Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture4 CAP25
Uploaded by
vishal kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views21 pagesTcp ip protocol
Original Title
Lecture4_CAP25
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTcp ip protocol
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views21 pagesLecture4 CAP25
Uploaded by
vishal kumarTcp ip protocol
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
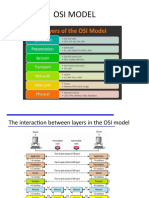
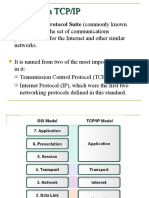
TCP/IP Model
Introduction
• The Internet Protocol Suite (commonly known as
TCP/IP) is the set of communications protocols
used for the Internet and other similar networks.
• It is named from two of the most important
protocols in it:
– Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and
– Internet Protocol (IP), which were the first two
networking protocols defined in this standard.
Comparison Between TCP/IP and OSI
model
Application Layer
• This layer is comparable to the application,
presentation, and session layers of the OSI
model all combined into one
• It provides a way for applications to have
access to networked services
• It is widely-known layer for the exchange of
user information
Application Layer Contd…
• The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is
used to transfer files that make up the Web
pages of the World Wide Web.
• The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is used for
interactive file transfer.
• The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is
used for the transfer of mail messages and
attachments.
Application Layer Contd…
• Presentation Layer does Encryption-
Decryption and Compression-Decompression
of Data
• This layer allows a process to add checkpoints
which are considered as synchronization
points into stream of data
Application Layer Contd…
Transport Layer
• This layer acts as the delivery service used by the
application layer.
• Two protocols used are TCP and UDP.
• The choice is made based on the application's
transmission reliability requirements.
• The transport layer also handles all error detection
and recovery.
Transport Layer Contd…
• It uses checksums, acknowledgements, and
timeouts to control transmissions and end to end
verification
• Unlike the OSI model, TCP/IP treats reliability as
an end-to-end problem
• TCP provides a one-to-one, connection-oriented,
reliable communications service
• UDP provides a one-to-one or one-to-many,
connectionless, unreliable communications
service
Transport Layer Contd…
• A message is divided into segments; each
segment contains sequence number, which
enables this layer in reassembling the
message.
Transport Layer Contd…
• Message is reassembled correctly upon arrival
at the destination and replaces packets which
were lost in transmission
• Connection Control : It includes 2 types :
– Connectionless Transport Layer : Each segment is
considered as an independent packet and delivered
to the transport layer at the destination machine.
– Connection Oriented Transport Layer : Before
delivering packets, connection is made with
transport layer at the destination machine.
Network Layer
• This layer is also known as Internet Layer. The
main purpose of this layer is to organize or
handle the movement of data on network.
• By movement of data, we generally mean
routing of data over the network
• This layer is responsible for addressing,
packaging, and routing functions
Network Layer Contd…
• The core protocols of the Internet layer are IP, ARP,
ICMP, and IGMP.
• The Internet Protocol (IP) is a routable protocol
responsible for IP addressing, routing, and the
fragmentation and reassembly of packets.
• The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is
responsible for the resolution of the Internet layer
address to the Network Interface layer address such
as a hardware address.
Network Layer Contd…
• The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is
responsible for providing diagnostic functions and
reporting errors due to the unsuccessful delivery of
IP packets
• The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is
responsible for the management of IP multicast
groups.
Network Layer Contd…
• It translates logical network address into physical
address. Concerned with circuit, message or packet
switching.
• Routers and gateways operate in the network layer.
Network Layer Contd…
Data Link Layer
• Data link layer is most reliable node to node
delivery of data
• It forms frames from the packets that are received
from network layer and gives it to physical layer
• It also synchronizes the information which is to be
transmitted over the data. Error controlling is easily
done.
Data Link Layer Contd…
• Protocols of this layer determine which of the
devices has control over the link at any given
time, when two or more devices are connected
to the same link.
Data Link Layer Contd…
• Error control is achieved by adding a trailer at the end of the
frame.
• Duplication of frames are also prevented by using this
mechanism.
• Frames are the streams of bits received from the network
layer into manageable data units.
• This division of stream of bits is done by Data Link Layer.
Physical Layer
• Physical layer is the lowest layer of all. It is
responsible for sending bits from one computer to
another.
• This layer is not concerned with the meaning of the
bits and deals with the physical connection
• This layer defines electrical and physical details
represented as 0 or a 1.
Physical Layer Contd…
• This layer defines the rate of transmission which is
the number of bits per second.
• It deals with the synchronization of the transmitter
and receiver. The sender and receiver are
synchronized at bit level.
• Devices must be connected using the following
topologies: Mesh, Star, Ring and Bus.
• Physical Layer defines the direction of transmission
between two devices: Simplex, Half Duplex, Full
Duplex
You might also like
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP IP MODELDocument29 pagesOSI and TCP IP MODELHarsh IsamaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Network ModelsDocument21 pagesChapter 02 Network ModelsFarhan TamzidNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Introduction and Layer OverviewDocument23 pagesTCP/IP Introduction and Layer OverviewSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to TCP/IP Protocol LayersDocument25 pagesIntroduction to TCP/IP Protocol LayersSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1Abdirazak ImanNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document151 pagesModule 1tharunn6364No ratings yet
- UCCN1004 - Lect8 - Intro To Layered Model and ProtocolsDocument31 pagesUCCN1004 - Lect8 - Intro To Layered Model and ProtocolsVickRam RaViNo ratings yet
- # TCP/IP Protocol Layers:-1.application Layer: Protocols UsedDocument8 pages# TCP/IP Protocol Layers:-1.application Layer: Protocols UsedPRIYANSHU KUMARNo ratings yet
- What Is The OSI ModelDocument17 pagesWhat Is The OSI ModelBilisumaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 ITA1006 TH VL2023240102674 2023-08-01 Reference-Material-IDocument32 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 ITA1006 TH VL2023240102674 2023-08-01 Reference-Material-IAnanya MachaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 TCP, OSIDocument36 pagesLecture 2 TCP, OSImubeen naeemNo ratings yet
- Network BasicsDocument41 pagesNetwork Basicsdarknetbot307No ratings yet
- DC Module 1-2Document35 pagesDC Module 1-2Adam MichelleNo ratings yet
- 19-203-0802 Computer Commu-Nication and Net - Working: Professional Elective - IV SEM-8Document45 pages19-203-0802 Computer Commu-Nication and Net - Working: Professional Elective - IV SEM-8Ťèjùźź ȚèjùNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCSE308L TH VL2023240100950 2023-04-24 Reference-Material-VDocument28 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCSE308L TH VL2023240100950 2023-04-24 Reference-Material-VManan SantokiNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 - ModelsDocument24 pagesSlide 1 - ModelsHarsh SinghalNo ratings yet
- The OSI Model and Tcp/Ip Protocol SuiteDocument48 pagesThe OSI Model and Tcp/Ip Protocol SuiteJeet KarmakarNo ratings yet
- OSI MODEL AssDocument16 pagesOSI MODEL AssMatovu HerbertNo ratings yet
- Fig.1.14 Logical Connections Between Layers of The TCP/IP Protocol SuiteDocument34 pagesFig.1.14 Logical Connections Between Layers of The TCP/IP Protocol SuiteNadeem PashaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 6 Data Communication and Networking: BY Muhammad AfzalDocument36 pagesLecture 5 - 6 Data Communication and Networking: BY Muhammad AfzalHamzah AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Classification of ComputersDocument29 pagesLec 1 Classification of ComputersKhawaja RameezNo ratings yet
- 2 Osi-TcpipDocument62 pages2 Osi-TcpipTutun Juhana100% (1)
- Cloud NetworkingDocument26 pagesCloud NetworkingHeliosNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument82 pagesNetworkDavidoffNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Network ModelsDocument9 pagesFundamental Network ModelsSailas Khulumani TshabanguNo ratings yet
- Tcp-Ip ModelDocument3 pagesTcp-Ip ModelTaimoor ZubairNo ratings yet
- OSI Layers and TCP/IP Protocols ExplainedDocument40 pagesOSI Layers and TCP/IP Protocols Explainedty juNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (1)Document50 pagesLecture 3 (1)NANDINI AGGARWAL 211131No ratings yet
- Data Comunication CH 1Document22 pagesData Comunication CH 1Desalegn sirnaNo ratings yet
- CCN Part 2Document13 pagesCCN Part 2116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Network Fundamental ConceptsDocument125 pagesChapter 2. Network Fundamental ConceptsBereketNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Network ModelDocument78 pagesUnit 2 Network Modelmichaljonny02No ratings yet
- Network Protocol and TCPDocument5 pagesNetwork Protocol and TCPJoshua SantillanaNo ratings yet
- Data Comm & NetworkingDocument8 pagesData Comm & NetworkingTea BletaNo ratings yet
- network protocol architecturesDocument17 pagesnetwork protocol architecturesamash.emillyNo ratings yet
- OSI MODELDocument19 pagesOSI MODELPranav SaiNo ratings yet
- Internet Architecture and Performance MetricsDocument14 pagesInternet Architecture and Performance MetricsnishasomsNo ratings yet
- The OSI Model: A Guide to the Seven Layer ModelDocument38 pagesThe OSI Model: A Guide to the Seven Layer Modelpriyasingh1682No ratings yet
- Computer Networks Model ComparisonDocument419 pagesComputer Networks Model ComparisonMihai Viorel HirtNo ratings yet
- Understanding the OSI Model in 40 CharactersDocument29 pagesUnderstanding the OSI Model in 40 CharacterscvigaNo ratings yet
- OSI Reference Model: Standardization, in The Year 1984Document9 pagesOSI Reference Model: Standardization, in The Year 1984anjali prasadNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Water Resources and ElectricityDocument26 pagesMinistry of Water Resources and ElectricitymeshelNo ratings yet
- 4.osi LayersDocument48 pages4.osi LayersSami AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document8 pagesAssignment 1malashishNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocol Suite and Network Topology GuideDocument40 pagesTCP/IP Protocol Suite and Network Topology GuideANANYANo ratings yet
- Lecture10 C1Document18 pagesLecture10 C1mister anonymousNo ratings yet
- Week2-Application Layer FixDocument38 pagesWeek2-Application Layer FixBaekhyuneeNo ratings yet
- TCP-IP Protocol SuiteDocument28 pagesTCP-IP Protocol SuiteDhanwanth JP100% (1)
- "Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away": Layer 7: Application LayerDocument3 pages"Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away": Layer 7: Application LayerAndres GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Network Layers Lecture 1Document23 pagesNetwork Layers Lecture 1syabo.00315660No ratings yet
- Understand Networking Protocols and Models in 40 CharactersDocument31 pagesUnderstand Networking Protocols and Models in 40 CharactersERICK LOUIS ADOKONo ratings yet
- Networking Basics & OSI Reference ModelDocument79 pagesNetworking Basics & OSI Reference Modelwisedotblue100% (1)
- NETWORK MODELS LAYERS LECTUREDocument45 pagesNETWORK MODELS LAYERS LECTUREVicent B KawunguNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip Protocol SuiteDocument17 pagesTcp/Ip Protocol Suitemadhavi gulhaneNo ratings yet
- Osi LayersDocument42 pagesOsi LayersBhoomika Bansal100% (1)
- 6OSI ReferencemodelDocument43 pages6OSI Referencemodelgokul adethyaNo ratings yet
- REFERENCE MODELS: OSI AND TCP/IPDocument19 pagesREFERENCE MODELS: OSI AND TCP/IPkalpana.gangwarNo ratings yet
- Seminar Osi ModelDocument25 pagesSeminar Osi Model5DSX4zKSNo ratings yet
- Ccna Ipv4 AddressingDocument103 pagesCcna Ipv4 AddressingntimamaoNo ratings yet
- Cap404 Ca2 - 081849Document12 pagesCap404 Ca2 - 081849vishal kumarNo ratings yet
- The Relational ModelDocument46 pagesThe Relational ModelYash jangidNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Capital Structure - TheoriesDocument39 pagesUnit 5 Capital Structure - Theoriesvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Dbms CommandsDocument56 pagesDbms CommandsKavya VyasNo ratings yet
- The Relational ModelDocument46 pagesThe Relational ModelYash jangidNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 RM1Document18 pagesUnit 4 RM1vishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Reveivables ManagementDocument43 pagesUnit 4 Reveivables Managementvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 FACTORINGDocument14 pagesUnit 4 FACTORINGvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Managing and Transforming DataDocument2 pagesManaging and Transforming Datavishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Using FunctionsDocument3 pagesUsing Functionsvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Capital BudgetingDiscounted TechniquesDocument22 pagesUnit 4 Capital BudgetingDiscounted Techniquesvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- How To Import Different File Types Into Google SheetsDocument2 pagesHow To Import Different File Types Into Google Sheetsvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Managing Values, Rows, Cells, orDocument1 pageManaging Values, Rows, Cells, orvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Inserting Non-Text ElementsDocument5 pagesInserting Non-Text Elementsvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- GPS Tracker TK102 ConfigDocument16 pagesGPS Tracker TK102 Confignairam2003No ratings yet
- Free Switch Cookbook - AssignmentsDocument2 pagesFree Switch Cookbook - AssignmentsEl MohssinNo ratings yet
- Technical Description: FBP FieldbusplugDocument12 pagesTechnical Description: FBP FieldbusplugDellendo FarquharsonNo ratings yet
- A StrumDocument4 pagesA StrumRedy KwNo ratings yet
- Amateur Photographer - 19 December 2015Document116 pagesAmateur Photographer - 19 December 2015stamenkovskibNo ratings yet
- Technician's Handbook For Release 9.0Document479 pagesTechnician's Handbook For Release 9.0icns01No ratings yet
- J430i ManualDocument57 pagesJ430i ManualimranayobNo ratings yet
- DHCP ServerDocument5 pagesDHCP ServerFaris JawadNo ratings yet
- Error Generating PDF Document ObieeDocument2 pagesError Generating PDF Document ObieeKatrinaNo ratings yet
- The History of DevOps & NetDevOpsDocument8 pagesThe History of DevOps & NetDevOpsCyber PunkNo ratings yet
- Wisp Clus18 Cisco SD WanDocument40 pagesWisp Clus18 Cisco SD Wandeltakio@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- SmartQ Manual: Setup and Use Guide for SmartQ DevicesDocument30 pagesSmartQ Manual: Setup and Use Guide for SmartQ DevicesrickallNo ratings yet
- 3BSE036352-510 A en AC 800M 5.1 Controller Hardware Product GuideDocument194 pages3BSE036352-510 A en AC 800M 5.1 Controller Hardware Product GuideMaykolth BarrantesNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technologies (ICT)Document8 pagesInformation and Communication Technologies (ICT)Ha? HalamanNo ratings yet
- Rabbit 3000 Microprocessor: Data SheetDocument38 pagesRabbit 3000 Microprocessor: Data SheetJose Luis Castro AguilarNo ratings yet
- 6631 BasebandDocument3 pages6631 BasebandHafssa AIT AMAR75% (4)
- Your Reliance Communications BillDocument2 pagesYour Reliance Communications Billaakash1004No ratings yet
- Mpls VPN BasicDocument11 pagesMpls VPN BasicNlend IsraëlNo ratings yet
- HP Switch Software - Using The CLIDocument9 pagesHP Switch Software - Using The CLIZach RandolfNo ratings yet
- IDU-E Series: RADWIN Indoor UnitDocument2 pagesIDU-E Series: RADWIN Indoor UnitfonpereiraNo ratings yet
- UnixDocument2 pagesUnixnagarjuna5026243No ratings yet
- Cloud OnBoard Fundamentals DeckDocument196 pagesCloud OnBoard Fundamentals DeckAnonymous gkJcMw100% (1)
- Gigabyte Ga 970a d3p r1.0 - SchematicDocument35 pagesGigabyte Ga 970a d3p r1.0 - Schematicgledyson gueNo ratings yet
- Connection String For Connecting To Data Sources in VBDocument10 pagesConnection String For Connecting To Data Sources in VBMuneeb Khan100% (3)
- What Are The Current Hot Research Topics in Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesWhat Are The Current Hot Research Topics in Cloud Computingلمسة املNo ratings yet
- Ex2300 Ethernet Switch DatasheetDocument12 pagesEx2300 Ethernet Switch Datasheetnaufal irfanNo ratings yet
- Facebook GuidelinesDocument16 pagesFacebook Guidelinesshazia_tabassumNo ratings yet
- Python Network Programming - Course Applications GuideDocument185 pagesPython Network Programming - Course Applications GuideMihai Catalin Teodosiu100% (1)
- Physical Support ADocument28 pagesPhysical Support ASilviu VornicescuNo ratings yet
- Sparkylinux 4.4 x86 64 Multimedia - Iso.package ListDocument94 pagesSparkylinux 4.4 x86 64 Multimedia - Iso.package ListKele Ion IonNo ratings yet