0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views17 pagesTCP/IP Model Layers & Protocols
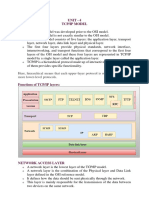
The document discusses the layers and protocols in the TCP/IP model. It describes the physical/data link, network, transport and application layers. The network layer uses IP, ARP, RARP, ICMP and IGMP. The transport layer uses TCP, UDP and SCTP. The application layer uses protocols like HTTP, FTP, TELNET, DNS, SNMP and SMTP.
Uploaded by
allaccess335Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views17 pagesTCP/IP Model Layers & Protocols
The document discusses the layers and protocols in the TCP/IP model. It describes the physical/data link, network, transport and application layers. The network layer uses IP, ARP, RARP, ICMP and IGMP. The transport layer uses TCP, UDP and SCTP. The application layer uses protocols like HTTP, FTP, TELNET, DNS, SNMP and SMTP.
Uploaded by
allaccess335Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd