Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Systems of The Human Body
Systems of The Human Body
Uploaded by
Arcee Tobillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
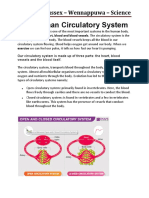
4 views2 pagesThe circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood contains plasma and blood cells, with plasma carrying nutrients and proteins, and blood cells including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The heart has four chambers separated by valves that ensure blood flows in one direction through the heart and body.
Original Description:
Original Title
SYSTEMS OF THE HUMAN BODY copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood contains plasma and blood cells, with plasma carrying nutrients and proteins, and blood cells including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The heart has four chambers separated by valves that ensure blood flows in one direction through the heart and body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesSystems of The Human Body
Systems of The Human Body
Uploaded by
Arcee TobilloThe circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through arteries, veins, and capillaries. Blood contains plasma and blood cells, with plasma carrying nutrients and proteins, and blood cells including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The heart has four chambers separated by valves that ensure blood flows in one direction through the heart and body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
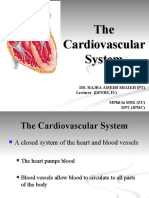
SYSTEMS OF THE HUMAN BODY
CIRCULATORY /CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
-blood
-blood vessels
-heart
An average human has about 5 liters (over a gallon) of blood.
Plasma makes up half of the content of blood.
Plasma contains the protein to prevent blood clot.
Plasma also contains glucose and other dissolved nutrients.
Half of the blood contains blood cells
Blood cells: red blood cells – carries oxygen to the tissues
white blood cells – fight infections
Platelets – smaller cells that help blood to clot
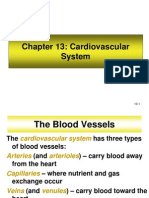
Blood Vessels:
arteries, veins, and capillaries
Arteries – carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
Veins – carry blood back to the heart
Capillaries – connect the arteries to the veins
Heart: Chambers, Valves, Vessels, Wall, Conduction System
Chambers – upper two chambers are called atria and the lower two are
called ventricles
Muscular Walls (septa or septum) – divides the heart into two sides
Valves:
tricuspid – between the right atrium and the right ventricle
pulmonary – between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery
mitral – between left atrium and left ventricle
aortic – between left ventricle and aorta
These valves open when blood passes through them and then close to
keep the blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
You might also like
- Anatomy Lec.6Document5 pagesAnatomy Lec.6aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument19 pagesCirculatory SystemСоня КропельницкаяNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PPT FeDocument26 pagesCardiovascular System PPT FeAngel Grace GaliasNo ratings yet
- BioDocument2 pagesBiokathlynanne.cadizNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDaniel PancuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SysDocument10 pagesCirculatory SysnaviNo ratings yet
- Biologia 3Document3 pagesBiologia 3Alejandro GraciaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary and Cardio SystemDocument7 pagesPulmonary and Cardio SystemEduardo Niepes Jr.No ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument7 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionRalph Emerson RatonNo ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory System Working With Other Organ SystemsDocument76 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory System Working With Other Organ SystemsNot allowedNo ratings yet
- SystemDocument63 pagesSystemBeth Rubin RelatorNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemNaiomiNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems Objective 2-1Document4 pagesTransport Systems Objective 2-1darielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- Medical Science Part 2Document21 pagesMedical Science Part 2Gauge FalkNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) Is A Condition in WhichDocument9 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) Is A Condition in WhichmelwuaniehNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascularsystem 090820055728 Phpapp02Document75 pagesCardiovascularsystem 090820055728 Phpapp02muhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Cardiovascular System: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth EditionDocument3 pagesChapter 12: Cardiovascular System: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth Edition117320No ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument9 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionRiazell Antonio DungcaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument3 pagesCirculatory System Noteshannah peloniaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) Is ADocument14 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) Is APaul John HipolitoNo ratings yet
- 3.4 - The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pages3.4 - The Circulatory SystemDjejNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Circulatory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Cardiovascular SystemDocument69 pagesChapter 13: Cardiovascular SystemFidaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Systemapi-297526590No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Systemurooj100% (1)
- 1 Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pages1 Cardiovascular SystemWaltz PadlanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System The Lymphatic System The Immune SystemDocument18 pagesThe Circulatory System The Lymphatic System The Immune SystemSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- القلبDocument11 pagesالقلبNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Biology Class NotesDocument1 pageBiology Class NotesSebastian RăileanuNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardio Vascular SystemguptaasitNo ratings yet
- Heart by Aritra SahaDocument15 pagesHeart by Aritra SahaAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument9 pagesCirculatoryJason Vinluan Carinan100% (1)
- CardiovascularDocument30 pagesCardiovascularKristine Joy Librando EscalanteNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Chapter 23 Section 1Document17 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Chapter 23 Section 1thegedusNo ratings yet
- The Human Circulatory System: Grade 9 - Sussex - Wennappuwa - ScienceDocument23 pagesThe Human Circulatory System: Grade 9 - Sussex - Wennappuwa - ScienceSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument44 pagesCirculatory SystemAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument20 pagesVascular SystemHama HamidNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument71 pagesCirculatory SystemAnas Mustafa HashmiNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument30 pagesCardiovascularBeverly LavillaNo ratings yet
- 2 CardioDocument26 pages2 Cardiorashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocument6 pagesCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular System 1 2Document19 pagesCardio Vascular System 1 2hamafron05No ratings yet
- Blood CirculationDocument8 pagesBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNo ratings yet
- Angelo Jhuan ScienceDocument2 pagesAngelo Jhuan ScienceGoldenaholicNo ratings yet
- A Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument10 pagesA Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseBarben Balaquit100% (1)
- Parts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsDocument47 pagesParts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsJasmin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Handouts Science and Health VI The HeartDocument3 pagesHandouts Science and Health VI The HeartjairaestrellaNo ratings yet
- احلام 1 PDFDocument7 pagesاحلام 1 PDFEhab Alaa Abd Al-AmeerNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (Circulatory System)Document18 pagesGen Bio (Circulatory System)Kit KathNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesCirculatory SystemYzza Veah Esquivel100% (2)
- Anatomy of CVSDocument22 pagesAnatomy of CVSAreej TariqNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Heart and Blood NotesDocument3 pagesHeart and Blood NotesarjaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartAnnNo ratings yet
- Research Questions-: How The Blood FlowsDocument5 pagesResearch Questions-: How The Blood FlowsAasritha SenagapallyNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet