Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Practice Assignment
Uploaded by
tekadam.charo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesLa pratique de l'électricité
Original Title
laboratory practice Assignment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLa pratique de l'électricité
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesLaboratory Practice Assignment
Uploaded by
tekadam.charoLa pratique de l'électricité
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
laboratory practice Assignment
Ndah Andrew Wanje UBa22TP0219
Ndinwa Kisito Ngawe UBa22TP0220
Tekadam Fotie Emeran UBa22T0141
Ntam Joel Fukah Uba22TP0206
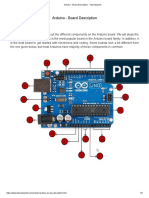
ARDUINO UNO BOARD
The Arduino UNO board has six analog input pins A0 through A5. These pins can read the
signal from an analog sensor like the humidity sensor or temperature sensor and convert it
into a digital value that can be read by the microprocessor
The following are various elements of an ADRUINO UNO board (Microcontroller) and their
functions.
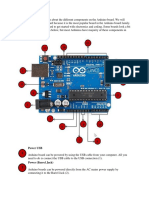
Power USB (1)
Arduino board can be powered by using the USB cable from your computer. All
you need to do is connect the USB cable to the USB connection (1)
Power (Barrel Jack) (2)
Arduino boards can be powered directly from the AC mains power supply by
connecting it to the Barrel Jack (2)
Voltage Regulator (3)
The function of the voltage regulator is to control the voltage given to the
Arduino board and stabilize the DC voltages used by the processor and other
elements
Crystal Oscillator (4)
The crystal oscillator helps Arduino in dealing with time issues. How does
Arduino calculate time? The answer is, by using the crystal oscillator. The
number printed on top of the Arduino crystal is 16.000H9H. It tells us that the
frequency is 16,000,000 Hertz or 16 MHz
Arduino Reset (5,17)
You can reset the Arduino board, i.e., start the program from the beginning. You
can reset the UNO board in two ways. First, by using the reset button (17) on
the board. Second, you can connect an external reset button to the Arduino pin
labelled RESET (5)
Pins (3.3, 5, GND, Vin) (6,7,8,9)
• 3.3V (6) − Supply 3.3 output volt
• 5V (7) − Supply 5 output volt
• Most of the components used with Arduino board works fine with 3.3
volt and 5 volt.
• GND (8)(Ground) − There are several GND pins on the Arduino, any of
which can be used to ground your circuit.
• Vin (9) − This pin also can be used to power the Arduino board from an
external power source, like AC mains power supply
Analog pins (10)
The Arduino UNO board has six analog input pins A0 through A5. These pins
can read the signal from an analog sensor like the humidity sensor or
temperature sensor and convert it into a digital value that can be read by the
microprocessor
Main microcontroller (11)
Each Arduino board has its own microcontroller (11). You can assume it as the
brain of your board. The main IC (integrated circuit) on the Arduino is slightly
different from board to board. The microcontrollers are usually of the ATMEL
Company. You must know what IC your board has before loading up a new
program from the Arduino IDE. This information is available on the top of the IC.
For more details about the IC construction and functions, you can refer to the
data sheet
ICSP pin (12)
Mostly, ICSP (12) is an AVR, a tiny programming header for the Arduino
consisting of MOSI, MISO, SCK, RESET, VCC, and GND. It is often referred to as
an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), which could be considered as an
"expansion" of the output. Actually, you are slaving the output device to the
master of the SPI bus
Power LED indicator (13)
This LED should light up when you plug your Arduino into a power source to
indicate that your board is powered up correctly. If this light does not turn on,
then there is something wrong with the connection
TX and RX LEDs (14)
On the board, you can find two labels: TX (transmit) and RX (receive). They
appear in two places on the Arduino UNO board. First, at the digital pins 0 and 1,
to indicate the pins responsible for serial communication. Second, the TX and
RX led (13). The TX led flashes with different speed while sending the serial
data. The speed of flashing depends on the baud rate used by the board. RX
flashes during the receiving process
Digital I/O (15)
The Arduino UNO board has 14 digital I/O pins (15) (of which 6 provide PWM
(Pulse Width Modulation) output. These pins can be configured to work as input
digital pins to read logic values (0 or 1) or as digital output pins to drive
different modules like LEDs, relays, etc. The pins labeled “~” can be used to
generate PWM
AREF (16)
AREF stands for Analog Reference. It is sometimes, used to set an external
reference voltage (between 0 and 5 Volts) as the upper limit for the analog input
pins
You might also like
- Arduino - Board DescriptionDocument4 pagesArduino - Board DescriptionGetz23No ratings yet
- Introduction To An Arduino - Arduino Basics - Arduino OverviewDocument25 pagesIntroduction To An Arduino - Arduino Basics - Arduino OverviewSrikanth Pinisetti100% (1)
- Jhoanie Marie P. Cauan Bsece 4 - 1 CPEN 105B Engr. Andy A. DizonDocument5 pagesJhoanie Marie P. Cauan Bsece 4 - 1 CPEN 105B Engr. Andy A. DizonJhoanie Marie CauanNo ratings yet
- Arduino Basics & Programming For Beginners With Internet of Things ProjectsDocument243 pagesArduino Basics & Programming For Beginners With Internet of Things Projectsaisl_2100% (6)
- Arduino UNO Microcontroller-VvbDocument121 pagesArduino UNO Microcontroller-VvbrahularokiyaNo ratings yet
- University of Buea: College of Technology (Department of Mechanical Engineering) MET413: WorkshopDocument25 pagesUniversity of Buea: College of Technology (Department of Mechanical Engineering) MET413: Workshopkevin15No ratings yet
- Week#2 - C Data Types and Arduino PlatformDocument27 pagesWeek#2 - C Data Types and Arduino PlatformMade KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Temperature Monitoring by Microcontroller Using ArduinoDocument44 pagesTemperature Monitoring by Microcontroller Using Arduinojp2udhayaNo ratings yet
- Arduino IOT PDFDocument36 pagesArduino IOT PDFKevin Del Rosario EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Aur BasicsDocument49 pagesAur BasicsAswathy AswathyNo ratings yet
- Arduino Quick Guide123Document51 pagesArduino Quick Guide123Madhav ReddyNo ratings yet
- Practical - 1 - : To Study Arduino Development BoardDocument5 pagesPractical - 1 - : To Study Arduino Development BoardAastha MehtaNo ratings yet
- V: Building Iot With Arduino &raspberry Pi: VunitDocument41 pagesV: Building Iot With Arduino &raspberry Pi: VunitPonraj ParkNo ratings yet
- Arduino NotesDocument27 pagesArduino NotesJames JosephNo ratings yet
- Arduino - Hardware DescriptionDocument8 pagesArduino - Hardware DescriptionYogesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Arduino Reviewer FromDocument3 pagesArduino Reviewer FromMarchery AlingalNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm System With Using ArduinoDocument34 pagesFire Alarm System With Using ArduinoMinesh panchalNo ratings yet
- Arduino ProjectDocument18 pagesArduino Projectdv4vgwhsp9No ratings yet
- Book OverviewDocument266 pagesBook OverviewJANTA GROUPNo ratings yet
- Obstacle Avoiding Final PreparationDocument37 pagesObstacle Avoiding Final PreparationRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENTt ROBOTICSDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENTt ROBOTICSHannah TotaoNo ratings yet
- Keshav Memorial Institute of Technology (An Autonomous Institute)Document3 pagesKeshav Memorial Institute of Technology (An Autonomous Institute)PRERANA YEKKELENo ratings yet
- AC Project ReportDocument31 pagesAC Project ReportSharif Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Control DC Motor 1Document79 pagesBluetooth Control DC Motor 1jp2udhayaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics: Arduino Uno: Christopher John I. Gayta, Ece, EctDocument27 pagesBasic Electronics: Arduino Uno: Christopher John I. Gayta, Ece, EctMonaisa Darimbang-MayoNo ratings yet
- 2 - Arduino Board - Arduino IDE - LED Control - PWMDocument33 pages2 - Arduino Board - Arduino IDE - LED Control - PWMReda FakihNo ratings yet
- Iot CodesDocument50 pagesIot CodesJayasree BaluguriNo ratings yet
- Fall Semester 2021-22Document12 pagesFall Semester 2021-22Samridhi JNo ratings yet
- Arduino UNODocument6 pagesArduino UNOsalmanNo ratings yet
- RegulatorDocument53 pagesRegulatorSurya MonNo ratings yet
- DC Power Monitor With INA209 and ArduinoDocument57 pagesDC Power Monitor With INA209 and Arduinojp2udhaya100% (2)
- Arduino Uno: Operating System CPUDocument21 pagesArduino Uno: Operating System CPUJemz VillaretNo ratings yet
- Components DetailsDocument14 pagesComponents DetailssukanyagggNo ratings yet
- 37 Sensor Kit UserGuide SunRoboticsDocument82 pages37 Sensor Kit UserGuide SunRoboticsDIPESHNo ratings yet
- Railway Track Crack DeductionDocument63 pagesRailway Track Crack Deductionjp2udhayaNo ratings yet
- IOT PracticalsDocument28 pagesIOT PracticalsmuskanbandariaNo ratings yet
- Prototype (Final)Document16 pagesPrototype (Final)Manish JangidNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things Lab (IOT) : Laboratory Practical FileDocument36 pagesInternet of Things Lab (IOT) : Laboratory Practical FileAnkit Prakash ChingNo ratings yet
- SSK Guide PDFDocument50 pagesSSK Guide PDFbhaskarjalanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ArduinoDocument5 pagesIntroduction To ArduinoAnika Gabrielle SeNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Prototyping Devlopment BoardsDocument25 pagesUnit-5 Prototyping Devlopment BoardsDr K SANTOSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Programming With Arduino and Raspberry PiDocument26 pagesAssignment: Programming With Arduino and Raspberry PiSUNEESHKUMAR PNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things (Iot)Document54 pagesInternet of Things (Iot)nitinsomanathanNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno: Arduino Uno R3 Front Arduino Uno R3 BackDocument4 pagesArduino Uno: Arduino Uno R3 Front Arduino Uno R3 Backjuan diegoNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno: Pin DescriptionDocument6 pagesArduino Uno: Pin DescriptionRuhina AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Based Home AutomationDocument27 pagesBluetooth Based Home AutomationAitha DeepakNo ratings yet
- Arduino IDE Programming - Simple Interrupt ApplicationDocument18 pagesArduino IDE Programming - Simple Interrupt ApplicationPearl Joyce SubereNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno Pin Diagram, Specifications, Pin Configuration & ProgrammingDocument5 pagesArduino Uno Pin Diagram, Specifications, Pin Configuration & ProgrammingkezsoloNo ratings yet
- ArdinoDocument8 pagesArdinojohn lockNo ratings yet
- Arduino Board UnoDocument4 pagesArduino Board Unoholej18237No ratings yet
- Ardrio FeaturesDocument2 pagesArdrio FeaturesShilpa chaudhariNo ratings yet
- Tajuk 3 - Function of Hardware N Components (ARDUINO UNO BOARD)Document36 pagesTajuk 3 - Function of Hardware N Components (ARDUINO UNO BOARD)mikengei1No ratings yet
- Arduino: Introduction & Programming: Course InstructorDocument29 pagesArduino: Introduction & Programming: Course InstructorHuma Qayyum MohyudDin100% (1)
- Arduino "Getting Started" Tutorial: HardwareDocument7 pagesArduino "Getting Started" Tutorial: HardwareMax dos santos ramosNo ratings yet
- Arduino UnoDocument8 pagesArduino UnoTrafalgar LawNo ratings yet
- Iot 4Document5 pagesIot 4Zuhaib AyazNo ratings yet
- Sobirov. Asilzoda: ArduinoDocument26 pagesSobirov. Asilzoda: ArduinoasilzodaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - RA3CO35 - Embedded SystemsDocument24 pagesLab Manual - RA3CO35 - Embedded SystemsPoonam singhNo ratings yet
- Exploring Arduino: Tools and Techniques for Engineering WizardryFrom EverandExploring Arduino: Tools and Techniques for Engineering WizardryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)