Professional Documents
Culture Documents
File 745537160
Uploaded by
u18175113Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
File 745537160
Uploaded by
u18175113Copyright:
Available Formats
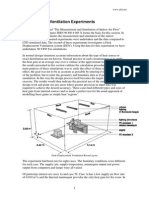
The Computational Fluid Dynamics( CFD) model is created using Ansys Workbench figure, in the
DesignModeller extension with the exact same confines as the real- life cardboard model of the structure.
Having the overall confines of 320 x 240 x 145 mm. The CFD model is also resolve into the four area as with
cardboard model, as depicted in figure 31 below. The heater is circled in red and is modelled as spherical
point with a periphery of 35 mm and a height of 50 mm. The dimension of the CFD model and its features
are the same as the experimental cardboard model, the door bay( door of the bedroom, area A) is 80 mm x
110 mm, the window bay( window of the chesterfield, area B) is 60 mm x 60 mm. The door outlet( this the
kitchen door, of area C) is a 50 mm x 110 mm and the window outlet( which is the restroom window) is a 35
mm x 50 mm. The interior door that leads to the restroom, area D is also 50 mm x 110 mm. The two scripts
that are dissembled for this structure design are show in figure 33 and 34 below, where the position of the
heater is at different locales within the envelope of the structure model. Figure 33 is script 1 where the heater
is placed in the bedroom, area A, in front of the door bay, same as the position of the heater as expressed in
figure x for script 1 of the trial. The same applies for script 2, the heater is placed in the kitchen, area C just
like how it's does for script 2 for the trial as seen in figure 34 These two simulation scripts will be used as a
confirmation process by comparing the results of the simulations results with those of the experimental
results. By validating these two results using one another, the conclusion on whether the trial and simulations
were executed duly can be drawn and whether or not the results attained are accurate andreliable.However,
the trial and simulations will be concluded to have been duly conducted and successful with accurate and
dependable results, If the results are analogous and have a closerelation.However, also the confirmation
process will be concluded to have been unprofitable with inconclusive results, If the results of the trial and
simulations are too different and don't show any correlation. Mathematical Models Using the immense pool
of information from once studies under section2.5 of the Literature study, the fine model consists of the
governing equations, turbulence models and the boundary conditions. For the simulations, the energy
equation is actuated during the set-up part of the Fluent Flow process. thus, the governing equation are those
of mass and instigation conservation and of the Reynold’s Average Navier- Stoke equations. The gravitational
effect is actuated at a magnitude of 9,81 m/ s2 acting down in the perpendicular direction, the perpendicular
direction is denoted by the z- axis on the model. The Renormalization Group of the k- Ꜫ turbulence model
appertained to as the RNG k- Ꜫ turbulence model with standard wall functions is enforced for the simulation.
This is because it’s the stylish suited turbulence model for simulations that have low Reynolds figures just
like this bone . The standard k- Ꜫ turbulence model can also be used for this case indeed those its more
accurate at high Reynolds figures. For the boundary conditions, the heat transfer is taken to do via forced
convection and thus, a heat transfer measure of 5,3 W/m2.K is applied. The fluid parcels, in this case of air
are kept constant and the fluid is assumed to be incompressible. The air speed used for the simulation is 2,6
m/ s which corresponds to the final addict speed. For the heater, a constant heat flux of 135 kW/ m2 is
applied. From section2.5 of the Literature study, it's known that the Numerical styles for a simulations using
CFD consists of the discretization scheme, numerical results, and confluence of the result. The simulations
will run at steady- state and the SIMPLE algorithm is used to grease the pressure- haste coupling. 1st order
discretization schemes are used for instigation, turbulent kinetic energy( k), turbulent dispersion energy( Ꜫ),
and also for the energy equation whilst pressure is formalized. For the result to meet, the values of the
regularized gauged residuals must be below 10(- 4) for the durability, instigation, and pressure equations. For
the energy equation the value of the residuals must be below 10(- 7) in order to achieve confluence of the
result at the end of the chosen number of duplications.
Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- Hollow Blocks Reduction - 2004Document10 pagesHollow Blocks Reduction - 2004jjrNo ratings yet
- File 823868060Document1 pageFile 823868060u18175113No ratings yet
- Open Foam Overview in Water TurbineDocument9 pagesOpen Foam Overview in Water Turbinehelmi_69No ratings yet
- Simulated Annealing: Basics and Application ExamplesDocument13 pagesSimulated Annealing: Basics and Application ExamplesRicardo Alejos100% (1)
- ADE 1D StabilityDocument6 pagesADE 1D StabilityMartin AntoNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design Tool for SF6 Gas Circuit BreakerDocument8 pagesOptimal Design Tool for SF6 Gas Circuit BreakermeraatNo ratings yet
- DeLaval NozzleDocument4 pagesDeLaval NozzlespolverinoNo ratings yet
- CFD and Low-Fidelity Model Optimization of Hypersonic Intake GeometryDocument12 pagesCFD and Low-Fidelity Model Optimization of Hypersonic Intake GeometryAhmad SalahNo ratings yet
- Documents - Pub - SPC 407 Supersonic Amp Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics AnsysDocument41 pagesDocuments - Pub - SPC 407 Supersonic Amp Hypersonic Fluid Dynamics Ansyssun rise1No ratings yet
- 3D CFD Displacement Ventilation ExperimentsDocument12 pages3D CFD Displacement Ventilation ExperimentsArun MaliNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of A Dynamic Model ForDocument13 pagesTheoretical and Experimental Investigation of A Dynamic Model ForCaio EstevesNo ratings yet
- Timothy Ganesan Paper A LAGRE EDDY SIMULATION (LES) CODE FOR TURBULENT FLOWS: VALIDATION AGAINST A TURBULENT FLOW AROUND A SINGLE SURFACE-MOUNTED CUBICLE OBSTACLE EXPERIMENT. Symposium (2008) - AccDocument8 pagesTimothy Ganesan Paper A LAGRE EDDY SIMULATION (LES) CODE FOR TURBULENT FLOWS: VALIDATION AGAINST A TURBULENT FLOW AROUND A SINGLE SURFACE-MOUNTED CUBICLE OBSTACLE EXPERIMENT. Symposium (2008) - Acctim.ganesan8668No ratings yet
- Optimum Temperature Gradients in Tubular Reactors-I: Olegh Bilocs NealDocument12 pagesOptimum Temperature Gradients in Tubular Reactors-I: Olegh Bilocs NealSandip LadvaNo ratings yet
- File 480147378Document1 pageFile 480147378u18175113No ratings yet
- Malaviya National Institute of TechnologyDocument42 pagesMalaviya National Institute of TechnologypavankeeralaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab Report'Izzad AfifNo ratings yet
- Natural Convection Square Cavity BenchmarkDocument16 pagesNatural Convection Square Cavity Benchmarkjmms21No ratings yet
- One-Way Coupled Integral Boundary LayerDocument3 pagesOne-Way Coupled Integral Boundary Layerrahpooye313No ratings yet
- Integrating CFD and Building SimulationDocument7 pagesIntegrating CFD and Building SimulationJoaquim MonteiroNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of Optimal Hardware CoolingDocument10 pagesCFD Analysis of Optimal Hardware CoolingAmjadRiazNo ratings yet
- CFD analysis of heat transfer in a 2D tube bundleDocument7 pagesCFD analysis of heat transfer in a 2D tube bundleShashank JhaNo ratings yet
- CFD Mini ProjectDocument11 pagesCFD Mini ProjectSujay PrabhatNo ratings yet
- CO2 Depressurisation OLGADocument8 pagesCO2 Depressurisation OLGAMaheshNo ratings yet
- Control de Procesos 2021 IIDocument7 pagesControl de Procesos 2021 IIBrayanNo ratings yet
- Design of Thermal Systems: Mr. S. V. Yadav Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument52 pagesDesign of Thermal Systems: Mr. S. V. Yadav Department of Mechanical EngineeringVishal BholeNo ratings yet
- Turbin99 IIDocument12 pagesTurbin99 IIKristijan HorvatNo ratings yet
- Parallel-Tempering Cluster Algorithm For Computer Simulations of Critical PhenomenaDocument5 pagesParallel-Tempering Cluster Algorithm For Computer Simulations of Critical Phenomenaedgemitter8049No ratings yet
- Shahirah-VLSI SystemDocument14 pagesShahirah-VLSI SystemELAYARAJA ARUCHUNANNo ratings yet
- Crispo Group Pin Fin ProjectDocument16 pagesCrispo Group Pin Fin Projectvince madroneroNo ratings yet
- A Theoretical Analysis and CFD Simulation On The Ceramic Monolith Heat ExchangerDocument12 pagesA Theoretical Analysis and CFD Simulation On The Ceramic Monolith Heat ExchangerMohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Electro-Thermal Simulation of Lithium Ion Battery For EV/HEV ApplicationsDocument11 pagesElectro-Thermal Simulation of Lithium Ion Battery For EV/HEV ApplicationsSagar PatilNo ratings yet
- 1.pdf 2 PDFDocument20 pages1.pdf 2 PDFMurtadha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Flat Plate Photovoltaic-Thermal (PVT) ModelsDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Flat Plate Photovoltaic-Thermal (PVT) ModelsWalamanNo ratings yet
- Lumped Single Mechanism PV Cell I-V ModelDocument2 pagesLumped Single Mechanism PV Cell I-V ModelFouad GhebriouNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Blade Temperatures Using Iterative Conjugate Heat TransferDocument4 pagesGas Turbine Blade Temperatures Using Iterative Conjugate Heat TransferMehdi TaherifarNo ratings yet
- High-Order Central ENO Finite-Volume Scheme with Adaptive Mesh RefinementDocument7 pagesHigh-Order Central ENO Finite-Volume Scheme with Adaptive Mesh RefinementAdriana SterlingNo ratings yet
- SenkinDocument26 pagesSenkinSudip AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Measuring saturation properties of waterDocument6 pagesMeasuring saturation properties of waterKalson UmpuNo ratings yet
- (Doi 10.1002/3527601996.ch13) Wittig, Sigmar Vöhringer, Otmar Kim, Soksik - High Intensity Combustors - Steady Isobaric Combustion (DFG SF High-Int. Combust. O-BK) - Numerical Modelling of CombuDocument17 pages(Doi 10.1002/3527601996.ch13) Wittig, Sigmar Vöhringer, Otmar Kim, Soksik - High Intensity Combustors - Steady Isobaric Combustion (DFG SF High-Int. Combust. O-BK) - Numerical Modelling of CombuawarialocksNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Model For The Spatial Distribution of Temperature in A Motored DI Diesel EngineDocument17 pagesA Simplified Model For The Spatial Distribution of Temperature in A Motored DI Diesel EnginePariotis EfthimiosNo ratings yet
- Natural Convection Heat Transfer in Fluent CFDDocument24 pagesNatural Convection Heat Transfer in Fluent CFDAnwar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- J.p.holman Heat RansferDocument8 pagesJ.p.holman Heat RansferSerkan GecimNo ratings yet
- Generic Gas Turbine Combustor: Description of The CombustorDocument7 pagesGeneric Gas Turbine Combustor: Description of The CombustorStanley BoswellNo ratings yet
- The Mathematical Mode of Combined Drying Process Off Cherries With The Usage of Extra High Frequency Currents in Oscilatory Mode of Operation. SummaryDocument1 pageThe Mathematical Mode of Combined Drying Process Off Cherries With The Usage of Extra High Frequency Currents in Oscilatory Mode of Operation. SummaryElena RotariNo ratings yet
- Solar CollectorDocument9 pagesSolar CollectorMohamed Anas NafirNo ratings yet
- Advanced CFD Tools For Multi-Stage Turbine Analysis: AlgebraicDocument12 pagesAdvanced CFD Tools For Multi-Stage Turbine Analysis: AlgebraicEr M HnNo ratings yet
- PB2Document8 pagesPB2Thor L. LemmingerNo ratings yet
- CFD Calculations of S809Document8 pagesCFD Calculations of S809kubacrNo ratings yet
- A Compact Model For Heat Sinks With Experimental VerificationDocument6 pagesA Compact Model For Heat Sinks With Experimental VerificationVitorPlácidoNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Diameter Ratio For Alpha-Type Stirling EnginesDocument6 pagesOptimization of Diameter Ratio For Alpha-Type Stirling EnginesEmiliano VelázquezNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat RatioDocument5 pagesSpecific Heat RatioPaolo QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Report of Fluent Simulation of Aerofoil NACA 4412Document19 pagesReport of Fluent Simulation of Aerofoil NACA 4412احمد عبد المحمود100% (3)
- Solution of Steady-State, Convective Transport Equation Using An Upwind Finite Element SchemeDocument9 pagesSolution of Steady-State, Convective Transport Equation Using An Upwind Finite Element SchemechrissbansNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Low-Mach Number Gas Flame PropagationDocument10 pagesModelling of Low-Mach Number Gas Flame Propagationfrancesco_sm64No ratings yet
- Numerical and Experimental Study On Temperature Crossover in Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersDocument17 pagesNumerical and Experimental Study On Temperature Crossover in Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersRisto FilkoskiNo ratings yet
- Douglas Gomes-COBEM - Estendido - Rev - Com - 01Document8 pagesDouglas Gomes-COBEM - Estendido - Rev - Com - 01Douglas GomesNo ratings yet
- Factorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodFrom EverandFactorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodNo ratings yet
- The Future of Power Systems: Challenges, Trends, and Upcoming ParadigmsDocument16 pagesThe Future of Power Systems: Challenges, Trends, and Upcoming ParadigmsAndres ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Teach Empathy With LiteratureDocument3 pagesTeach Empathy With LiteratureSantiago Cardenas DiazNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Page 1 of 2 Sub Code: KEE302Document2 pagesTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Page 1 of 2 Sub Code: KEE302AvinäshShärmaNo ratings yet
- Effect of In-Store Shelf Spacing On PurchaseDocument20 pagesEffect of In-Store Shelf Spacing On Purchasesiddeshsai54458No ratings yet
- Abstract PracticeDocument4 pagesAbstract PracticerifqiNo ratings yet
- Sample Interview Questions – Promoting Diversity and InclusionDocument3 pagesSample Interview Questions – Promoting Diversity and InclusionLiah Piano-Beast UchihaNo ratings yet
- Design Steel Concrete Composite StructuresDocument1 pageDesign Steel Concrete Composite StructuresDinuSkyNo ratings yet
- An Approach To Predict The Failure of Water Mains Under Climatic VariationsDocument16 pagesAn Approach To Predict The Failure of Water Mains Under Climatic VariationsGeorge, Yonghe YuNo ratings yet
- Medical Imaging - Seminar Topics Project Ideas On Computer ...Document52 pagesMedical Imaging - Seminar Topics Project Ideas On Computer ...Andabi JoshuaNo ratings yet
- A320 - Command Upgrade - Trainee1 01 Jan 24Document19 pagesA320 - Command Upgrade - Trainee1 01 Jan 24Ankit YadavNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - A Perspective On TestingDocument41 pagesCh1 - A Perspective On TestingcnshariffNo ratings yet
- PTE - Template - Essay All TypesDocument8 pagesPTE - Template - Essay All TypeskajalNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 7 - CDDocument4 pagesPROBLEM 7 - CDRavidya ShripatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Mean and Variance of Discrete Random Variable: Grade 11 - Statistics & ProbabilityDocument26 pagesLesson 4: Mean and Variance of Discrete Random Variable: Grade 11 - Statistics & Probabilitynicole MenesNo ratings yet
- ApplicationDocument11 pagesApplicationKamal Ra JNo ratings yet
- ZFDC 20 1HDocument1 pageZFDC 20 1Hkentier21No ratings yet
- Other Books NewDocument136 pagesOther Books NewYashRaj ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of History as a Social ScienceDocument14 pagesNature and Scope of History as a Social SciencejustadorkyyyNo ratings yet
- Skills and Techniques in Counseling Encouraging Paraphrasing and SummarizingDocument35 pagesSkills and Techniques in Counseling Encouraging Paraphrasing and SummarizingjaycnwNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Bece Mock 2024Document6 pagesSocial Studies Bece Mock 2024awurikisimonNo ratings yet
- EDCO - Catalog - 8 - 2017 - Floor GrindingDocument64 pagesEDCO - Catalog - 8 - 2017 - Floor GrindinghrithikvNo ratings yet
- Equipment & Piping Layout T.N. GopinathDocument88 pagesEquipment & Piping Layout T.N. Gopinathhirenkumar patelNo ratings yet
- Phy 111 - Eos Exam 2015Document7 pagesPhy 111 - Eos Exam 2015caphus mazengeraNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide in The Preparation of Purchase Request (PR), Purchase Order (PO) and Other Related DocumentsDocument26 pagesQuick Guide in The Preparation of Purchase Request (PR), Purchase Order (PO) and Other Related DocumentsMiguel VasquezNo ratings yet
- Engine Cpta Czca Czea Ea211 EngDocument360 pagesEngine Cpta Czca Czea Ea211 EngleuchiNo ratings yet
- Facts About SaturnDocument7 pagesFacts About SaturnGwyn CervantesNo ratings yet
- SIKA Concrete Repair Site HandbookDocument24 pagesSIKA Concrete Repair Site HandbookkeesinvongNo ratings yet
- Danica Seleskovitch-Mariann A Lederer: Interpréter Pour TraduireDocument17 pagesDanica Seleskovitch-Mariann A Lederer: Interpréter Pour TraduireGarima KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Indiana University PressDocument33 pagesIndiana University Pressrenato lopesNo ratings yet
- Autonomy Necessity and Love by Harry FrankfurtDocument14 pagesAutonomy Necessity and Love by Harry FrankfurtjamesdigNo ratings yet