0% found this document useful (0 votes)
412 views4 pagesRWH Calculation Examples
This document provides three examples of sizing rainwater tanks and pipes for different applications:
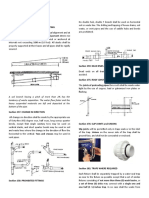
1) A residential development with a 200m2 roof and 5 bedrooms, requiring a 2m3 tank to meet 462m3 annual demand and providing 50.2% of rainwater and 25.4% of total water needs.
2) A factory with a 5,000m2 roof and 500 workers, requiring a 50m3 tank to meet 8,504m3 annual demand and providing 55.9% of rainwater needs.
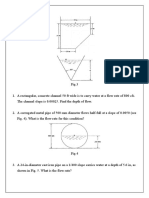
3) Sizing a 25mm copper pipe for a factory bathroom, calculating a flow rate of 0.70L/s and verifying the 2.56
Uploaded by
calvin chanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
412 views4 pagesRWH Calculation Examples
This document provides three examples of sizing rainwater tanks and pipes for different applications:
1) A residential development with a 200m2 roof and 5 bedrooms, requiring a 2m3 tank to meet 462m3 annual demand and providing 50.2% of rainwater and 25.4% of total water needs.
2) A factory with a 5,000m2 roof and 500 workers, requiring a 50m3 tank to meet 8,504m3 annual demand and providing 55.9% of rainwater needs.
3) Sizing a 25mm copper pipe for a factory bathroom, calculating a flow rate of 0.70L/s and verifying the 2.56
Uploaded by
calvin chanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd