Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genelec Monitor Focusing Template
Uploaded by
pakypaky33Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genelec Monitor Focusing Template
Uploaded by
pakypaky33Copyright:
Available Formats
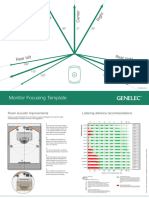
Center
ht
Le
Rig
ft
30° 0° 30°
r l e f t Re ar ri
Re a g ht
100° 100°
110° 110°
120° 120°
ITU-R BS.775-3
Monitor Focusing Template
Room acoustic improvements Listening distance recommendations
Several acoustic improvements can be made in a typical rectangular room where an audio
monitoring setup is installed. Here are a few suggestions.
0.5 1 1.5 2 3 5 10 15 (m)
A
106 101 98 96 95 93 92 65 m3
8320A
SAM Monitor Models
Cut the room front corners at 30 degree 100 95 92 90 89 87 86 2'300 ft3 0.22 s
angle using high-mass materials (concrete,
A A 8330A 110
102
105
97
102
94
100
92
98
90
97
89
96
88
75 m3
2'650 ft3 0.23 s
bricks, multi layered gypsum board, etc).
In case building materials have medium 8340A 111 108 106 104 102 101 85 m3
101 98 96 94 92 91 3'000 ft3 0.24 s
mass, make sure to fill the empty space
113 110 108 105 104 103 95 m3
behind these walls with mineral wool. 8350A 104 101 99 96 95 94 3'350 ft3 0.25 s
110 105 102 100 98 96 95 75 m3
B 8331A 105 100 97 95 93 91 90 2'650 ft3 0.23 s
B Use a combination of absorption and 116 111 108 106 104 102 101 85 m3
8341A
B diffusion on the side wall surfaces. Note
107 102 99 97 95 93 92 3'000 ft3 0.24 s
that thin layers of porous absorbers only 8351B 119 114 110 108 106 104 103 95 m3
107 102 98 96 94 92 91 3'350 ft3 0.25 s
reduce HF reflections.
124 118 115 113 111 108 107 110 m3
8361A 115 109 106 104 102 99 98 3'900 ft3 0.26 s
C
115 111 110 107 105 104 110 m3
1032C 3'900 ft3 0.26 s
MAI-0062. Genelec Document BBAGE027b. Copyright Genelec Oy 04.2020. All data subject to change.
If the room is large enough, use diffusive 105 101 100 97 95 94
and absorbing element(s) on the back wall. 118 115 113 110 108 106 106 125 m3
S360A 112 109 107 104 102 100 100 4'420 ft3 0.27 s
D 115 113 110 108 106 106 125 m3
1237A 109 107 104 102 100 100 4'420 ft3 0.27 s
Control low frequency room resonances
112 109 107 105 105 120 m3
using a large amount of absorption ma- 1238CF/DF 102 99 97 95 95 4'250 ft3 0.26 s
C terial for example in the back of the room
116 113 110 108 108 170 m3
1238A/AC 111 108 105 103 103 6'000 ft3 0.29 s
and in the ceiling. Carefully designed and
located panel resonator absorbers can 120 117 113 111 110 200 m3
1234A/AC 115 112 108 106 105 7'100 ft3 0.31 s
also be used.
D 124 121 118 114 113 400 m3
1236A 119 116 113 109 108 14'200 ft3 0.43 s
E
Use a combination of absorption and 1.6 3.2 5 6.5 9.8 16.5 32 50 (ft)
diffusion above the listening area to reduce Distance from the monitor (meters, feet)
acoustic reflections from the ceiling.
Room volume Listening Distances and SPL
The short-term and long-term sound pressure levels (SPL)
listed take into consideration the typical room volume and
Room reverbation time (RT60) reverberation time for each monitor (right margin, based
on ITU-R BS.1116). If the reverberation time is longer, it will
mainly affect the long-term SPL that will be higher than
Short-term sound pressure levels
shown.
Maximum short-term sine wave sound pressure level averaged
E 102 from 100 Hz to 3 kHz, measured in half-space, on-axis.
97 Peak levels are higher. This number tends to under-estimate
headroom by 4 dB, based on typical immersive standards and
Not Recommended Distances
audio content. For more detailed information, please contact When the distance to the monitor is too short, summing of
Genelec. sound from multiple drivers is not happening as designed.
