10/23/2023
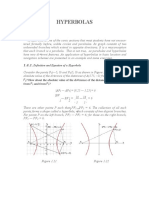
A hyperbola is the set of all points in a plane whose
difference of distances from two fixed points is constant.
The section of a right circular cone by a plane which is
parallel to the axis of a cone.
1
� 10/23/2023
FOCI - fixed points of the hyperbola. “c” distance from the center.
TRANSVERSE AXIS - the line passing through vertices and foci
CONJUGATE AXIS - the line through the center and
perpendicular to the transverse axis.
CENTER - the midpoint of the segment joining the foci.
VERTICES - the point of intersection of the hyperbola with the
transverse axis. “a” distance from the center.
CO-VERTICES – the points “b” distance from the center
LATUS RECTUM – a chord of the hyperbola through either focus,
perpendicular to the transverse axis and terminated by the curve.
CONJUGATE Hyperbola – the hyperbola oriented vertically.
RECTANGULAR Hyperbola – the hyperbola whose transverse axis
and conjugate axis are equal.
Asymptote – A line which the hyperbola will never crossed.
2
� 10/23/2023
Directrices
dPF1 ( x c)2 y 0 dPF 2 ( x c)2 y 0
2 2
P(x,y) PF ' PF 2a
( x c) 2 y 0 ( x c ) 2 y 0 2a
2 2
2a
2 2
( x c)2 y 2 ( x c) 2 y 2
x 2 2cx c 2 y 2 4a 2 4a ( x c ) 2 y 2 x 2 2cx c 2 y 2
4cx 4a 2 4a ( x c) 2 y 2
cx a 2 a ( x c) 2 y 2
cx a
2
2 2
a ( x c)2 y 2
c 2 x 2 2a 2 cx a 4 a 2 x 2 2cx c 2 y 2
c 2 x 2 2a 2 cx a 4 a 2 x 2 2a 2 cx a 2 c 2 a 2 y 2 Dividing both sides by a2b2
c 2 x 2 a 2 x2 a 2 y 2 a 2c 2 a 4
b 2 x 2 a 2 y 2 a 2b 2
c 2
a 2
x 2
a y a c a
2 2 2 2 2
a 2b 2
2 2
ab
Note : b2 c2 a2
c 2
a2 x2 a2 y2 a2 c2 a2 Theequation of the hyperbola:
b 2 x 2 a 2 y 2 a 2b 2
x2 y 2
1
a2 b2
3
� 10/23/2023
( 0,0)
Horizontal Vertical
x2 y 2 y 2 x2
Equation: 2 2 1 Equation: 2 2 1
a b a b
4
� 10/23/2023
( , )
Horizontal Vertical
x h y k y k x h
2 2 2 2
Equation: 1 Equation: 1
a2 b2 a2 b2
x2 y2 y2 x2 x h y k y k x h
2 2 2 2
Equation: 1 1 1 1
a2 b2 a2 b2 a2 b2 a2 b2
Orientation: Horizontal Vertical Horizontal Vertical
Center: 0,0 0,0 h, k h, k
Vertices: a,0 0, a ha, k h, k a
Co-vertices: 0, b b,0 h, k b hb, k
Foci: c,0 0, c hc, k h, k c
Endpoints of b2 b2 b2 b2
LR: c, , c h c, k h , k c
a a a a
a a a a
Directrices: x y x h y k
e e e e
5
� 10/23/2023
Find the vertices, foci, eccentricity, the equation of
Example 1 the asymptotes, the length of the latus rectum, and
sketch the graph of the hyperbola 4 y 9 x 36 .
2 2
Solution: Transform the given equation of the hyperbola to standard form.
y2 x2
4 y2 9x2 36 1
9 4
Transverse axis is on the y-axis:
a2 9 a 3 b2 4 b 2
Center: 0,0
Vertices: 0,0 a 0,03 0, 3
Covertices: 0b,0 0 2,0 2,0
Example 1 Solution: Other Properties of Hyperbola
Sketch:
Foci: c2 a2 b2 93 13 c 13
F 0 13,0
c 13
Eccentricity: e 1.202
a 3
a 3
Asymptotes: y x y x
b 2
Length of Latus Rectum:
2b2 2 2 8
2
LR
a 3 3
6
� 10/23/2023
Find the equation of the hyperbola which has the
Example 2 foci of the ellipse 9 x 2 4 y 2 36 as vertices and
the vertices of the ellipse as the foci. Sketch the
graph.
