Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHEM111 Week 16 Acid Chlorides Acid Anhydrides and Esters 1
CHEM111 Week 16 Acid Chlorides Acid Anhydrides and Esters 1
Uploaded by
Ace Arcega0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views21 pagesThis document discusses acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, esters, and inorganic acid derivatives. Acid chlorides are formed by replacing the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid with a chlorine atom. Acid anhydrides are formed from two carboxylic acid molecules bonded together after removal of a water molecule. Esters are formed by the reaction of alcohols with carboxylic acids or acid anhydrides. Inorganic acids such as sulfuric, phosphoric and nitric acids also form esters and derivatives when reacted with alcohols.
Original Description:
Chemistry 111 week 16 PDF
Original Title
CHEM111-Week-16-Acid-Chlorides-Acid-Anhydrides-and-Esters-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, esters, and inorganic acid derivatives. Acid chlorides are formed by replacing the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid with a chlorine atom. Acid anhydrides are formed from two carboxylic acid molecules bonded together after removal of a water molecule. Esters are formed by the reaction of alcohols with carboxylic acids or acid anhydrides. Inorganic acids such as sulfuric, phosphoric and nitric acids also form esters and derivatives when reacted with alcohols.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views21 pagesCHEM111 Week 16 Acid Chlorides Acid Anhydrides and Esters 1
CHEM111 Week 16 Acid Chlorides Acid Anhydrides and Esters 1
Uploaded by
Ace ArcegaThis document discusses acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, esters, and inorganic acid derivatives. Acid chlorides are formed by replacing the hydroxyl group of a carboxylic acid with a chlorine atom. Acid anhydrides are formed from two carboxylic acid molecules bonded together after removal of a water molecule. Esters are formed by the reaction of alcohols with carboxylic acids or acid anhydrides. Inorganic acids such as sulfuric, phosphoric and nitric acids also form esters and derivatives when reacted with alcohols.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
ACID CHLORIDES,
ACID ANHYDRIDES and ESTERS
ACID CHLORIDE
• An acid chloride is a carboxylic acid derivative in
which the —OH portion of the carboxyl group,
• Has been replaced with a —Cl atom.
• Thus, acid chlorides have the general formula:
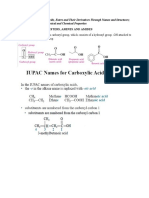
• Acid chlorides are named in either of two
ways:
• Rule 1: Replace the -ic acid ending of the
common name of the parent carboxylic
acid with -yl chloride.
• Rule 2: Replace the -oic acid ending of
the IUPAC name of the parent
carboxylic acid with -oyl chloride.
PREPARATION OF ACID
CHLORIDE
• Preparation of an acid chloride from its
parent carboxylic acid involves reacting
the acid with one of several inorganic
chlorides (PCl3, PCl5, or SOCl2).
• The general reaction is:
• Acid chlorides react rapidly with water,
in a hydrolysis reaction, to regenerate
the parent carboxylic acid.
• Acid chlorides are useful starting
materials for the synthesis of other
carboxylic acid derivatives, particularly
esters and amides.
• Synthesis of esters and amides using
acid chlorides is a more efficient
process than ester and amide synthesis
using a carboxylic acid.
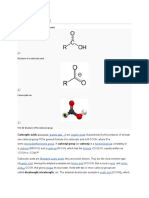
ACID ANHYDRIDES
• Structurally, acid anhydrides can be
visualized as two carboxylic acid
molecules bonded together after
removal of a water molecule from the
acid molecules.
• Symmetrical acid anhydrides both R groups
are the same) are named by replacing the
acid ending of the parent carboxylic acid
name with the word anhydride.
• Mixed acid anhydrides (different R groups
present) are named by using the names of
the individual parent carboxylic acids (in
alphabetic order) followed by the word
anhydride.
• In general, acid anhydrides cannot be formed by
directly reacting the parent carboxylic acids together.
• Instead, an acid chloride is reacted with a
carboxylate ion to produce the acid anhydride.
• Like acid chlorides, they cannot exist in
biological systems, as they undergo
hydrolysis to regenerate the parent
carboxylic acids.
• Reaction of an alcohol with an acid
anhydride is a useful method for
synthesizing esters.
ESTERS
and
ANHYDRIDES
OF
INORGANIC ACIDS
• Inorganic acids such as:
• Sulfuric, phosphoric, and nitric acids
react with alcohols to form esters in a
manner similar to that for carboxylic
acids.
• A phosphate ester is an organic
compound formed by reaction of an
alcohol with phosphoric acid.
PHOSPORIC ACID ANHYDRIDES
• Three biologically important phosphoric acids exist:
• Phosphoric acid, diphosphoric acid, and triphosphoric
acid.
• Phosphoric acid, the simplest of the three acids,
undergoes intermolecular dehydration to produce
diphosphoric acid.
• All three phosphoric acids undergo
esterification reactions with alcohols,
producing species such as:
• Structural similarities between a
carboxylic acid anhydride and
diphosphoric acid.
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry,: Alcohols, Ethers, EpoxidesDocument69 pagesOrganic Chemistry,: Alcohols, Ethers, EpoxidesilhamfaturachmanagusNo ratings yet
- 10carboxylic Acids Bengalan GlydelDocument43 pages10carboxylic Acids Bengalan GlydelAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingFrom EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument20 pagesCarboxylic AcidsAdam Callan-Sidat83% (6)
- Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines and AmidesDocument24 pagesCarboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines and AmidesAnyhaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other AcidDocument48 pagesCarboxylic Acids, Esters, and Other AcidDe Gala ShailynNo ratings yet
- Acid AnhydrideDocument19 pagesAcid AnhydridejbsorianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Carbohydrates HandoutDocument49 pagesChapter 4 Carbohydrates HandouthazimNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 18 - Carboxylic Acids andDocument43 pagesOrganic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 18 - Carboxylic Acids andPoorvKumarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 19 Carboxylic Acid & DerivativesDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 19 Carboxylic Acid & DerivativesZuhailimuna MudaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument13 pagesCarboxylic AcidJeremy NayagamNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic 2Document8 pagesCarboxylic 2johnsmithprayNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 CarbohydrateDocument79 pagesCHP 1 Carbohydrateستي نوراسيقينNo ratings yet
- Esters (Rcoor) : Prepared by DR Eslam RoshdyDocument17 pagesEsters (Rcoor) : Prepared by DR Eslam Roshdymohamedhosammds5No ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument15 pagesCarboxylic Acidsmadhu bonamNo ratings yet
- L4 - Acids, Esters and Its DerivativesDocument48 pagesL4 - Acids, Esters and Its DerivativesAlexNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesDocument9 pagesCarboxylic Acids and DerivativesGregory JohnNo ratings yet
- DAY 6 Carboxylic Acids For MCATDocument50 pagesDAY 6 Carboxylic Acids For MCATIan HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Importance of CarbohydrateDocument71 pagesImportance of CarbohydrateJasveen SainiNo ratings yet
- 2 CarbohydratesDocument88 pages2 CarbohydratesYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives PDFDocument12 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Derivatives PDFÏt's RîçkgãrçīäNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Aldehydes KetonesDocument16 pagesCarboxylic Acid Aldehydes KetonesNorman Rafael EspejoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Noor Ullah M.Phil Biochemistry& Molecular Biology Lecturer IPMS, KMUDocument45 pagesCarbohydrates: Noor Ullah M.Phil Biochemistry& Molecular Biology Lecturer IPMS, KMUharisNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument33 pagesCarboxylic Acidswelfred indinoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Ch104 Organic AcidsDocument111 pages2019 Ch104 Organic Acidsgenesis gengerNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, Preparation, Physical Properties, and Chemical ReactionsDocument22 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, Preparation, Physical Properties, and Chemical ReactionsDivyansh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - 07-08-2020Document7 pagesLecture 7 - 07-08-2020jaisypatel19No ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument30 pagesCarboxylic AcidsWaniya IrfanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.7 Carboxylic Acids & Their DerivativesDocument53 pagesChapter 2.7 Carboxylic Acids & Their Derivatives0JTINGNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument33 pagesCarboxylic AcidsLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNo ratings yet
- ALDEHYSES (Autosaved)Document46 pagesALDEHYSES (Autosaved)az713511No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Alcohols Ethers and EpoxidesDocument68 pagesChapter 9 Alcohols Ethers and EpoxidesLinearNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesCarboxylic Acid: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDipti BagdeNo ratings yet
- Structure of A Carboxylic AcidDocument7 pagesStructure of A Carboxylic AcidKajal SinghNo ratings yet
- Molecular Composition of CellsDocument92 pagesMolecular Composition of CellsJb PalmaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives.: Lecture Notes in Chem. 206 (Organic Chemistry II) Dr. Joel R. SalazarDocument53 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives.: Lecture Notes in Chem. 206 (Organic Chemistry II) Dr. Joel R. SalazarPaul Jhon EugenioNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Chemical Properties of Carboxylic AcidDocument12 pagesPreparation and Chemical Properties of Carboxylic AciddayhunterNo ratings yet
- LayoutDocument55 pagesLayoutHenok Moges KassahunNo ratings yet
- Ester: Organic Chemistry 2016Document21 pagesEster: Organic Chemistry 2016Huntal NapitNo ratings yet
- Further Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesFurther Organic ChemistryRobbing_HoodNo ratings yet
- Intro To Carbohydrates PDFDocument80 pagesIntro To Carbohydrates PDFJessie FixNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument39 pagesCarbohydratesjoicebalneg2003No ratings yet
- Ester: For Other Uses, SeeDocument15 pagesEster: For Other Uses, SeemeritnasaNo ratings yet
- 11acyl Halideisrael Jude P.Document16 pages11acyl Halideisrael Jude P.Angelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Carbohydartes Structure and Biological FunctionsDocument16 pagesModule 3: Carbohydartes Structure and Biological FunctionsMadhuri GuptaNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Reactions of EthersDocument54 pagesPreparation and Reactions of EthersEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesCarboxylic AcidVishu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Campbell6e Lecture Ch16Document38 pagesCampbell6e Lecture Ch16Shai Sta CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates&Nucleic Acids-GrbDocument71 pagesCarbohydrates&Nucleic Acids-GrbRamesh Babu GarlapatiNo ratings yet
- Introducing Carboxylic AcidsDocument24 pagesIntroducing Carboxylic AcidsRohini SelvarajahNo ratings yet
- Alkohol Eter EpoksidaDocument73 pagesAlkohol Eter EpoksidaGepsa AprilianaNo ratings yet
- Topic-Carbohydrates: Life'S Sweet Molecules Prepared By-Shweta BakshiDocument89 pagesTopic-Carbohydrates: Life'S Sweet Molecules Prepared By-Shweta BakshiDhyey PandyaNo ratings yet
- A 1Document29 pagesA 1Christopher WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10Document29 pagesChemistry 10Javed QasimNo ratings yet
- Cac Bo EngliDocument4 pagesCac Bo EngliLinh ĐồngNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument11 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsAmon RicoNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes & KetonesDocument27 pagesAldehydes & KetonesDe Gala ShailynNo ratings yet
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidFrom EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidNo ratings yet