughout the organtzation;
©) ensuring that the integrity of the quality management system is maintained when changes ta the
quality management system are planned and implemented.
6 Planning
61. Actionsto address risks and opportunities
6.1 Whon planning for the quality management system, the organization shall consider the issues
referred to in 4.1 and the requirements referred! to in .2 and determine the risks and opportunities that
ood tn headdrasced tn:
a) give assurance that the quality management system can achieve its intended result(s};
b) enhance desirable effects;
©) prevent, or reduce, undesired offerts;
d) achieve improvement,
4 (© 80 2015 = Alt igh
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
6.1.2 The organization shall plan:
a) actions to address these risks and opportunities;
b) how to:
1) Integrate and implement the actions Inve tts quallky management system processes (see 4,4);
2), evaluate the elfectiveness of these actions.
Actions taken to address risks and epportunities shall be proportionate to the potenti
‘canformity of products and services,
impact on the
NOTE 1 Options ta adress risks can inchade avoiding 18k, taking Fisk in order ti purse an sipportunity,
eliminating the risk source, changlag the likelthoad or consequences, sharing the risk, or retaining risk by
Injormed decision
NOTE2 — Opportunities can lead to the adoptionofnew practices, launching new products, opening new markets,
addressing new clients, builting partnerships, using new technology and other desirable and viable possibilities
to address the organization's or its customers’ needs.
62 Quality objectives and planning to achieve them
6.2.1 ‘The organization shall establish quality objectives at relevant functions, levels and processes
needed for the quality management system.
‘The quality objectives shall:
a) beconsistent with the quality policy:
b) bemeasurable;
6) take into account applicable requirements:
dd} berelevantto conformity of products and services.and to enhancement of customer satisfaction;
«) bemonitored:
f) becammunicated;
B) beupiated as appropriate
‘The organization shall maintain documented information on the quality objectives.
6.2.2 When planning how to achieve its quality objectives, the organization shall determine:
a) whatwill be done;
1b) what resources will be required:
©) who willie responsibte,
d) when it will be completed;
fe) how the results will be evaluated,
63° Planning of changes
‘When the organization determines the need for changes tothe quality management system, thechanges
shall be carried out in a planned manner (see 4.4),
© 1502015 All rights reser 5
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
‘The organization shall consider:
a) the purpose of the changes and their potential consequences;
b)_ the integrity of the quality management systom:
1) theavailability of resources;
) the allocation or reallocation of responsibilities and authorities,
7 Support
Resources
TAA General
‘The organization shall determine and provide the resources needed for the establishment,
implementation, maintenance and continual improversent of the quatity management system.
‘The organization shall consider:
a) the capabilities of and constraints on, existing internal resources;
b)_ whatneeds to he obtained from external providers.
7A2 People
‘The organization shall determineand provide the persons necessary forthe effective Implementation of
its quality management system and for the operation and control ofits processes,
744° Infrastructure
‘The organization shall determine, provide and maintain the Infrastructure necessary for the operation
of its processes and to achieve conformity af productsand services,
NOTE — Infrastructure-cam incite:
5} butldingsand assactated wtilities;
b) equipment, including hardware and software;
1) transportation resources:
dd) toform:
n and communication technology.
7.414 Environment for the operation of processes
‘The organization shall determine, provide and maittaln the env ironment necessary forthe operation of
its processes and to achieve conformity of products and services.
NOTE _Asuitableenvironment can be a combination of human and pliysical factors, such as:
8} social (e.g. non-discriminatory, calm, nen-confrantational);,
) psychological (e.g-stress-reducing, burnaut prevention, emotionally protective}:
©) physical fe temperature, heat, humidity, light, airflow, hygiene, noise),
“These Factors can differ substantially depending on the products and services provided.
6 (© 80 2005 = Alt rghgerosoevod
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
7.1.5 Monitoring and measuring resources
71.5. General
‘The organization shall determine and provide the resources needed to ensure valid and reliable results
when monitoring or measur ingis used to verify the conformity of productsand ser vices tarequirements.
‘The organization shall ensure that the resdurces provided:
8) aresultable for the speeifictype of monitaring and measurement activities being undertaken;
b) are maintained to ensure their continuing fitness for their purpose.
‘The organization shall retsin appropriate documented information asevidence of fitness for purpose of
the monitoring and measurement cesources.
7.15.2 Measurement traceability
When measurement traceability isa requirement, aris considered by the organizatLon to be an essential
part of providing confidence in the validity of measurement results, measuring equipment shail ber
8) calibrated or verified, or both, at specified intervals, or priartouse,against measurement standards
traceable to international or national measurement standards; when no suel standards exist, the
basis used for calibration or verification shall be retained as documented infarmation;
b) identified in order to determine thelr status;
©) safeguarded from adjustments, damage or deterioration that would invalidate the cal
and subsequent measurement results.
‘The organization shall determine if the validity of previous measurement results tras been adversely
affected when measuring equipment is ound to be unfit for is intended purpose, and shall take
appropriate action as necessary.
74.6 Organizational knowledge
‘The arganization shall determine the knowledge necessary for the aperation of its pracesses and to
achieve conformity of products and services.
This knowledge shall be maintained and he maile available to the extent necessary,
‘When addressing changing needs and trends, the organization shall consider its current knowledge and
determine how to acquire graccess any necessary additional knowledge and required updates.
NOTE 1 Organizational knowledge is knowledge specific to the organization itis gained ly experience. It is
Information that is used and shared ta achiovo tho organization's abjectives.
NOTE2 Organizational knowledge can be based om:
2) internal sources (e.g: intellertual property: Knowledge gained from experience; lessons learned from
failures and successful projects; capturing and sharing undacumented koowledge and experience: the resultsaf
improvements in prucesses, products and services):
),_etetnalsoureds (e.g stadards: academia: conferences: gathering knowledge trem customers orexterral
providers)
7.2 Competence
‘The organization shall:
8) determine the necessary competence of person{s) doing work wader its control that affects the
performance and effectiveness of the quality management system
© 1502015 All rights reserve 3
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
bb) ensunethatthese personsarecompetenton the basis ofappropriate education, training, orexperlence;
1 where applicable, take actions to acquire the necessary competence, and evaluate the effectiveness
ofthe artions taken;
dd) retain appropriate documented information as evidence of competence.
Nore ___Apmleaie ations cn include fr exami the posto af trang to, the mentoring for he re
‘assignment of currently employed persons; or the hiring or contracting of competest persons,
7.3 Awareness
‘The onganization shall ensure that persons doing work under the organization's control are aware of:
8) the quality poliey;
b)_ relevant quality objectives;
9. theircontribution to the effectiveness of the quality management system, including the benefits of
improved performance;
4) the implications of not conforming with the quality management system requirements,
7.4 Communication
‘The organization shall determine the internal and external communications relevant to the quality
management system, including:
3) onwhat itwill communicate:
b) when to communicate;
with whom to eammunicate:
6) how tocommunicate;
©) who communicates,
7.8 Documented information
75.1 General
‘The organization's quality management system shatl include:
8) documented information required by this International Standard;
b) documented information determined by the organization as being necessary for Lhe effectiveness of
the quality management system.
NOTE The extent of documented information for a quality management system can ditfer from one
‘organtzation to another due to:
— the size af organization and its type of a
ities, processes, products and servis:
— the complexity of processes. and thetr interactions;
— the competence of persons,
a (© 80 2005 = Alt rghgerosoevod
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
7.5.2 Creatingand updating
‘When creating and updating decumented information, the organization shall ensure appropriate:
i) identification and deseription fe.g.a title, date, author ar reference number);
b) format (e.g. language, software version, graphics) and media (e.g, paper, electronic);
©) review-and approval for suitability and adequacy,
7.5.3 Control of documented information
7.5.31 Documented information required by the quality management system and by this International
Standard shall be controlled te ensure:
a) its availableand suitable for use, whereand when it is needed;
b) itis adequately protected (e.g, from lass of confidentislity, improper use, or loss of integrity).
7.5.3.2 For the control of documented information, the organization shall address: the following
activities, as applicable:
a) distribution, aceess, retrieval and use;
bb) storage and preservation, including preservation of legibility;
©) control of changes fe.g. version contral);
id) retention and disposition.
Documented information of external origin determined by the organizationto benecessary forthe planaing,
and operation of the quality management system shall be identified as appropriate, and be controlled.
Documented informa
retained as evidence of conformity shall be proterted from unintended alterations.
NOTE —_Ancess cam imply adecision regarding the permission ta view tie dacumentes
permission and authority to view and change the decumented information,
foemation any, or the
8 Operation
8.1 Operational planning and control
‘The organization shall plan, implement and control the processes (see 4.4) nevded to meet the
requirements for the provision of products and services, and to implement the actions determined in
Clause 6, by:
a) determining the requirements for the products and services:
bb) establishing criteria for:
1) the pracesses;
2). the acceptance of products-and services;
©) determining the resources needed taachiove conformity to the praductand service requirements;
id) implementing control of the processes in accordance with the criteria;
©) determining and keeping dacumented information to the extent necessary!
1) to have confidence that the processes have been carried outs planned;
© 1502015 All rights reser 9
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
2), to demonstrate the conformity of praducts and services to their requirements.
NOTE “Keeping” implies both the maintatning and the retaining of documented information.
‘The outpat of this planning shall be suitable for the organization's operations.
‘The organization shall control planned changes and review the consequences of unintended changes,
taking action to mitigate any adverse effects, as necessary.
‘The organization shall ensure that outsourced processes are controtled (se 8-4),
8.2 Requirements for products and services
82.1 Customer communication
‘Communication with customers shall inetude:
8) providing information relating to products and services:
b} handling enquiries, contracts or orders, including changes:
obtaining customer feedback relating to products and services, including customer complaints;
d) handling or controlling customer property:
©) establishing specific requirements far contingency actions, when relevant.
82.2 Determining the requirements related to products and services
‘When determining the requirements for the products and services ta be offered to customers, the
organization shall ensure thats
8) the requirements for the productyand services are defined, including:
1) atiyapplicable statutory and regulatory requirements:
2). these considered necessary by the organization;
b)_ the organization can meet the claimsfar the products and services it offers.
&23 Heview of requirements related to products and services
82.3.1 The organization shall ensure that it has the ability to meet the requirements far products and
services to be offered to castomers, The organization shall conduct a review before committing to supply
products and services to a customer, to include:
5) requirements specified by the customer, including the requirements far delivery and post
delivery activities;
1b) requirements not stated by the customer, but necessary for the specified or intended use. when known:
requirements specified by the arganization;
)__ statutory and regulatory requirements applicable to the products atid services;
©) contract or order requirements differing fram those previously expressed.
‘The organization shall ensure that contract ar order requirements differing fram those previously
defined are resolved.
10 (© 80 2005 = Alt rghgerosoevod
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
The custamer’s requirements shall be confirmed by the organization before acceptance, when the
customer does not provide a documented statement of their requirements,
NOTE — In-same situations, such as internet sales, a formal review is impractical for each order: Instead, the
review can cover relevant prouluct information, such as catalogues or advertising material,
8.2.3.2 The organization shail recain documented information, as applicable:
a) onthe results of the neviews
b) onany new requirements forthe products and services.
8.24 Changes to requirements for products and services
‘The organization shall ensurethat relevant documented information isamended, ane that relevant persons
aremade aware ofthechanged requirements, when the requirementsfor products and-servicesare changed.
8.3 Design and development of products and services
83.1 General
‘The organization shall establish, implement and maintain a design and development proves that is
appropziateto ensure the subsequent provision of products and services.
8.3.2 Design and development planning
Indetermining the stages and controls for design and development, the organization shall consider:
8) the nature, duration and complexity of the design and development activities;
b) the required process stages, including applicable design and development reviews;
©) the required design and development verification and validation activities;
d)_ the responsibilitiesand authoritiosinvolued in the desig
il development process;
©} the internal and external resource needs for the desipn and development of products and services;
£) theneed te control interfaces between persons involved in the design and development prucess;
g) the neod for involvement of custoniers and users in the design and develsipment process;
fh} the requirements for subsequent provisien of products and services;
1) the level at contro! expected for the design and development process by customers and other
relevant interested parties;
J} the documented information needed to demonstrate that design and development requirements
ave been met.
2.3.3 Design and development inputs
‘The organization shall determine the requirements essential for the specific types of praducts and
services to be designed and developed. The organization shall consider:
a) functional and performance requirements;
b)
©) statutory and regulatory requirements:
formation derived from previous similar design and development act
© 1502015 All rights reserve a
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
d) standards or codes of practice that the organization has committed to implement;
©) potential consequences of failure due ta the nature of the products.and services.
Inputs shall be adequate for design and development purposes, complete and unambiguous.
Conflicting design and development inputs shall be resolved.
‘The organization shall retain documented information an design and development inputs.
83.4 Design and development controls
‘The organization shall apply controls to the design and development process to ensure that:
a) the results to be achieved are defined;
b)_ reviews are conducted to evaluate the ability of the results of design and development co meot
requirements,
verification activities are conducted to ensure that the design and develapment outputs meet the
input requirements;
4) validation activities are conducted to ensure that the resulting products and services meet the
requirements For the specified application or intended use:
©) any necessary actions are taken on problems determined during the reviews, or verification and
validation activities;
1) documented information of these activities is retained.
NOTE Design and development reviews, verification and validation have distinet purposes. They can be
‘conducted separately or in any combination, asis suitable for the products and services of the organtzation.
&3.5 Design and development outputs
“The organization shall ensure that design and development outpots:
5) meet the input requirements;
b)_areadequate for the subsequent processes for the provision of products.and services:
‘9 includeorreference monitoringand measuring requirements, as appropriate, and acceptance criteria;
‘©. specifythe charaeteretics ofthe produstsand services that are essentia for their intended purpose
and their safe and proper provision,
‘The organization shall retain documented information on design and development outputs,
83.6 Design and development changes
‘The organization shall identify, review and control changes: made during, or subsequent to, the design
and development af products and services, to the extent necessary to ensure that there is no adverse
impact on conformity to requirements,
‘The organization shall retain documented informationan:
8) design and development changes:
b) theresults of reviews:
©). the authorization of the changes;
)__theactions taken to prevent adverse impacts
12 eso 20n enor
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
84 Control of externally provided processes, products and services
B41 General
‘The organization shall ensure that externally provided processes, products and serviews conform to
requirements.
‘The organization shal determine the controts to be applied to externally provided processes, products
and services when:
fi) products and services from external pravidersare intended farincorporatioa intatheargantration’s
own products and services:
b) products and services are provided directly to the customer(s) by external providers on behalf of
the organization;
©) a process, or part of a process, s provided by an external provider as a result of a decision by the
organization.
The organization shall determine and apply criteria for the evaluation, selection, monitoring of
performance, aid re-evaluation of external providers, based on their ability to provide processes or
Products and services in accordance with requirements, The organization shall retain documented
Information of these activities and any necessary actions arising from the evaluations,
84.2 Type and extent of control
‘The organization shall ensuré that externally provided processes, praducts and services do not
adversely affect the organization's ability to consistently deliver conforming products and services to
its customers.
‘The organization shall:
a} ensurethat externally provided pracessesremain within the contro ofits quality management system;
b) define both the controls that it intends to.apply to an external provider and those itintendsto apply
to the resulting output;
©) take into consideration:
1) the potential impact of the externally provided processes, products and services on the
organization's ability to consistently meet customer and applicable statutary and regulatory
requirements;
2). the effectiveness ufthe controls applied by the external provider;
determine the verification, or other activities, necessary to ensure that the externally provided
processes, products and services meet requirements.
8.4.4 Information for external providers
‘The organization shall ensure the adequacy af requirements prior ta their communication to the
external provider.
‘The rganization shall communicate to external providers its requirements for:
8) the processes, productsand services to be provid
b) theapproval
1) productsand services;
2) mothods, processes and equipment;
© 1502015 All rights reser 13
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
3). the release of products and services;
competence, including any required qualiticatian of persons;
1) the extornal providors' interactions with the organization;
©) coatroland monitoring of the external pruviders’ performance to be applied by the organization;
verification or validation activities that the orgamtization, oF tts customer, intends to perform at the
external providers’ premises.
@&5 Production and service provision
8.5.1 Control of production and service provision
‘The organization shall implement productian and service provision under controlled conditions.
Controlled conditions shall include, as applicable:
a) the availability of documented information that defines:
1) the characteristics nf the products to be produced, the services to be provided, oF the activities
to be performed;
2). the results to he achieved:
b)_ the availability and use of suitable monitoring and measuring resources:
the implementation of monitoringand measurementactivitiesat appropriate stages to verify that
criteria for control of processes or outputs, and acceptance criteria for products and services,
have been met:
4). theuse of'suitable infrastructure and environmont for the operation af processes:
©) the appointment of competent persons, including any required qualification;
the validation, and periadic revalidation, of the ability to achieve planned! results of the processes
for peaduction and service pravision, where the resulting autput cannot be verified by subsequent
monitoring or measurement:
8) the implementation ofactions tn prevent human error:
h) the implementation of release, delivery and post-delivery activities.
85.2 Identification and traceability
‘The organization shail use sultable means to identify outputs when it is necessary to ensure the
‘eonformity of products and services.
‘The organization shall identify the status of outputs with respect to- monitoring and measurement
requirements throughout peoductian and service provision,
‘The organization shalleontrol theunique identification ofthe outputs when traceability is «requirement,
and shall retain the documented information necessary to-enable traceability.
8.5.3 Property belonging to customers or external providers
‘The organization shall exercise care with property belonging to customers or external providers while
it is under the organization's control or being used hy the organization,
‘The organization shall identify, verify, protect and safeguard customers’ or external providers’ property
provided for use or incorporation into the praducts and services.
4 (© 80 2015 = Alt igh
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
When the property of a customer or external provider is lost, damaged or otherwise found to be
unsuitable for use, the organization shall report this to the customer or external provider and retain
documented information on what has occurred.
NOTE A customer's or excernal provider's property can include macerial, components, tools and equipment,
premises, intellectual property and personal data,
8.5.4 Preservation
‘The organization shall preserve the outputs during production and service pravision, to the extent
necessary to ensure conformity to requirements,
NOTE Preservation can include identification, ‘handling, contamination control, packaging, storage,
transmission or transportation, and protection,
85.5 Post-delivery activities
‘The organization shall meet requirements for postedelivery activities associated with the products
and servives,
Indetermining the extent of past-delivery activities that are required, the organization shall consider:
a) statutory and regulatory requirements;
b) the potential undesired consequences associated with its products and services,
©) the nature, use and intended lifetime of its produets and services;
4) customer requirements;
fe) customer feedback.
NOTE Post-delivery activities can include actions under warranty provisions. centractual obligations suchas
‘maintenance serviees, and supplementary services such as recycling or final disposal
4.5.6 Control of changes
‘The organization shall review and control changes for production or service provision, to the extent
hhecessary to ensure continulng conformity with requirements,
‘The organization shall retain dacumented information describing the results of the review of changes,
the person(s) authorizing the change, and any necessary actions arising from the review,
8.6 Release of products and services
‘The organization shall implement planned arrangements, at appropriate stages, to verify that the
product and service requirements have been met,
‘The release of productsand services to the customer shall not proceed until the planned arrangements
have boon satisfactorily completed, unless otherwiseapproved by arelevantauthority and,asapplicable,
by the customer.
The organization shall retain documented information an the retease of products and services. The
documented information shall include:
a) evidence of canformity with the acceptance criter
b} traceability to the person(s) authorizing the release.
© 1502015 All rights reser 15
ISO/FDIS 9001:2015(E)
87 Control of nonconforming outputs
87.1 Theorganization shall ensure that outputs that do not confarm tothelreequirements are identified
and controlled to prevent their unintended use ar delivery.
‘The organization shall take appropriate action base don the nature of thenonconformity andits effecton
the conformity of products and services. This shall alsa apply to nonconforming products and services
detected after delivery of products, during or after the pravision of services.
‘The organization shall deal with nonconforming outputs in one or more af the following ways;
8) correction:
b) segregation, containment, return or suspension of provision of products and services;
©) informing the customer;
6) obtaining authorization far acceptance under concession,
Confarmity to the requirements shall he verified when nonconforming outputs are corrected.
7.2. The organization shall retain documented information that:
a) describesthe nonconformity;
1b) descrihesthe actionstaken;
Q) describesany concessions obtained:
) identifies the authority deciding the action in respect of the nonconformity.
9 Performance evaluation
9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation
911 General
‘The organization shall determine:
a) What needs to he monitored and measured:
b)_ the methods for monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation needed to ensure valld results;
©). when the monitoringand measuring shall be performed:
id) when the results fram monitoring. and measurement shall he analysed and evaltiated
‘Theonganization shallevaluatethe performanceand the effectiveness ofthe quality management system.
‘The orgentzation shall retain appropriate documented information asevidence of the results
942 Customer satisfaction
‘The onganisatian shall manitor customers’ perceptions af the degree to which their needs and
‘epectations have been fulfilled, The organization shall determine the methods for obtaining, monitoring
and reviewing this information.
NOTE Examples of monitoring customer perceptions can inchule customer surveys, customer feedback on
delivered products and services, meetings with customers, marketshare analysts, compliments, warranty claims
and dealer reports.
16 (© 80 2015 = Alt igh
1SO/FDES 9001:2015(E)
9.1.3 Analysis and evaluation
‘The organization shall analyse and evaluate appropriate data and information arising from monitoring
and measurement.
‘The recults ef analysis shall be used teevaluate:
a) conformity of products and services;
b) the dopree of customer satisfaction;
©) the performance and effectiveness of the quality management system;
d)_ ifplanning has been implemented effectively;
©) the effectiveness of actionstaken to address risks and apportunities;
1) the performance af external providers;
8) the need for improvements tothe quality management system,
NOTE — Methodsto analyse data can include statistical techniques.
92 Internal audit
9.2.1 ‘The organization shall conduct internal audits at planned intervals to provide information on
‘whether the quality management system:
a) conforms to.
1) the organization's own requirements for its quality management system,
2) the requirements of this International Standard:
1b) is effectively implemented and maintained.
9.2.2 ‘The organivation shall
a) plan, establish, implement.and maintain an audit progeamme(s) tneluding the frequency, methods,
responsibilities, planning requirements and reporting, which shall take into consideration the
importance vf the processes concerned, changes affecting the organization, and the results of
Previous audits;
b) define the audit criteria.and scope for each audit;
©) select auditors and conduct audits to ensure objectivity and the impartiality of the audit process;
censure that the results of the audits are reported ta relevant management;
take appropriate correction and correctiveactinns without undue delay:
retain documented information as evidence of the implementation of the audit programme and the
audit results.
NOTE See 180 19011 for guidance.
© 1502015 All rights reserve 7
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Quality Management Principles and Practices Impact On The Companies' Quality PerformanceDocument11 pagesQuality Management Principles and Practices Impact On The Companies' Quality Performanceمختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- ISO Guide 30 2015Document9 pagesISO Guide 30 2015مختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- Design & Development ISODocument4 pagesDesign & Development ISOمختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- كورسDocument3 pagesكورسمختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- Design & Development ISODocument6 pagesDesign & Development ISOمختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- 9001 وﺰﻳﻵا مﺎﻈﻧو ةدﻮﺠﻟا Quality and ISO 9001 system يرﻮﻧ ﻲﻨﻏ ﺪﻴﻌﺳ د.اDocument5 pages9001 وﺰﻳﻵا مﺎﻈﻧو ةدﻮﺠﻟا Quality and ISO 9001 system يرﻮﻧ ﻲﻨﻏ ﺪﻴﻌﺳ د.امختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- Operational Procedures ISODocument11 pagesOperational Procedures ISOمختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- 7 Quality Management Principles ISO 9001 2015Document1 page7 Quality Management Principles ISO 9001 2015مختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- LD - POL - .320 CQI and IRCA Online Exams Reasonable Adjustment Policy v3 - 021123Document1 pageLD - POL - .320 CQI and IRCA Online Exams Reasonable Adjustment Policy v3 - 021123مختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- Flyer 3.1477549 1Document2 pagesFlyer 3.1477549 1مختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- Salerno KochanSalerno KochanDocument12 pagesSalerno KochanSalerno Kochanمختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 LA-Workshop ManualDocument54 pagesISO 9001 LA-Workshop Manualمختار حنفىNo ratings yet
- CQI and IRCA Online Exams IT Equipment and Systems Requirements PDFDocument3 pagesCQI and IRCA Online Exams IT Equipment and Systems Requirements PDFمختار حنفىNo ratings yet