0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views11 pagesMyringotomy
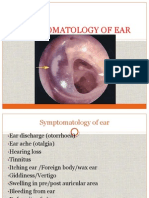
Myringotomy is a surgical incision into the eardrum to relieve pressure and drain fluid from the middle ear. It is indicated for acute or recurrent otitis media with a bulging eardrum, otitis media with effusion, and aero-otitis media. Contraindications include signs of a middle ear mass or vascular anomaly. Complications can include further middle ear infection, injury to the incudostapedial joint or stapes causing hearing loss, or injury to a high jugular bulb causing bleeding.
Uploaded by
shaheer HassanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views11 pagesMyringotomy
Myringotomy is a surgical incision into the eardrum to relieve pressure and drain fluid from the middle ear. It is indicated for acute or recurrent otitis media with a bulging eardrum, otitis media with effusion, and aero-otitis media. Contraindications include signs of a middle ear mass or vascular anomaly. Complications can include further middle ear infection, injury to the incudostapedial joint or stapes causing hearing loss, or injury to a high jugular bulb causing bleeding.
Uploaded by
shaheer HassanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd