0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views9 pages01 Prehistoric
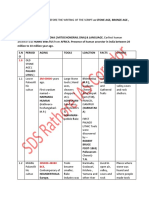
The Palaeolithic period in India began 500,000 years ago and lasted until 10,000 BC. Early humans such as Homo erectus used basic stone tools for hunting and lived in caves. The Middle Palaeolithic period saw the emergence of Homo sapiens as well as improved flake tools. During the Upper Palaeolithic period, Homo sapiens developed blade tools and created bone artifacts and ornaments. The Mesolithic period followed and was characterized by microlith tools and early rock paintings. In the Neolithic period, the development of polished stone tools and early agriculture emerged. The Chalcolithic period saw the beginnings of copper metallurgy alongside Neolithic practices.
Uploaded by
t4h56nkq9pCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views9 pages01 Prehistoric
The Palaeolithic period in India began 500,000 years ago and lasted until 10,000 BC. Early humans such as Homo erectus used basic stone tools for hunting and lived in caves. The Middle Palaeolithic period saw the emergence of Homo sapiens as well as improved flake tools. During the Upper Palaeolithic period, Homo sapiens developed blade tools and created bone artifacts and ornaments. The Mesolithic period followed and was characterized by microlith tools and early rock paintings. In the Neolithic period, the development of polished stone tools and early agriculture emerged. The Chalcolithic period saw the beginnings of copper metallurgy alongside Neolithic practices.
Uploaded by
t4h56nkq9pCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd