Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Essay 2
Uploaded by
michellebest365Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Essay 2
Uploaded by
michellebest365Copyright:
Available Formats
Essay title: Hydrogen bonds and their importance within living organisms
Hydrogen bonding occurs within many biological processes that are essential for life. It is the
attraction between the partially positive hydrogen atoms and the partially negative oxygen
atoms. Due to it being a weak force, it is easily formed and broken. It is found in water
molecules, proteins and to stabilise DNA. For instance, hydrogen bonds form between water
molecules due to it being polar. The molecular structure contributes to its properties as it is
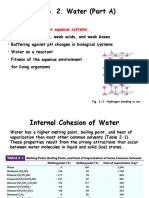
cohesive in the xylem of plants, it has a high latent heat of vaporisation as well as being a
good solvent and has a specific heat capacity meaning that a lot of energy would be needed
to raise the temperature of water which keeps the environment stable. When water is
heated, the bonds break which leads to the temperature of the water to rise. In addition,
water is involved in many other metabolic reactions such as waste removal, transporting
nutrients around the body, and maintaining body temperature. In biological molecules,
condensation reactions produce a water molecule during the formation of a bond and
hydrolysis breaks a bond by using a water molecule.
The polynucleotide molecule DNA had two antiparallel strands held together by hydrogen
bonds. It helps in stabilising its structure between the nitrogenous base pairs known as
complementary base pairing. The base Adenine pairs with Thymine and two hydrogen bonds
are formed between them whereas Guanine and Cytosine have three bonds. The hydrogen
bonds influence how DNA takes its shape and how it interacts with other molecules.
However, during semi-conservative replication, the DNA strands unwind due to the enzyme
DNA Helicase which leads to the bond breaking between the complementary bases. DNA
Polymerase joins the adjacent nucleotides together during a condensation reaction.
In proteins, hydrogen bonding occurs in tertiary structures between the R groups whereas in
secondary structures, the bonds form between the amino acid and carboxyl groups. In alpha
helixes, the bond leads to the helical shape and the beta sheets leads to folding. The
hydrogen bonds help to maintain the shape of the protein which determines its function.
Proteins also contain other bonds such as ionic bonds and disulfide bridges however,
hydrogen bonds are the weakest and therefore can easily be broken.
You might also like
- U1, T1, Molecules, transport and health.Document34 pagesU1, T1, Molecules, transport and health.linjiachen932No ratings yet
- CAP 2Document19 pagesCAP 2Francesca PrevitaliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry AKUEB Notes (SLO Vise)Document31 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry AKUEB Notes (SLO Vise)Yusam Mo100% (1)
- Neuroplasticity Is The Brains Ablity To Change Throught The Course of LifeDocument3 pagesNeuroplasticity Is The Brains Ablity To Change Throught The Course of Life22wck69jbxNo ratings yet
- Importance of Water and Buffers in BiochemistryDocument44 pagesImportance of Water and Buffers in Biochemistryrosecel jayson ricoNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 According To BookDocument36 pagesUnit 01 According To BookRezaul karimNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Bonding: The Essence of Life and Its Applications in MedicineDocument25 pagesHydrogen Bonding: The Essence of Life and Its Applications in MedicineBlaze PathNo ratings yet
- Biological Roles of Water - Why Is Water Necessary For Life - Science in The NewsDocument17 pagesBiological Roles of Water - Why Is Water Necessary For Life - Science in The NewsJoel SteveNo ratings yet
- (Lec2 (Chemistry of The CellDocument38 pages(Lec2 (Chemistry of The Cellبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Almonte, Jaezelle V. (Biochem Homework)Document5 pagesAlmonte, Jaezelle V. (Biochem Homework)Jaezelle AlmonteNo ratings yet
- Water QuestionsDocument3 pagesWater QuestionsLouie BalouieNo ratings yet
- Acosta, Niel Task 5Document3 pagesAcosta, Niel Task 5Algrin AcostaNo ratings yet
- Proteins interact through molecular surfacesDocument4 pagesProteins interact through molecular surfacesPercival Castro CarpioNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Bonding As Basis For LifeDocument2 pagesHydrogen Bonding As Basis For LifeAbhishek LeveNo ratings yet
- Almonte, Jaezelle V. (Biochem Homework)Document5 pagesAlmonte, Jaezelle V. (Biochem Homework)Jaezelle AlmonteNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Chemistry of Life 1.1 - Introduction: Figure 1.1: The Earth As Seen From SpaceDocument53 pages1 - The Chemistry of Life 1.1 - Introduction: Figure 1.1: The Earth As Seen From SpaceYuv DSNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY WATERDocument10 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY WATERArvin Kim QuibingcoNo ratings yet
- Biology STPM Lower 6 Chapter 1Document9 pagesBiology STPM Lower 6 Chapter 1kmbej91% (11)
- BiologyDocument387 pagesBiologyAaron Wong100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 1 STPM Sem1Document12 pagesBiology Chapter 1 STPM Sem1Jia Hui100% (4)
- Molecular BiologyDocument21 pagesMolecular BiologyvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument14 pagesBio Notesmaryamrizwan888No ratings yet
- Revision Notes - Unit 2 Ocr Biology A-LevelDocument26 pagesRevision Notes - Unit 2 Ocr Biology A-Levelapi-275024237No ratings yet
- 2.1-2.6 Biology Review 1Document21 pages2.1-2.6 Biology Review 1Victoria FinolNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument11 pagesBiological MoleculesYasasmi GunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument93 pagesBio Moleculeselena farahNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Biochemistry: BiomoleculesDocument91 pagesAspects of Biochemistry: BiomoleculesGeo NalobNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Study GuideDocument69 pagesAP Biology Study GuideEllie GriffinNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument91 pagesBIOMOLECULESFurret MasterNo ratings yet
- Science in The News: Skip To ContentDocument25 pagesScience in The News: Skip To ContentUmar Farouq Mohammed GalibNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Fo SNSHHHKHKDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Fo SNSHHHKHKJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Biology Sem1 Chap3Document128 pagesBiology Sem1 Chap3iki292No ratings yet
- Stability of EnzymesDocument3 pagesStability of EnzymesRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Quiz 12 - Water Carbon Chemistry Carbohydrates LipidsDocument11 pagesBiology Quiz 12 - Water Carbon Chemistry Carbohydrates LipidsMafalda SeabraNo ratings yet
- 2.1.2 Biology Ocr ADocument16 pages2.1.2 Biology Ocr AFatima AfifiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Biological Molecules: SummaryDocument9 pagesChapter 2: Biological Molecules: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Water Definition: in The Gaseous PhaseDocument4 pagesWater Definition: in The Gaseous PhaseRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- s15 Miller Chap 2a LectureDocument19 pagess15 Miller Chap 2a LectureYannis ZoldenbergNo ratings yet
- The Biological Importance of WaterDocument2 pagesThe Biological Importance of WaterRenee RoSe100% (1)
- Biochemistry WaterDocument3 pagesBiochemistry WaterRory DrewNo ratings yet
- SMB 104 Introduction 1Document29 pagesSMB 104 Introduction 1Shem Peter Mutua MutuiriNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Chemical Principles: Properties of WaterDocument5 pagesBiology Notes: Chemical Principles: Properties of WaterMuhammad AkramNo ratings yet
- Why water has a high specific heat capacity and the importance of its unique propertiesDocument6 pagesWhy water has a high specific heat capacity and the importance of its unique propertiespangaroad200No ratings yet
- BiologijaDocument17 pagesBiologijaNebojša Filipović 3No ratings yet
- BIO Unit One BabyDocument77 pagesBIO Unit One Babybisma nadeemNo ratings yet
- T02 Quiz AssignmentDocument3 pagesT02 Quiz AssignmentJhon Rey LagosNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of LifeDocument4 pagesChemicals of LifeZoeNo ratings yet
- SSABAKRISTU CHEMICALS OF LIFEDocument30 pagesSSABAKRISTU CHEMICALS OF LIFEkitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- BSC 2010 UF NotesDocument54 pagesBSC 2010 UF NotesSabrina KornNo ratings yet
- 26 Inorganic and Organic CompoundsDocument6 pages26 Inorganic and Organic CompoundsMark Allein AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- 2223 Apb Unit 1 Chem HWDocument4 pages2223 Apb Unit 1 Chem HWMartha Kate MorrisonNo ratings yet
- How water interactions determine biomolecular structureDocument23 pagesHow water interactions determine biomolecular structureJoana Marie Gantuangco-MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 - Water & PhospholipidDocument8 pagesLecture-3 - Water & PhospholipidSahil MittalNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Basis of Life ExplainedDocument87 pagesThe Chemical Basis of Life ExplainedTiyasha SarkarNo ratings yet
- Core Module 3 Water': Distribution and Importance of WaterDocument5 pagesCore Module 3 Water': Distribution and Importance of WaterJayden NgoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet