0% found this document useful (0 votes)
180 views2 pagesOSCE Shoulder Examination Checklist
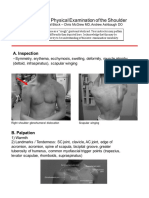
The document provides a checklist for examining a patient's shoulder, including 30 steps to systematically evaluate the shoulder through inspection, palpation, and assessing active and passive range of motion. Special tests are also described to further assess specific structures like the supraspinatus, biceps, and rotator cuff. The examination is completed by summarizing findings, suggesting additional assessments as needed, and thanking the patient.
Uploaded by
Kerlida SantosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
180 views2 pagesOSCE Shoulder Examination Checklist
The document provides a checklist for examining a patient's shoulder, including 30 steps to systematically evaluate the shoulder through inspection, palpation, and assessing active and passive range of motion. Special tests are also described to further assess specific structures like the supraspinatus, biceps, and rotator cuff. The examination is completed by summarizing findings, suggesting additional assessments as needed, and thanking the patient.
Uploaded by
Kerlida SantosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd