Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SPECILIZATION IN Cyber Security
Uploaded by
ASHISHCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SPECILIZATION IN Cyber Security
Uploaded by
ASHISHCopyright:
Available Formats
VEER MADHO SINGH BHANDARI
UTTARAKHAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY DEHRADUN
EFFECTIVE FOR 2021-22 BATCH
2ND YEAR TO 4TH YEAR
Eligible Branches to adopt as Specialization
1. B.Tech.- Computer Science & Engineering
2. B.Tech.- Electronics and Communication Engineering
3. B.Tech.- Electronics Engineering
Eligible branches to adopt specialization – CSE, ECE, Electronics Engineering Page 1
VEER MADHO SINGH BHANDARI
UTTARAKHAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY DEHRADUN
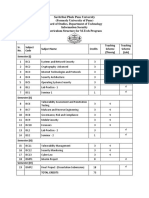
Evaluation Schemes for Specializations/Minor in B.Tech
Specialization in Cyber Security
Evaluation Scheme
Periods Total
S.N Code Sem Subject Marks Credits
L T P Internal External
1. 3rd Cyber Security and 3 0 0 50 100 150 3
SCS301 Investigati
on
Techniques
2. Cryptography and 3 0 0 50 100 150 3
SCS401 4th
Security Laws
3. SCS501 5th Risk Management 3 0 0 50 100 150 3
4. SCS601 6th Cyber Law 3 0 0 50 100 150 3
5. Risk Analysis And 3 0 0 50 100 150 3
SCS701 7th
Mitigation
6. Information 3 0 0 50 100 150 3
SCS801 8th
management
18 0 0 300 600 900 18
Eligible branches to adopt specialization – CSE, ECE, Electronics Engineering Page 2
VEER MADHO SINGH BHANDARI
UTTARAKHAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY DEHRADUN
L T P C
SCS301 CYBER SECURITY AND INVESTIGATION TECHNIQUES
3 0 0 3
Contents Hours
Unit 1 Introduction to Cyber Security: Overview of Cyber Security, Internet
Governance – Challenges and Constraints, Cyber Threats:- Cyber Warfare-Cyber
Crime-Cyber terrorism-Cyber Espionage, Need for a Comprehensive Cyber 8
Security Policy, Need for a Nodal Authority, Need for an International
convention on Cyberspace.
Unit 2 Cyber Security Vulnerabilities and Cyber Security Safeguards: Poor Cyber
Security Awareness. Cyber Security Safeguards- Overview, Access control,
Audit, Authentication, Biometrics, Cryptography, Deception, Denial of Service 8
Filters, Ethical Hacking, Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems, Response,
Scanning, Security policy, Threat Management.
Unit 3 Securing Web Application, Services and Servers: Introduction, Basic security for
HTTP Applications and Services, Basic Security for SOAP Services, Identity
8
Management and Web Services, Authorization Patterns, Security
Considerations, Challenges.
Unit 4 Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Intrusion, Physical Theft, Abuse of
Privileges, Unauthorized Access by Outsider, Malware infection, Intrusion
detection and Prevention Techniques, Anti-Malware software, Network based 8
Intrusion detection Systems, Network based Intrusion Prevention Systems, Host
based Intrusion prevention Systems,
Unit 5 Prevention Systems: Network based Intrusion Prevention Systems, Host based
Intrusion prevention Systems, Security Information Management, Network
Session Analysis, System Integrity Validation. Security Information
Management, Network Session Analysis, System Integrity Validation.
Suggested Readings:
1. Cyber Security: Power and Technology, by Martti Lehto, Pekka Neittaanmäki
2. Fundamental of Cyber Security: Principles, Theory and Practices, by Mayank Bhusan, Rajkumar
Singh Rathore, Aatif Jamshed
Eligible branches to adopt specialization – CSE, ECE, Electronics Engineering Page 3
VEER MADHO SINGH BHANDARI
UTTARAKHAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY DEHRADUN
L T P C
SCS401 CRYPTOGRAPHY AND SECURITY LAWS
3 0 0 3
Contents Hours
Unit 1 Cryptography and Network Security: Introduction to Cryptography, Symmetric
key Cryptography, Asymmetric key Cryptography, Message Authentication,
8
Digital Signatures, Applications of Cryptography. Overview of Firewalls- Types of
Firewalls, User Management
Unit 2 Security Protocols: VPN Security Security Protocols: - security at the Application
Layer- PGP and S/MIME, Security at Transport Layer- SSL and TLS, Security at 10
Network Layer-IPSec.
Unit 3 Cyberspace and the Law: Introduction, Cyber Security Regulations, Roles of
International Law, the state and Private Sector in Cyberspace, Cyber Security 8
Standards. The INDIAN Cyberspace, National Cyber Security Policy 2013.
Unit 4 Cyber Forensics: Introduction to Cyber Forensics, Handling Preliminary
10
Investigations, Controlling an Investigation, Conducting disk-based analysis,
Unit 5 Investigating Information-hiding: Investigating Information-hiding, Scrutinizing
E-mail, Validating E-mail header information, Tracing Internet access, Tracing 9
memory in real-time.
Suggested Readings:
1. Fundamental of Cyber Security: Principles, Theory and Practices, by Mayank Bhusan, Rajkumar
Singh Rathore, Aatif Jamshed
2. Cyber Security: Threats and Responses for Government and Business, by Jack Caravelli, Nigel Jones
Eligible branches to adopt specialization – CSE, ECE, Electronics Engineering Page 4
VEER MADHO SINGH BHANDARI
UTTARAKHAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY DEHRADUN
L T P C
SCS501 RISK MANAGEMENT
3 0 0 3
Contents Hours
Unit 1 Introduction risk management, elements of Credit Risk, outline and literature,
De_nition, market vs. credit Risk, The elements of credit risk: Default,
8
exposure, and loss given default (or recovery), Expected, unexpected loss, and
VaR, Credit exposure.
Unit 2 Pre-settlement and settlement risk, Measures of exposure, exposure pro_les,
12
Wrong-way and right-way risk, Models of Single Counterparty Default Risk.
Unit 3 Scoring, logit and probit, Ratings, Rating-based models: Credit Metrics, Credit
8
Portfolio View, Default rates implied from bond prices.
Unit 4 Modeling Default and Recovery: Portfolio Models, Actuarial Approach:
Mortality tables, Credit Risk+, Asset return models, correlated Defaults and
8
Credit Metrics for portfolios.
Introduction to Copula distributions, Vasicek model of correlated defaults.
Suggested Readings:
1. Data Science For Cyber-security, by Adams Niall M, Heard Nicholas A, Rubin-delanchy Patrick, Turcotte
Mellisa
2. Research Methods for Cyber Security, by Thomas W. Edgar, David O. Manz
3. Cybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting ...
By Erdal Ozkaya
Eligible branches to adopt specialization – CSE, ECE, Electronics Engineering Page 5
VEER MADHO SINGH BHANDARI
UTTARAKHAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY DEHRADUN
L T P C
SCS601 CYBER LAW
3 0 0 3
Contents Hours
Unit 1 Introduction to cyber law : Evolution of computer Technology, emergence
of cyber space. Cyber Jurisprudence, Jurisprudence and law, Doctrinal
approach, Consensual approach, Real Approach, Cyber Ethics, Cyber 10
Jurisdiction, Cyber Laws of other countries: EU GDPR, PIPEDA
(Canada), etc.
Unit 2 Information technology Act : Overview of IT Act, 2000, Amendments in
2008/2013 and Limitations of ITAct, Legal Recognition of Electronic
Records, Legal Recognition of Digital Signature, Certifying Authorities,
12
Cyber Crime and Offences, Network Service Providers Li- ability,
Unit 3 Cyber law and related Legislation : Patent Law, Trademark Law,
Copyright, Software Copyright or Patented, Do- main Names and
Copyright disputes, Electronic Data Base and its Protection, IT Act and
Civil Procedure Code, IT Act and Criminal Procedural Code, Relevant
Sections of Indian Evidence Act, Relevant Sections of Bankers Book
10
Evidence Act, Relevant Sections of Indian Penal Code, Relevant Sections
of Reserve Bank of India Act, Law Relating To Employees And Internet,
Alternative Dispute Resolution, Online Dispute Resolution (ODR).
Unit 4 Electronic Business and legal issues : Legal issues in Evolution and
development in E-commerce, paper vs paper less contracts E-Commerce 8
models- B2B, B2C, E security.
Unit 5 Application area : Business, taxation, electronic payments, supply chain,
EDI, E-markets, Emerging Trends.
Suggested Readings :
1. Handbook of Cyber Laws, by Vakul Sharma,Macmillan, 2002.
2. Cyber Security: Power and Technology, by Martti Lehto, Pekka Neittaanmäki
3. Fundamental of Cyber Security: Principles, Theory and Practices, by Mayank Bhusan, Rajkumar
Singh Rathore, Aatif Jamshed
4. Cyber Security: Threats and Responses for Government and Business, by Jack Caravelli, Nigel
Jones
Eligible branches to adopt specialization – CSE, ECE, Electronics Engineering Page 6
VEER MADHO SINGH BHANDARI
UTTARAKHAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY DEHRADUN
L T P C
SCS701 RISK ANALYSIS AND MITIGATION
3 0 0 3
Contents Hours
Unit 1 An Introduction to Risk Management: Introduction to the Theories of Risk
8
Management; The Changing Environment; The Art of Managing Risks
Unit 2 The Threat Assessment Process: Threat Assessment and its Input to Risk
12
Assessment; Threat Assessment Method; Example Threat Assessment;
Unit 3 Vulnerability Issues: Operating System Vulnerabilities; Application
Vulnerabilities; Public Domain or Commercial Off-the-Shelf Software;
Connectivity and Dependence; Vulnerability assessment for natural disaster, 8
technological hazards, and terrorist threats; implications for emergency response,
vulnerability of critical infrastructures;
Unit 4 The Risk Process: What is Risk Assessment? Risk Analysis; Who is
8
Responsible?
Unit 5 Tools and Types of Risk Assessment: Qualitative and Quantitative risk
Assessment; Policies, Procedures, Plans, and Processes of Risk Management;
Tools and Techniques; Integrated Risk Management; Future Directions: The
Future of the Risk Management.
Suggested Readings :
1. Malcolm Harkins, Managing Risk and Information Security, Apress, 2012.
2. Daniel Minoli, Information Technology Risk Management in Enterprise Environments,
Wiley, 2009.
3. Andy Jones, Debi Ashenden ,Risk Management for Computer Security: Protecting Your
Network & Information Assets, , 1st Edition, Butterworth-heinemann, Elsevier, 2005.
4. Andreas Von Grebmer, Information and IT Risk Management in a Nutshell: A pragmatic
approach to Information Security, 2008, Books On Demand Gmbh.
Eligible branches to adopt specialization – CSE, ECE, Electronics Engineering Page 7
VEER MADHO SINGH BHANDARI
UTTARAKHAND TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY DEHRADUN
L T P C
SCS801 INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
3 0 0 3
Contents Hours
Unit 1 DATABASE MODELLING, MANAGEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT
Database design and modelling - Business Rules and Relationship; Java
database Connectivity (JDBC), Database connection Manager, Stored 8
Procedures. Trends in Big Data systems including NoSQL - Hadoop
HDFS, MapReduce, Hive, and enhancements.
Unit 2 DATA SECURITY AND PRIVACY
Program Security, Malicious code and controls against threats; OS level
8
protection; Security – Firewalls, Network Security Intrusion detection
systems. Data Privacy principles. Data Privacy Laws and compliance.
Unit 3 INFORMATION GOVERNANCE
Master Data Management (MDM) – Overview, Need for MDM, Privacy,
8
regulatory requirements and compliance. Data Governance –
Synchronization and data quality management.
Unit 4 INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE
Principles of Information architecture and framework, Organizing
8
information, Navigation systems and Labelling systems, Conceptual
design, Granularity of Content.
Unit 5 INFORMATION LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT
Data retention policies; Confidential and Sensitive data handling, lifecycle
management costs. Archive data using Hadoop; Testing and delivering
big data applications for performance and functionality; Challenges with
data administration.
Eligible branches to adopt specialization – CSE, ECE, Electronics Engineering Page 8
You might also like
- Google AnalyticsDocument13 pagesGoogle AnalyticsPaul S100% (1)
- Malita E-Commerce WebsiteDocument129 pagesMalita E-Commerce WebsiteMio Betty J. MebolosNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of InfoSec: Overview, Assets, Risks & ControlsDocument4 pagesFundamentals of InfoSec: Overview, Assets, Risks & ControlsVishaal TataNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information SecurityDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Information SecurityjamesNo ratings yet
- Cyberlaws and SecurityDocument1 pageCyberlaws and Security17001009023 HINGULA BHATNo ratings yet
- Computer Security and Audit Assurance SyllabusDocument23 pagesComputer Security and Audit Assurance Syllabus20-6214 Nani DandaNo ratings yet
- Sem720 17 18Document2 pagesSem720 17 18Reshma BasuNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security NotesDocument106 pagesCyber Security NotesBhure VedikaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security syllabusDocument1 pageCyber Security syllabusshubh1996sriNo ratings yet
- MTech - Syllabus - Final 2.0Document23 pagesMTech - Syllabus - Final 2.0prasathNo ratings yet
- Scheme and Detailed Syllabus: M.Tech. Cyber SecurityDocument8 pagesScheme and Detailed Syllabus: M.Tech. Cyber SecurityNeeraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument3 pagesCyber Securitysweta.jethava24460No ratings yet
- UG 4-1 R19 CSE SyllabusDocument33 pagesUG 4-1 R19 CSE SyllabusMasimukkala SunithaNo ratings yet
- Information SecurityDocument2 pagesInformation Securityvowafe1088No ratings yet
- MCSCB Cyber SecurityDocument16 pagesMCSCB Cyber SecurityKrishna Kumaran ThampiNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Computer Science & EngineeringDocument39 pagesDiploma in Computer Science & Engineeringamitsingh63051No ratings yet
- CCIDF_SyllabusDocument2 pagesCCIDF_SyllabusShameena Begum RCENo ratings yet
- Network and System Security Course OverviewDocument3 pagesNetwork and System Security Course OverviewVibhuNo ratings yet
- (R17A0526) Information Security Digital NotesDocument143 pages(R17A0526) Information Security Digital NotesPrafulla Durgadhar GawandeNo ratings yet
- CSS (Computer System Security)Document162 pagesCSS (Computer System Security)Ashmit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- PESIT Bangalore South Campus: 10Cs835-Information and Network SecurityDocument3 pagesPESIT Bangalore South Campus: 10Cs835-Information and Network SecurityhanuscribdNo ratings yet
- Pune University IS Tech. SyllabusDocument9 pagesPune University IS Tech. SyllabusPav TechnicalsNo ratings yet
- Final Year BTech CSE Syllabus 2022-23Document59 pagesFinal Year BTech CSE Syllabus 2022-23Utkarsha SutarNo ratings yet
- AI 403 Cyber Security and ForensicsDocument2 pagesAI 403 Cyber Security and Forensicssomnath.sinhaNo ratings yet
- Unit3 CryptographyDocument87 pagesUnit3 CryptographyRαndσm thíngsNo ratings yet
- MTech Information Security FINAL 10052018Document20 pagesMTech Information Security FINAL 10052018sirisha vNo ratings yet
- 4 Year 1 Semester SyllabusDocument9 pages4 Year 1 Semester SyllabusYasham GhalibNo ratings yet
- Unit1 RoshanJameelDocument104 pagesUnit1 RoshanJameelSarfirey GamersNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument3 pagesCyber SecuritySAMAY N. JAINNo ratings yet
- Jntuh College of Engineering Hyderabad Dept of Computer Science and EngineeringDocument4 pagesJntuh College of Engineering Hyderabad Dept of Computer Science and EngineeringsidNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Pilani Campus Instruction DivisionDocument3 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani Pilani Campus Instruction DivisionGuntaas SinghNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science & Engineering: Syllabus BookletDocument27 pagesDepartment of Computer Science & Engineering: Syllabus Bookletarjun.lnmiitNo ratings yet
- Title 5Document2 pagesTitle 5М. ЭнэрэлтNo ratings yet
- ISE - 7th Sem SyllabusDocument17 pagesISE - 7th Sem SyllabusPraveen TPNo ratings yet
- BLOCKCHAI SyllabusDocument27 pagesBLOCKCHAI SyllabusChennamadhavuni SahithiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19VioletNo ratings yet
- Cybersecuritybyajaydask 230102175458 D7aa4485Document25 pagesCybersecuritybyajaydask 230102175458 D7aa4485Ramani VadlaNo ratings yet
- CSE2008 SyllabusDocument2 pagesCSE2008 SyllabusABHAY POTLURI 20BCI0017No ratings yet
- IS - Unit-I - Foundations of Information SecurityDocument106 pagesIS - Unit-I - Foundations of Information SecurityManav WalunjNo ratings yet
- Pg-Diploma in Cyber Security PDFDocument15 pagesPg-Diploma in Cyber Security PDFKang DedeNo ratings yet
- Common Subjects-5Document1 pageCommon Subjects-5varsha guptaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security PlanDocument4 pagesCyber Security PlanAhmed Al-AntaryNo ratings yet
- CSE403 Network SecurityDocument2 pagesCSE403 Network SecurityrajatNo ratings yet
- unit-1-cs-191cse046jDocument21 pagesunit-1-cs-191cse046jTRB hubNo ratings yet
- 53 Cyber Forensics MinorDocument19 pages53 Cyber Forensics MinorPrasanna VNo ratings yet
- IIT Jammu Times Offers Post Graduate Diploma in Cyber Security - BrochureDocument22 pagesIIT Jammu Times Offers Post Graduate Diploma in Cyber Security - BrochureKhushal OzaNo ratings yet
- Course Content - Information Security PDFDocument13 pagesCourse Content - Information Security PDFAvaneet RanjanNo ratings yet
- Zhang2019 A Security Scheme For Intelligent Substation Communications Considering Real-Time PerformanceDocument14 pagesZhang2019 A Security Scheme For Intelligent Substation Communications Considering Real-Time Performanceedsonpaveli-1No ratings yet
- Cyber Security Fundamentals and PracticesDocument6 pagesCyber Security Fundamentals and PracticesAravind VbkNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security - (R20a898896202)Document75 pagesCyber Security - (R20a898896202)anketsarkar964No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 6Document6 pagesGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 6Parshw PatelNo ratings yet
- System SecurityDocument4 pagesSystem SecurityTanishka MayekarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - UCS005E-Information and Network SecurityDocument2 pagesSyllabus - UCS005E-Information and Network Security2BA17CS056 SANTHOSHNo ratings yet
- Department of Information Technology National Instiute of Technology SrinagarDocument11 pagesDepartment of Information Technology National Instiute of Technology SrinagarAMRITESHWAR MISHRANo ratings yet
- Syllabus BCA 6th SemDocument4 pagesSyllabus BCA 6th Semvk421622No ratings yet
- BSBC 604 InformationsecurityDocument1 pageBSBC 604 InformationsecuritySurinder YadavNo ratings yet
- Pis SyllabusDocument2 pagesPis SyllabusM.K BhaiNo ratings yet
- IT Information Security SyllabusDocument2 pagesIT Information Security SyllabuslekhaNo ratings yet
- BE - IT CBCS VII & VIII Syllabus - Information Security-CbitDocument2 pagesBE - IT CBCS VII & VIII Syllabus - Information Security-Cbitmuninder ITNo ratings yet
- CT702-N Cyber SecurityDocument4 pagesCT702-N Cyber SecurityDevanshNo ratings yet
- Hardware Supply Chain Security: Threat Modelling, Emerging Attacks and CountermeasuresFrom EverandHardware Supply Chain Security: Threat Modelling, Emerging Attacks and CountermeasuresBasel HalakNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 PipeDocument1 pageLab 6 PipeJordan Zu'biNo ratings yet
- Iot - Esp8266 - 1Document20 pagesIot - Esp8266 - 1Shobha HebballiNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - SrsDocument12 pagesLec 2 - SrsUsman YousafNo ratings yet
- Reduce Costs: Blockchain Can Potentially Improve Efficiency in Global Trade by Greatly ReducingDocument2 pagesReduce Costs: Blockchain Can Potentially Improve Efficiency in Global Trade by Greatly ReducingAbdallah BalahaNo ratings yet
- MAQUE - M1 (Information and Communications Technology pt.1)Document8 pagesMAQUE - M1 (Information and Communications Technology pt.1)Kenneth Laraño MaqueNo ratings yet
- Data Engineering Study PlanDocument4 pagesData Engineering Study PlanEgodawatta PrasadNo ratings yet
- Prelim Task Performance in Airline/Flight Operations ManagementDocument7 pagesPrelim Task Performance in Airline/Flight Operations ManagementJohn IgnacioNo ratings yet
- AIM KTDocument29 pagesAIM KTNikitha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Data ScienceDocument25 pagesLecture 2-Data ScienceAmal ObeidallhNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 (Networking)Document53 pagesChapter-6 (Networking)Nasis DerejeNo ratings yet
- Lucknow Public College: Gomti Nagar Lucknow Project Synopsis Library ManagementDocument16 pagesLucknow Public College: Gomti Nagar Lucknow Project Synopsis Library Managementsandhya singhNo ratings yet
- Personal StatementDocument2 pagesPersonal StatementMabrouq Muhammad MarzouqNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 19 Jan 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 19 Jan 2024sayanmjv1854No ratings yet
- Corporate Email Usage Policy TemplateDocument3 pagesCorporate Email Usage Policy Templateadnansensitive5057No ratings yet
- It App Notes Discussion - ExcelDocument10 pagesIt App Notes Discussion - ExcelChristine Mae MapatacNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Digital Twin Manufacturing FrameworksDocument12 pagesAssessment of Digital Twin Manufacturing Frameworksazaz 01No ratings yet
- Oracle RAC For Beginners: Murali VallathDocument18 pagesOracle RAC For Beginners: Murali VallathmdrajivNo ratings yet
- Mandapriyanka (7 0)Document3 pagesMandapriyanka (7 0)kmrulesNo ratings yet
- Odoorpc Documentation: Release 0.6.2Document54 pagesOdoorpc Documentation: Release 0.6.2tibyanNo ratings yet
- 817 Typography Comp Appl SQPDocument6 pages817 Typography Comp Appl SQPHardik NarangNo ratings yet
- Vs 1250 Certified Node Js Developer BrochureDocument5 pagesVs 1250 Certified Node Js Developer BrochuremaqindiaNo ratings yet
- Best Resources To Learn Statistics - Analytics VidhyaDocument7 pagesBest Resources To Learn Statistics - Analytics VidhyaAshishAmitavNo ratings yet
- Contact Centre CapabilityDocument2 pagesContact Centre CapabilityshyamchepurNo ratings yet
- IoT Based A Smart Home Automation System Using Packet TracerDocument7 pagesIoT Based A Smart Home Automation System Using Packet TracerIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Grek PDFDocument427 pagesGrek PDFeranistisNo ratings yet
- SYS600 - Communication Programming InterfaceDocument86 pagesSYS600 - Communication Programming InterfaceNguyen DucNo ratings yet
- Forensic Examination ReportDocument20 pagesForensic Examination Reportaxmedx522No ratings yet
- Hevo Data - AssignmentDocument8 pagesHevo Data - Assignmentmansoor.jNo ratings yet