Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FA 2022 Small Size Export
FA 2022 Small Size Export
Uploaded by
teyexes931Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FA 2022 Small Size Export
FA 2022 Small Size Export
Uploaded by
teyexes931Copyright:
Available Formats
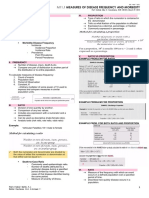
Public Health Sciences PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—Epidemiology and Biostatistics SECTION II 263
Precision vs accuracy
Precision (reliability) The consistency and reproducibility of a test. Random error precision in a test.
The absence of random variation in a test. precision standard deviation.
precision statistical power (1 − β).
Accuracy (validity) The closeness of test results to the true values. Systematic error accuracy in a test.
The absence of systematic error or bias in a test.
Accuracy Accuracy
High Low High Low
High High Low Low
Precision Precision
Incidence vs # of new cases Incidence looks at new cases (incidents).
Incidence = (per unit of time)
prevalence # of people at risk
# of existing cases (at a point in Prevalence looks at all current cases.
Recurrence Prevalence =
Total # of people time)
Incidence
in a population
Prevalence Prevalence
= Incidence rate × average duration
1 – prevalence of disease
Mortality Cure
Prevalence ≈ incidence for short duration disease Prevalence ∼ pretest probability.
(eg, common cold). prevalence PPV and NPV.
Prevalence > incidence for chronic diseases, due to
large # of existing cases (eg, diabetes).
SITUATION INCIDENCE PREVALENCE
survival time —
mortality —
Faster recovery time —
Extensive vaccine administration
risk factors
diagnostic sensitivity
New effective treatment started —
contact between patients with and — —
without noninfectious disease
contact between infected and
noninfected patients with airborne
infectious disease
FAS1_2022_06-PubHealth.indd 263 11/4/21 12:18 PM
264 SECTION II Public Health Sciences PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—Epidemiology and Biostatistics
Bias and study errors
TYPE DEFINITION EXAMPLES STRATEGIES TO REDUCE BIAS
Recruiting participants
Selection bias Nonrandom sampling Berkson bias—cases and/ Randomization (creates groups
or treatment allocation or controls selected from with similar distributions
of subjects such that hospitals (bedside bias) are of known and unknown
study population is not less healthy and have different variables)
representative of target exposures Ensure the choice of the right
population Attrition bias—participants lost comparison/reference group
Most commonly a sampling to follow up have a different
bias prognosis than those who
complete the study
Performing study
Recall bias Awareness of disorder alters Patients with disease recall Decrease time from exposure
recall by subjects; common in exposure after learning of to follow-up; use medical
retrospective studies similar cases records as sources
Measurement bias Information is gathered in a Using a faulty automatic Use objective, standardized,
systemically distorted manner sphygmomanometer and previously tested methods
Hawthorne effect—participants of data collection that are
change behavior upon planned ahead of time
awareness of being observed Use placebo group
Procedure bias Subjects in different groups are Patients in treatment group Blinding (masking) and
not treated the same spend more time in highly use of placebo reduce
specialized hospital units influence of participants and
Observer-expectancy Researcher’s belief in the An observer expecting researchers on procedures and
bias efficacy of a treatment changes treatment group to show signs interpretation of outcomes
the outcome of that treatment of recovery is more likely to as neither are aware of group
(also called Pygmalion effect) document positive outcomes assignments
Interpreting results
Confounding bias Factor related to both exposure An uncontrolled study shows Multiple/repeated studies
and outcome (but not on an association between Crossover studies (subjects act
causal path) distorts effect drinking coffee and lung as their own controls)
of exposure on outcome (vs cancer; however, people who Matching (patients with
effect modification, in which drink coffee may smoke more, similar characteristics in both
the exposure leads to different which could account for the treatment and control groups)
outcomes in subgroups association Effect modification—
stratified by the factor) association is shown
differently in individual
subgroups due to stratification
by given factor even when
there is association between
exposure and outcome
Lead-time bias Early detection interpreted as Breast cancer diagnosed early Measure “back-end” survival
survival, but the disease by mammography may (adjust survival according to
course has not changed appear to exaggerate survival the severity of disease at the
time because patients are time of diagnosis)
known to have the cancer for
longer
FAS1_2022_06-PubHealth.indd 264 11/4/21 12:18 PM
You might also like
- Pages From First Aid (USMLE Step1) (2019)Document6 pagesPages From First Aid (USMLE Step1) (2019)George Russell0% (1)
- Detailed Lesson PLan in Grade 9Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson PLan in Grade 9Jeremy Pomar82% (11)
- Epidemiologic Data MeasurementsDocument2 pagesEpidemiologic Data MeasurementsYhel TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Measures of Disease Frequency and MorbidityDocument5 pagesMeasures of Disease Frequency and MorbidityRav Evan VigillaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Frequency, Magnitude of Association and Impact in EpidemiologiDocument6 pagesMeasures of Frequency, Magnitude of Association and Impact in EpidemiologiHaris PrayitnoNo ratings yet
- Public Health FADocument22 pagesPublic Health FAsaurabhdhakedgNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Epidemiology: Didik Setiawan, PHD., AptDocument28 pagesBasic Principles of Epidemiology: Didik Setiawan, PHD., AptMisgi Candra DasaNo ratings yet
- DYNAMICS OF DISEASE TRANSMISSION - MPH - DHA - 2011 - EdtDocument71 pagesDYNAMICS OF DISEASE TRANSMISSION - MPH - DHA - 2011 - EdtTin WannNo ratings yet
- CPH LAB ScreeningDocument6 pagesCPH LAB ScreeningCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- ERIC Notebook: Common Measures and Statistics in Epidemiological LiteratureDocument5 pagesERIC Notebook: Common Measures and Statistics in Epidemiological LiteratureTrần Khải VănNo ratings yet
- Outline - Biostats Lec Extra Inputs by SirDocument4 pagesOutline - Biostats Lec Extra Inputs by SirGelaNo ratings yet
- Vital Statistical Rate and RatiosDocument2 pagesVital Statistical Rate and Ratioskoyilada jhahnaviNo ratings yet
- FA - Public Health ScienceDocument24 pagesFA - Public Health ScienceMargaret GraceNo ratings yet
- FA 2022 Small Size ExportDocument2 pagesFA 2022 Small Size Exportteyexes931No ratings yet
- 5 - MPH - Epidemiologic Measures - Lecturer - 20201108Document57 pages5 - MPH - Epidemiologic Measures - Lecturer - 20201108Nuuraine NasirNo ratings yet
- USMLE Epidemiology and BiostatisticsDocument30 pagesUSMLE Epidemiology and Biostatisticsamir ali100% (1)
- Epidemiology: Principles and Methods: Department of Public Health, Faculty of MedicineDocument31 pagesEpidemiology: Principles and Methods: Department of Public Health, Faculty of MedicinejibrilNo ratings yet
- of PHDDocument129 pagesof PHDHimanshu GargNo ratings yet
- Common Measures and Statistics in Epidemiological LiteratureDocument6 pagesCommon Measures and Statistics in Epidemiological LiteratureMayson BaliNo ratings yet
- Measure of Morbidity and MortalityDocument4 pagesMeasure of Morbidity and MortalityMosama fayyazNo ratings yet
- Environmental Epidemiology: AbbreviationsDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Epidemiology: AbbreviationsOsbelNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases 1Document12 pagesCommunicable Diseases 1Kristian Jane de JesusNo ratings yet
- EpidemologyDocument22 pagesEpidemologyVivek MahaleNo ratings yet
- 07 Penalaran Klinis, Perjalanan Alamiah PenyakitDocument54 pages07 Penalaran Klinis, Perjalanan Alamiah PenyakitANISA SUGIYANTINo ratings yet
- Vaccine Efficacy, Effectiveness and Impact: G. HANQUET, KCE, 9 September 2017Document21 pagesVaccine Efficacy, Effectiveness and Impact: G. HANQUET, KCE, 9 September 2017Ana-Mihaela BalanuțaNo ratings yet
