Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zener Diode 1
Uploaded by
umar03029452584Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zener Diode 1
Uploaded by
umar03029452584Copyright:
Available Formats
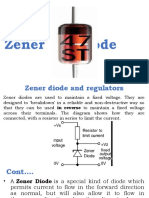
Zener Diode
A zener diode is a type of diode that conducts in both directions. In forward bias a zener diode behaves
exactly like a standard silicon diode. In reverse bias a zener diode will conduct and allow current to flow
when the applied voltage is greater than the zener voltage.
The zener voltage is a characteristic of a zener diode. Any given zener diode has a very specific fixed
zener voltage. Zener diodes are available in many different zener voltages ranging from 1.8 V up to
voltages in excess of 100 V.The maximum power handling is an important characteristic of a zener
diode. When current flows through a zener diode it dissipates energy and heats up. The power handling
of a zener diode determines how much power can be dissipated without damaging the zener diode
Zener diodes can be identified by the letter "Z" in the name or by having the zener voltage as part of the
name. For example a 1N4148 is a regular silicon diode whereas a BZX85c5v6 is a zener diode with a
zener voltage of 5.6 volts. In the image of zener diodes the blue and red examples are labelled 5v1 and
the smaller orange one is labelled BZX.
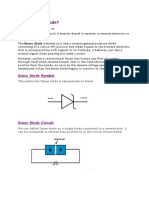
Forward Bias:
When the anode is connected to the battery positive the zener diode is forward biased and it
behaves in the same way as a silicon diode.The forward bias voltage across the zener diode is 0.7 V and
the potential difference across the 1 kΩ resistor is 5.3 V so that a current of 5.3 mA flows in the circuit.
You might also like
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- DiodeDocument13 pagesDiodeKarla MaalihanNo ratings yet
- A Zener Diode by Muhammad Arif RattarDocument2 pagesA Zener Diode by Muhammad Arif RattarMuhammad Arif RattarNo ratings yet
- The Zener DiodeDocument8 pagesThe Zener DiodemaanibrahimNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator and Its V-I CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator and Its V-I CharacteristicsRUPAM GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument13 pagesZener DiodePhenoमिनल IdiotsNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode 1Document1 pageZener Diode 1umar03029452584No ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument14 pagesZener DiodePrasanth. SNo ratings yet
- U-1 (Boe 8-18)Document11 pagesU-1 (Boe 8-18)Tisha SetiaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode ExplanationDocument6 pagesZener Diode ExplanationShubham SwamiNo ratings yet
- 3.zener DiodeDocument6 pages3.zener DiodethiliniNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument7 pagesZener DiodeMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Soumyadip Kalsa, Roll - 33, Sub - BiologyDocument13 pagesSoumyadip Kalsa, Roll - 33, Sub - BiologySMOKER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument3 pagesZener DiodeAMIT KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument15 pagesZener Diodeumar03029452584No ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode? Working Principle of Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode? Working Principle of Zener Diodepawan dhingraNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALANo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALANo ratings yet
- Dioda ZenerDocument2 pagesDioda ZenerGeorge TimpauNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument22 pagesZener DiodeRafath UmaimathNo ratings yet
- Diode - Definition, VI Characteristics, and Breakdown in Zener Diode - DiodeDocument8 pagesDiode - Definition, VI Characteristics, and Breakdown in Zener Diode - DiodehavejsnjNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeNeal John VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode - WikipediaDocument29 pagesZener Diode - WikipediaLupu DanielNo ratings yet
- What Is A Zener DiodeDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Zener DiodeSurendra PeddireddyNo ratings yet
- What Is A DiodeDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Diodedth dthNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode ProjectDocument16 pagesZener Diode ProjectJsmBhanot83% (6)
- Edger ChamiDocument17 pagesEdger ChamilekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Zenerdiodes 150209070235 Conversion Gate02Document29 pagesZenerdiodes 150209070235 Conversion Gate02Pushkin RathoreNo ratings yet
- ZDDocument29 pagesZDVikram TomerNo ratings yet
- 02 Zenerdiodes PPT PRPDocument29 pages02 Zenerdiodes PPT PRPVarsha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeMD. Abdullah Al NomanNo ratings yet
- Be Unit-IiDocument12 pagesBe Unit-Iihenryhorrid384No ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument3 pagesZener Diodekanak-825262No ratings yet
- Zener Diode: - Nakul Tekade, Shubham RaksheDocument7 pagesZener Diode: - Nakul Tekade, Shubham RaksheMr. NacNo ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode?Document4 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode?Riaz IsraniNo ratings yet
- Edu Expansion Presentation (Circuits)Document16 pagesEdu Expansion Presentation (Circuits)nandinigupta613No ratings yet
- University Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation TechnologyDocument6 pagesUniversity Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technologyvishnu ramaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial PDFDocument11 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator Tutorial PDFGunda TejaNo ratings yet
- Electronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeDocument10 pagesElectronics-Tutorials - Ws-The Zener DiodeVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- Zenner DiodeDocument23 pagesZenner DiodeKrishanu NaskarNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesZener Diode: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaApri ZaldyNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diode in Reverse Bias Condition: Basic Types of DiodesDocument7 pagesSemiconductor Diode in Reverse Bias Condition: Basic Types of DiodesrahulNo ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode - Its Principle Working and Example UsageDocument21 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode - Its Principle Working and Example UsageferdinandNo ratings yet
- ZenerDocument3 pagesZenerTajatNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument1 pageZener DiodeArasu LoganathanNo ratings yet
- 3 Zener DiodeDocument16 pages3 Zener DiodeGurudevNo ratings yet
- ZenerDocument14 pagesZeneraravindh rhssNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode TheoryDocument7 pagesZener Diode TheoryCarlos IbaNo ratings yet
- ZenerDocument5 pagesZeneraravindh rhssNo ratings yet
- Se - Elec - Simlab - Exp-6 - Roll No-1Document3 pagesSe - Elec - Simlab - Exp-6 - Roll No-1Lester DsouzaNo ratings yet
- ZenerdiodeDocument10 pagesZenerdiodeChintala Thrinadh 21BEE1006No ratings yet
- CH4 Special-Purpose DiodesDocument28 pagesCH4 Special-Purpose DiodesAyesha TahirNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesZener Diode - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument36 pagesZener DiodeSurajguptarocks100% (1)
- The Zener Diode orDocument1 pageThe Zener Diode orLupu DanielNo ratings yet
- ZenerdiodesDocument12 pagesZenerdiodesImran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument8 pagesZener Diodekumar_9583No ratings yet
- Basic-Electronics TB 4PDocument27 pagesBasic-Electronics TB 4Pمحمد رافد حميد B/23No ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument7 pagesZener DiodeLuiza Raluca100% (1)
- Lab Task 2Document2 pagesLab Task 2umar03029452584No ratings yet
- Ict CoverDocument2 pagesIct Coverumar03029452584No ratings yet
- Zener DiodesDocument12 pagesZener Diodesumar03029452584No ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals-Lec-04Document8 pagesProgramming Fundamentals-Lec-04umar03029452584No ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals-Lec-05Document7 pagesProgramming Fundamentals-Lec-05umar03029452584No ratings yet
- University of Agriculture Appointment and Condition of Service StatuesDocument17 pagesUniversity of Agriculture Appointment and Condition of Service Statuesumar03029452584No ratings yet