55 m3 Long-term sound pressure levels
0.21 s long-term RMS sound pressure level, measured in
1'950 ft3Maximum
half-space, on-axis, with simulated programme signal according
to IEC 60268-5 (limited by driver unit protection circuit).
You might also like
- ANSI Z535.1-2006 (R2011) : American National StandardDocument14 pagesANSI Z535.1-2006 (R2011) : American National StandardMary Rose MillanNo ratings yet
- Wine Box PandaDocument19 pagesWine Box PandaKarl100% (1)
- Pantone Color ChartDocument14 pagesPantone Color ChartSevet Gnow Drachir100% (2)
- 1/7 (Row1 Col1)Document7 pages1/7 (Row1 Col1)renato_aleman_1No ratings yet
- Amia Srinivasan Reviews Other Minds' by Peter Godfrey-Smith and The Soul of An Octopus' by Sy MontgomeryDocument8 pagesAmia Srinivasan Reviews Other Minds' by Peter Godfrey-Smith and The Soul of An Octopus' by Sy MontgomeryKuba WirusNo ratings yet
- NoiseDocument220 pagesNoisemedrascomNo ratings yet
- Materialismo vs. Dualismo: las principales respuestas al problema de la concienciaDocument64 pagesMaterialismo vs. Dualismo: las principales respuestas al problema de la concienciaIgnacio CeaNo ratings yet
- Genelec Monitor Focusing Template 231221 213837Document2 pagesGenelec Monitor Focusing Template 231221 213837pakypaky33No ratings yet
- Document sections and locationsDocument1 pageDocument sections and locationsAdlan TarendraNo ratings yet
- Leg Profile-AP-64-AP-64Document1 pageLeg Profile-AP-64-AP-64Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Laser Cannon 34mm - A4Document2 pagesLaser Cannon 34mm - A4Peter BrunerNo ratings yet
- 2008 4GGSM 4G#RO MDO294 0164 - eSQAC - Clear - AlarmDocument23 pages2008 4GGSM 4G#RO MDO294 0164 - eSQAC - Clear - Alarmkhina luthfiNo ratings yet
- Golden Treasure ChestDocument2 pagesGolden Treasure ChestdavidamaruNo ratings yet
- Bronze Treasure ChestDocument2 pagesBronze Treasure ChestdavidamaruNo ratings yet
- Chart - Stitch FiddleDocument1 pageChart - Stitch FiddleCharlotte CrouchNo ratings yet
- Rhino HeadDocument8 pagesRhino HeadSARABIA papeleria y regalosNo ratings yet
- Rhino HeadDocument8 pagesRhino HeadALEJANDRONo ratings yet
- PP-001 Universal2 Pump Seal Reference ChartDocument1 pagePP-001 Universal2 Pump Seal Reference Chartandres roblezNo ratings yet
- Leg Profile-AP-63-AP-63Document1 pageLeg Profile-AP-63-AP-63Hikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Cell Availability: Kpi InformationDocument23 pagesCell Availability: Kpi InformationHaryadi syamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Technical Lot 3 DescriptionDocument1 pageTechnical Lot 3 DescriptionMons DelmendoNo ratings yet
- A B C E F G H C D D: AzoteaDocument1 pageA B C E F G H C D D: AzoteaGustavo Róssiter VargasNo ratings yet
- Manual Expl - View E-403 XL Rev ADocument3 pagesManual Expl - View E-403 XL Rev AArturo R. MalavéNo ratings yet
- Ownership and permission of HFE vacuum systemsDocument11 pagesOwnership and permission of HFE vacuum systemsAlexandru SavuNo ratings yet
- Fig X SectionDocument1 pageFig X SectionLe NobitaNo ratings yet
- Final Vasant Kunj Site-ModelDocument1 pageFinal Vasant Kunj Site-Modelsanjay gautamNo ratings yet
- Adc SchematicDocument1 pageAdc SchematicFernando FamaniaNo ratings yet
- Among Us LINESDocument4 pagesAmong Us LINESjanneth guzmanNo ratings yet
- My LATESTFXForecastsfor JUNE30Document3 pagesMy LATESTFXForecastsfor JUNE30api-26441337No ratings yet
- Group Leader Development 14-7-2022Document10 pagesGroup Leader Development 14-7-2022Lancar Jaya PrintingNo ratings yet
- Precursor MBDocument1 pagePrecursor MBJoshua C. CastilloNo ratings yet
- East Side East Side: "C" Docks "C" DocksDocument1 pageEast Side East Side: "C" Docks "C" DocksAckley FooserNo ratings yet
- Nifty Derivatives Report Shows Sector Wise Rollover TrendsDocument7 pagesNifty Derivatives Report Shows Sector Wise Rollover TrendscdranuragNo ratings yet
- MB90F025F Rev1.0Document1 pageMB90F025F Rev1.0simooo32No ratings yet
- AlienDog A4 FreeDocument10 pagesAlienDog A4 FreeCarlaNo ratings yet
- Merry Christmas Mr. Lawrence-FluteDocument2 pagesMerry Christmas Mr. Lawrence-FluteBruno Del BenNo ratings yet
- ALLOY C19010: Exceptional Performance Versatile Product Global AvailabilityDocument8 pagesALLOY C19010: Exceptional Performance Versatile Product Global Availabilitystrip1No ratings yet
- Stratified Sampling of CapsuleDocument23 pagesStratified Sampling of Capsulemailtorubal2573No ratings yet
- National Health Targets - All Dhbs Shorter Stays in EdDocument24 pagesNational Health Targets - All Dhbs Shorter Stays in EdJuana AtkinsNo ratings yet
- Site Pt. Duta Alam Sumatera Kecamatan Merapi Barat, Kabupaten Lahat, Provinsi Sumatera SelatanDocument1 pageSite Pt. Duta Alam Sumatera Kecamatan Merapi Barat, Kabupaten Lahat, Provinsi Sumatera SelatandejomarlubNo ratings yet
- Main Campus Map RevisedDocument2 pagesMain Campus Map Revisedm.rautenbach00No ratings yet
- Leg Profile-AP-63A-AP-63ADocument1 pageLeg Profile-AP-63A-AP-63AHikmat B. Ayer - हिक्मत ब. ऐरNo ratings yet
- Board SchematicDocument1 pageBoard SchematicJOSE LENIN RIVERA VILLALOBOS0% (1)
- DS Armstrong METAL Lay-In-MicroLook-Axal Vector enDocument2 pagesDS Armstrong METAL Lay-In-MicroLook-Axal Vector enAshraf AbdellatefNo ratings yet
- Laser Cannon 1-18 - A4Document6 pagesLaser Cannon 1-18 - A4Peter BrunerNo ratings yet
- Wilmington MarketDocument4 pagesWilmington Marketapi-26444160No ratings yet
- 25-MAY-18 02-Jun-2018 12:56 24.090M Span Substructure-ABT - STDDocument1 page25-MAY-18 02-Jun-2018 12:56 24.090M Span Substructure-ABT - STDFatima AhmedNo ratings yet
- Genelec Step by Step Setup Guide Ed 2015Document2 pagesGenelec Step by Step Setup Guide Ed 2015GaryRubioNo ratings yet
- Eis Me Aqui TromboneDocument2 pagesEis Me Aqui TromboneIury AugustoNo ratings yet
- Viva La Vida - UPGRADEDocument2 pagesViva La Vida - UPGRADEVinícius Gleriano de MoraesNo ratings yet
- The Aspen Iconic (12 Sep 23)Document45 pagesThe Aspen Iconic (12 Sep 23)DIWAKAR VERMANo ratings yet
- Sma Activation Code For Extended Warranty: Order FormDocument1 pageSma Activation Code For Extended Warranty: Order Formaabbcc ccbbaaNo ratings yet
- Residential area elevation and land use detailsDocument1 pageResidential area elevation and land use detailsharishNo ratings yet
- Startup Civil Consultants: Typical Cross-Section of Rigid PavementDocument1 pageStartup Civil Consultants: Typical Cross-Section of Rigid PavementKA25 ConsultantNo ratings yet
- LAYOUTDocument1 pageLAYOUTarvin jay santarinNo ratings yet
- Ryobi 10 in. Table Saw Repair SheetDocument10 pagesRyobi 10 in. Table Saw Repair SheetdigitaltextNo ratings yet
- Directional Clutch 16H Ats DWHDocument6 pagesDirectional Clutch 16H Ats DWHSyahdiNo ratings yet
- Merry Christmas Mr. LawrenceDocument1 pageMerry Christmas Mr. Lawrenceckun kit yipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chart Pattern SecretDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Chart Pattern SecretorderterimakasihNo ratings yet
- 2013 Topo MapDocument1 page2013 Topo MapAtharva INo ratings yet
- The Aspen PPT (12 Sep 2023)Document62 pagesThe Aspen PPT (12 Sep 2023)DIWAKAR VERMANo ratings yet
- The Aspen Sales PPT 25 Jan 2023 v3 PDFDocument59 pagesThe Aspen Sales PPT 25 Jan 2023 v3 PDFOlga VinturNo ratings yet
- Symposium Series No. 54 © 2008 Icheme: Raw Data 5-Year Average Linear (5-Year Average)Document1 pageSymposium Series No. 54 © 2008 Icheme: Raw Data 5-Year Average Linear (5-Year Average)potatoteddyNo ratings yet
- Leds-C4 The One 2015Document836 pagesLeds-C4 The One 2015VEMATELNo ratings yet
- Shorebird Color Flagging Protocol on the East Asian-Australasian FlywayDocument6 pagesShorebird Color Flagging Protocol on the East Asian-Australasian FlywaynguoitinhmaquaiNo ratings yet
- Dolabella SlidesCarnivalDocument33 pagesDolabella SlidesCarnivalDaniel DeniegaNo ratings yet
- Referencias Colores 2020Document6 pagesReferencias Colores 2020CURRO LOPEZ TATTOONo ratings yet
- Area of Study 1:: Musictechstudent - Co.ukDocument7 pagesArea of Study 1:: Musictechstudent - Co.ukPapageorgiou VasoNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Loudnes CurveDocument1 pageAcoustics Loudnes CurveAlenMomirovićNo ratings yet
- CameleonDocument29 pagesCameleonArkadiusz StrzeszewskiNo ratings yet
- Signal Strength Colour Code ChartDocument2 pagesSignal Strength Colour Code ChartDhiraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Addition Color by Number BaseballDocument2 pagesAddition Color by Number Baseballsuryacsn2004No ratings yet
- Understanding Surface Mount Resistor Marking CodesDocument1 pageUnderstanding Surface Mount Resistor Marking CodesThe1LegendNo ratings yet
- Spiral Sweater Graph (Double Crochet) - Stitch FiddleDocument2 pagesSpiral Sweater Graph (Double Crochet) - Stitch FiddleEsra MenteseNo ratings yet
- Noise Pollution Guide: Causes, Effects & SolutionsDocument3 pagesNoise Pollution Guide: Causes, Effects & SolutionsChie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Formal Properties: Elements of Art: ColorDocument11 pagesFormal Properties: Elements of Art: ColorPaula AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- CPAR Final Exam ReviewerDocument9 pagesCPAR Final Exam ReviewerJUSTINE MARIGUNDONNo ratings yet
- Principia QualiaDocument86 pagesPrincipia Qualiascribbly bibblyNo ratings yet
- Cla108f Cla115sDocument1 pageCla108f Cla115sAMIR 'IZZUDDIN BIN ABDUL SHAFRI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet of SoundDocument7 pagesWork Sheet of SoundAhsan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Mind, consciousness, yishi, duh, and um in other languagesDocument26 pagesMind, consciousness, yishi, duh, and um in other languagestchouang_zu100% (1)
- Proceedings of INTER-NOISE 2016 on Noise ControlDocument2 pagesProceedings of INTER-NOISE 2016 on Noise Controlmrapsouthern6256No ratings yet
- PS-Swatch CMYK Color Patches by NumbersDocument19 pagesPS-Swatch CMYK Color Patches by NumbersGeorgi VelkovNo ratings yet
- Mixing Primary ColorsDocument7 pagesMixing Primary ColorsBenjie SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Aerial/Underground: Fiber Optic Splice GuideDocument1 pageAerial/Underground: Fiber Optic Splice GuideRobert HedrickNo ratings yet
- JakofixDocument23 pagesJakofixNaresh ButaniNo ratings yet
- A Primer On Wine Spectral AnalysisDocument6 pagesA Primer On Wine Spectral AnalysisArtur FalcãoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 AnpcDocument19 pagesUnit 4 AnpcJohn WickNo ratings yet