- Incident vs. Prevalent Cases and Measures of OccurrenceDocument4 pagesIncident vs. Prevalent Cases and Measures of OccurrencebejarhasanNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology: Principles and Methods: Department of Public Health, Faculty of MedicineDocument31 pagesEpidemiology: Principles and Methods: Department of Public Health, Faculty of MedicineFatwa Dea Ramdani OctaviyasminNo ratings yet
- Vector Borne Diseases: Presentator: Atikah Najla RodhiahDocument15 pagesVector Borne Diseases: Presentator: Atikah Najla RodhiahTengku Mossadeq Al QornyNo ratings yet
- Measures of MorbidityDocument29 pagesMeasures of MorbidityJohnsonNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease EpidemiologyDocument25 pagesInfectious Disease Epidemiologykarki Keadr Dr100% (1)
- Foundation 1.2Document2 pagesFoundation 1.2ANDRIANNE FAGUTAONo ratings yet
- Epidemiology (Measurement of Morbidity)Document29 pagesEpidemiology (Measurement of Morbidity)zghkrgypnqNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Types of Epidemiology EditedDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Types of Epidemiology Editedfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- Disease Detectives NotesDocument4 pagesDisease Detectives NotesOwen LiuNo ratings yet
- Gen EpidemiologyDocument88 pagesGen EpidemiologyShibu Sebastian100% (1)
- Natural Immunity StudiesDocument43 pagesNatural Immunity StudiesT WootNo ratings yet
- EpidemiologyDocument67 pagesEpidemiologyChrystel Mae PañaresNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology (Ms. Palicpic)Document7 pagesEpidemiology (Ms. Palicpic)Royce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Epi & Biostats Review GuideDocument5 pagesEpi & Biostats Review GuideSamaneh Bolourchi100% (3)
- Epidemiology of Communicable DiseasesDocument3 pagesEpidemiology of Communicable Diseasessarguss14100% (4)
- Vaccine Vs Mutation COVID-19: Faiza HatimDocument37 pagesVaccine Vs Mutation COVID-19: Faiza HatimRosi AmaliaNo ratings yet
- DD Cheat Sheet 21-22Document2 pagesDD Cheat Sheet 21-22loki anshNo ratings yet
- Case Report Case Series Cross-Sectional EcologicDocument5 pagesCase Report Case Series Cross-Sectional EcologicWacky BlankNo ratings yet
- Bioe 211 - Screening and Public Health SurveillanceDocument3 pagesBioe 211 - Screening and Public Health Surveillancebabalegaspi09No ratings yet
- Definition, Approach, and Methods of Epidemiological Control of NCDDocument24 pagesDefinition, Approach, and Methods of Epidemiological Control of NCDAisyah Nabila PutriNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Related To Failure To Avoid Pathogen Secondary To Exposure To COVID-19Document2 pagesRisk For Infection Related To Failure To Avoid Pathogen Secondary To Exposure To COVID-19Yessamin Paith Roderos100% (1)
- Rates and Ratios EHSM Skills Helivar Palac TransDocument6 pagesRates and Ratios EHSM Skills Helivar Palac TransJohn Benedict BondocNo ratings yet
- Epido Copar CHNPDocument13 pagesEpido Copar CHNPSuzanne Kyla CabuenasNo ratings yet
- 02 - Epidemiological Indicators MeasuresDocument33 pages02 - Epidemiological Indicators MeasuresESSA GHAZWANINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Infectiongeorgeborja414726100% (3)
- 4 - Analytical EpidemiologyDocument20 pages4 - Analytical EpidemiologyMuhammad Zubair Bhutta100% (1)
- Presentation On Epidemiology StudiesDocument14 pagesPresentation On Epidemiology Studiesmsufdar9No ratings yet
- Natural Immunity StudiesDocument42 pagesNatural Immunity StudiesThomas WootersNo ratings yet
- 7 DR Armyn Surveillance in DisasterDocument59 pages7 DR Armyn Surveillance in DisasterMuhammad Nur DelaphanEnamNo ratings yet
- Epidemiologic MeasurementsDocument7 pagesEpidemiologic MeasurementsHadeel A. AlkayedNo ratings yet
- Measurements in EpidemiologyDocument2 pagesMeasurements in EpidemiologyJoanne JardinNo ratings yet
- The Dynamics of Disease TransmissionDocument18 pagesThe Dynamics of Disease TransmissionJ MNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients: A practical approachFrom EverandInfectious Diseases in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients: A practical approachOriol ManuelNo ratings yet
- Particle emission concept and probabilistic consideration of the development of infections in systems: Dynamics from logarithm and exponent in the infection process, percolation effectsFrom EverandParticle emission concept and probabilistic consideration of the development of infections in systems: Dynamics from logarithm and exponent in the infection process, percolation effectsNo ratings yet
- English in Urgent Care Medicine – Anglictina V Urgentní Medicíne: Textbook – UcebniceFrom EverandEnglish in Urgent Care Medicine – Anglictina V Urgentní Medicíne: Textbook – UcebniceNo ratings yet
- Jurnal LapasDocument7 pagesJurnal LapasHps DayatNo ratings yet
- OC Set B NEWDocument18 pagesOC Set B NEWmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Assignment Pad104 DraftDocument15 pagesAssignment Pad104 DraftAnis MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Andariki AyurvedamDocument6 pagesAndariki AyurvedammurugangdNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Connecting Children With Nature - InfoSheet PDFDocument4 pagesBenefits of Connecting Children With Nature - InfoSheet PDFotiliaglamNo ratings yet
- Faisal Hossan - Introduction To Effective Caring - MJS - PPTDocument14 pagesFaisal Hossan - Introduction To Effective Caring - MJS - PPTJshadekNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Neuro Physiology and Anatomy Notes by DR of 2027-28Document91 pagesOsmosis Neuro Physiology and Anatomy Notes by DR of 2027-28tariq ullahNo ratings yet
- Explain The Interpretation of Hemoglobin Result (Low Indicator Result)Document5 pagesExplain The Interpretation of Hemoglobin Result (Low Indicator Result)Gede NgurahNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Schedule A Mock Interview at WWW - Eguru.oooDocument65 pagesVocabulary: Schedule A Mock Interview at WWW - Eguru.oooKavitha ManchikantiNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 2CK Notes With AdditionsDocument103 pagesUSMLE Step 2CK Notes With AdditionsLuong Anh100% (1)
- Cultural Management of BananaDocument42 pagesCultural Management of Bananaomag matalamNo ratings yet
- ParonikiaDocument5 pagesParonikiaNyimas Irina SilvaniNo ratings yet
- Dyskal em Ia: Rs Hana CharitasDocument11 pagesDyskal em Ia: Rs Hana Charitasdwi nugroho prastowoNo ratings yet
- Igcse Revision Discursive WritingDocument4 pagesIgcse Revision Discursive WritingAryaa MurarkaNo ratings yet
- Pneumothoraks Jurnal RadiologiDocument9 pagesPneumothoraks Jurnal RadiologiRachmi MerrinaNo ratings yet
- VISANNE - Obat Untuk EndometriosisDocument39 pagesVISANNE - Obat Untuk EndometriosisroykelumendekNo ratings yet
- Data Rawat Inap2Document152 pagesData Rawat Inap2Muhammad Aqiem MuttaqinNo ratings yet
- Arian Boci: IDU Abstract of STOP AIDSDocument2 pagesArian Boci: IDU Abstract of STOP AIDSAni KorcaNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Health System ReviewDocument132 pagesMalaysia Health System ReviewsriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument119 pagesIntroduction To PharmacologyYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Community Case StudyDocument67 pagesCommunity Case StudyKathleen Daban RagudoNo ratings yet
- Physician Assisted Suicide (Pros & Cons, Arguments For and Against, Advantages & Disadvantages of Euthanasia or Doctor-Assisted Suicice)Document5 pagesPhysician Assisted Suicide (Pros & Cons, Arguments For and Against, Advantages & Disadvantages of Euthanasia or Doctor-Assisted Suicice)Lyana MahaliNo ratings yet
- Strength & Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) : WebsiteDocument7 pagesStrength & Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) : WebsiteIvan VeriswanNo ratings yet
- Outpatient Asthma Management Without Rescue BronchodilatorsDocument4 pagesOutpatient Asthma Management Without Rescue BronchodilatorsHerald Scholarly Open AccessNo ratings yet
- HFDocument162 pagesHFOmar AyashNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal Reading SmaDocument182 pagesKumpulan Soal Reading SmaAry PutraNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOLOGYDocument69 pagesIMMUNOLOGYMoses DumbuyaNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric RoadsDocument15 pagesPiezoelectric RoadsraincanNo ratings yet
- Art:10.1007/s00464 016 4771 7Document176 pagesArt:10.1007/s00464 016 4771 7Radu MiricaNo ratings yet