Solution: Transform the given equation of the ellipse to standard form.
ELLIPSE: HYPERBOLA:
2 2
x y Orientation: Conjugate Hyperbola
9x2 4 y2 36 1
4 9 Center: 0,0
Orientation: Vertical Ellipse
a2 9 a 3 b2 4 b 2
Vertices: 0, 5 a 5
Center: 0,0
Foci: 0, 3 c 3
Vertices: 0,0a 0,03 0, 3 b2 c 2 a 2 9 5 4
b2
Covertices: 0b,0 0 2,0 2,0 Covertices:
Foci: 0,0c 0,0
5 0, 5 0b,0 02,0 2,0
Example 2 Solution: Other Properties of Hyperbola
c 3 Sketch:
Eccentricity: e 1.3416
a 5
a 5
Asymptotes: y x y x
b 2
Length of Latus Rectum:
2b2 2 2
2
8 8 5
LR
a 5 5 5
Endpoints of Latus Rectum:
4 5
ELR , 3
5
7
� 10/23/2023
Find the center, the vertices, the co-vertices, the length of
Example 3 transverse axis, the conjugate axis and the latus rectum, the
eccentricity, the foci and the equation of directrices of the
hyperbolas 9 x 16 y 36 x 96 y 252 0 .
2 2
Solution: Transform the given equation of the hyperbola to standard form.
9x2 16 y2 36x 96 y 252 0 Equation in Standard Form:
x 2 y 3 1
2 2
9x2 36x 16 y2 96 y 252
16 9
9 x2 4x 16 y2 6 y 252 Orientation: Horizontal Hyperbola
Center: 2,3
9 x 4x 4 16 y 6 y 9 252 36 144
2 2
a2 16 a 4
9 x 2 16 y 3 144
2 2
b 9
2
b 3
9 x 2 16 y 3 144
2 2
c a b 169 25
2 2 2
144 144 c2 25 c 5
Example 3 Solution: Other Properties of Hyperbola
c 5
Center: 2,3 Eccentricity: e 1.25
a 4
Vertices: 2 a,3 24,3 Asymptotes:
V1 6,3 and V2 2,3 b 3
y x k y x k @ 2,3
a 4
Covertices: 2,3b 2,33 3
3 2 k k 126k 18;6
CV1 2,6 and CV2 2,0 4
3 3 3 9
y1 x and y2 x
Foci: 2c,3 25,3 4 2 4 2
F1 7,3 and F2 3,3 Length of Latus Rectum:
2b2 2 3 18 9
2
Length of Transverse Axis 2a 2 4 8 LR
a 4 4 2
Length of Conjugate Axis 2b 2 3 6
8
� 10/23/2023
Example 3 Solution: Other Properties of Hyperbola
Endpoints of Latus Rectum: Sketch:
9
ELR 25,3
4
a 4 16
Directrices:d
e 5 5
4
16 16
x h x 2
5 5
26 6
x1 and x2
5 5
Find the center, the vertices, the covertices, the length of
Example 4 transverse axis, the conjugate axis, the eccentricity, and the
foci of the hyperbola x 12 y 2 2
1
16 25
Solution:
x 1 y 2 1
2 2
Vertices:1 a,2 1 4,2
16 25 V1 5,2 and V2 3,2
Orientation: Horizontal Hyperbola
Covertices: 1,2 b 1,2 5
Center: 1,2 CV1 1,7 and CV2 1, 3
a2 16 a4
b2 25 b5 Foci: 1 c,2 1 41,2
c2 a2 b2 16 25 41
F1 1 41,2 and F2 1 41,2
c2 41 c 41 Length of Transverse Axis 2a 2 4 8
c 41
Eccentricity: e 1.601 Length of Conjugate Axis 2b 2 5 10
a 4
9
� 10/23/2023
Example 4 Solution: Other Properties of Hyperbola
Endpoints of Latus Rectum: Sketch:
25
ELR 1 41,2
4
a 4 16
Directrices: d
e 41 41
4
16 16
x h x 1
41 41
4116 4116
x1 and x2
41 41
References
You may study hyperbolas by watching these videos.
1. Conic Sections: The Hyperbola part 1 of 2
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i6vM82SNAUk
2. Conic Sections: The Hyperbola part 2 of 2
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Xahrwp6LkI
10