Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L3 - Adolescents With Special Nutritional Needs
Uploaded by
angelsonarguellesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L3 - Adolescents With Special Nutritional Needs
Uploaded by
angelsonarguellesCopyright:
Available Formats
FIRST TERM
NUR810 APPLIED NUTRITION & DIET THERAPY
PROFESSOR: Prof. Geralynne Medrana & Prof. Leah Marie Navarro
LECTURE TRANSCRIPT
PRELIMS OUTLINE RESULTS OF ALCOHOL ON PREGNANT MOTHERS
(ESPECIALLY IF ADOLESCENT)
● Unit 3 - Adolescents with Special Nutritional Needs ● Spontaneous abortion
○ Pregnant Adolescent ○ Miscarriage; before 20 wks AOG
○ Substance Abuse ● LBW deliveries
○ Adolescent Athlete ○ Less than 5 lbs, 8 oz, 2500 g
○ Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) ● Cognitive compromise
○ Weight Concerns and Eating Disorders ○ Brain processes and information storage,
resulting in impairment of memory, attention,
perception, thinking
ADOLESCENTS WITH SPECIAL NUTRITIONAL NEEDS ● Abruptio placenta
○ Placental detachment from uterine wall, partly
PREGNANT ADOLESCENT or totally
● Pregnant women have high incidence in the following ● Mental retardation
conditions: ○ Below average overall intellectual functioning
○ Iron-Deficiency Anemia (IDA) and deficits in adaptive behavior
○ Low birth weight
○ Cephalopelvic disproportion ADOLESCENT ATHLETE
● Women do not have adequate prenatal care due to: ● Energy level intake: 1800-2000 kcal/day
○ Fear, denial, and dependency to adults ● Carbs; Total caloric intake: 60-70%
○ Partners may also be minors (unless sexually ● Usual endurance exercises (triathlon):
abused) ○ Running
● Obese pregnant adolescents still need additional caloric ○ Swimming
intake for additional nourishment ○ Cycling
● Main problems in a pregnant adolescent: ● Primary health teaching: Rehydrate
○ Imbalanced nutrition less than body ○ Fluid needs may be greater than the thirst, so
requirements dehydration is possible
○ Knowledge deficit related to importance of ● Hyponatremia is the effect of overhydration (without
nutrition equivalent sweating)
○ Knowledge deficit related to body changes ● Nutrition: carbs, protein, fats
○ Knowledge deficit related to prenatal care ● Lb/Pound sweat loss: weighing before and after
activity of athletes; 1lb sweat loss = 2 cups water
SUBSTANCE ABUSE ● Carbohydrate of athletes: energy drinks and
CNS DEPRESSANT carbohydrate loading
● ALCOHOL + EXERCISE = CNS depressant ● Protein of athletes: protein and amino acid
● Causes of CNS depressant supplements
○ Decreased glucose secretion from liver ● Ergogenic aids: substances or devices that enhance
○ Hypoglycemia energy production, use or recovery and provide athlete
○ Early fatigue during exercise with a competitive advantage (e.g. creatinine, steroids)
○ Prohormones and steroids
CHRONIC ALCOHOL INGESTION ■ To increase muscle mass and
● ALCOHOL + HPN strength
● Results of chronic alcohol ingestion ○ Peptide hormones
○ Hypertension ■ To increase skeletal muscle mass and
○ Cardiomyopathy decrease body fat
○ Heart failure
PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (PMS)
● Etiology is unknown
Recommended alcohol intake ● Possible factors contributing to PMS:
1 drink for women per day ○ Progesterone and estrogen imbalance
2 drinks for men per day ■ Progesterone causes constipation
○ Low levels of endorphins
○ Abnormal prostaglandin
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME ■ Prostaglandins causes diarrhea
● ALCOHOL + PREGNANCY ■ Prostaglandins are hormone-like
● Has direct toxic effects on fetal development substances that affect several bodily
○ Microcephaly functions, including inflammation,
○ Epicanthal folds pain and uterine contractions
○ Low nasal bridge ○ Fluid imbalance
○ Small philtrum ○ Nutritional deficiency
○ Thin upper lip ● Signs and symptoms
ANTONIO, BALABA, BARCENA, BONSOL | 2NUR-1 1
○ Bloating, breast tenderness ○ Addresses core issues
○ Edema, headache, backache ○ Teach how to control responses
○ Diarrhea or constipation ○ Interprofessional team approach (referred to
○ Acne, appetite changes, food cravings psychiatrists)
● 4 Pillars of Health
○ Diet ANOREXIA NERVOSA
■ Low in fat and sodium ● Patient severely REJECTS food causing:
■ High in carbohydrates ○ Extreme weight loss
■ 2L of water ○ Low basal metabolic rate (BMR)
■ No alcohol or caffeine ○ Exhaustion
○ Exercise ● Puts food in mouth but spits its out (NOT vomit)
○ Stress management ● Management:
○ Sleep and rest ○ Must be fed carefully
○ Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
EMOTIONAL ■ It is the effort to change thinking
● Mood swings patterns to change behavior
● Decreased libido ■ By reconsidering old beliefs and
● Social withdrawal changing unhelpful behavior, many
● Forgetfulness people start feeling differently
MANAGEMENT
● K-Sparing Diuretics (Potassium-sparing)
○ Sheds extra water weight
● Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)
○ Water soluble vitamins to treat anemia
● Progesterone
○ Repairs endometrium, decreases contraction
for implantation
● NSAIDs
○ Reduce pain
○ Inhibits prostaglandins
DIET
● Low fat, low sodium, high CHO
● 2L water intake
● Avoid caffeine
EXERCISE
STRESS MANAGEMENT
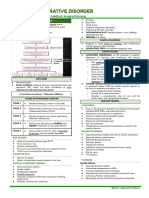
AVOIDANT OR RESTRICTIVE FOOD INTAKE DISORDER
REST AND SLEEP ● Patient have restrictive eating related to emotional
problems or GI problems/symptoms
● Dependence on enteral feeding or oral nutritional
WEIGHT CONCERNS and EATING DISORDERS supplements
● Weight loss supplements
○ May have side effects
○ Proper and well balanced diet and activity is
better
BINGE EATING DISORDER
● Eating, in a discrete period of time (within 2 hours), an
amount of food that is definitely larger than what most
people would eat in a similar period of time under
similar circumstances
● Lack of control over eating during a period of time
BULIMIA NERVOSA
● Food addiction = coping mechanism
● Recurrent episodes of binge eating
● Sense of lack of control
● Self-evaluation unduly influenced by weight or body
shape
● Recurrent and inappropriate compensating behavior
● Vomiting, use of laxatives for twice a week for three
months or longer
● Management:
○ Mindfulness-based activities (e.g. eating
awareness training)
ANTONIO, BALABA, BARCENA, BONSOL | 2NUR-1 2
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureAnne Lorraine Bringas93% (27)
- The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit-2Document28 pagesThe Neonatal Intensive Care Unit-2api-457873289No ratings yet
- PT104 MidtermsDocument13 pagesPT104 MidtermsANGELI SIAOTONGNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine Nutrition Block Exam Study FocusDocument61 pagesClinical Medicine Nutrition Block Exam Study FocusSohil PatelNo ratings yet
- A Dre No CorticoidsDocument2 pagesA Dre No CorticoidsAlbert CorderoNo ratings yet
- Review EndocrineDocument12 pagesReview EndocrineJezzabel Kyra BadayosNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 RLE Week 4Document28 pagesNCM 116 RLE Week 4Christel Mariz SantellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 78 Weight LossDocument2 pagesChapter 78 Weight LossNisreen SalameNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 - Animal Form and FunctionDocument5 pagesBio 11 - Animal Form and FunctionNikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Terazosin Drug Study Group 4Document3 pagesTerazosin Drug Study Group 4Michelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument7 pagesDrug Study - IbuprofenajNo ratings yet
- 06 - LEC Therapeutic Diet For Selected Pathological ConditionsDocument21 pages06 - LEC Therapeutic Diet For Selected Pathological ConditionsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Final Patient Care PresentationDocument19 pagesFinal Patient Care Presentationapi-511008469No ratings yet
- PUBHEALTH Non Communicable Diseases Prevention and ControlDocument13 pagesPUBHEALTH Non Communicable Diseases Prevention and ControlHenro WeiNo ratings yet
- Parkinsons Presentation Case StudyDocument33 pagesParkinsons Presentation Case Studyapi-287759747No ratings yet
- Garcinia SlidesDocument4 pagesGarcinia Slidesapi-570986190No ratings yet
- PediatricDocument63 pagesPediatricReya Mae OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Dietary Balances, Regulation of Feeding, Obesity and Starvation, Vitamins & MineralsDocument62 pagesDietary Balances, Regulation of Feeding, Obesity and Starvation, Vitamins & MineralsPrixie AntonioNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Presentation 1Document12 pagesCerebral Palsy Presentation 1api-438626249No ratings yet
- 03 - LEC Functional Role of Food and Its NutrientsDocument17 pages03 - LEC Functional Role of Food and Its NutrientsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Body System - Endocrine SystemDocument69 pagesDrugs Affecting The Body System - Endocrine SystemFaye JavierNo ratings yet
- Nutr 482 PosterDocument1 pageNutr 482 Posterapi-662212007No ratings yet
- BLS 01 HX and PE of The Newborn, Child, and Adolescent 11 - 08 and 12 - 06 (Updated)Document17 pagesBLS 01 HX and PE of The Newborn, Child, and Adolescent 11 - 08 and 12 - 06 (Updated)Nikka ReyesNo ratings yet
- TPN and Pregnancy: Related To Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument37 pagesTPN and Pregnancy: Related To Hyperemesis Gravidarumapi-319236078No ratings yet
- Section B - Group 6Document94 pagesSection B - Group 6CHRISTIAN ASHLEY PASCUANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Relationship of Nutrition & HealthDocument4 pagesChapter 1: The Relationship of Nutrition & Healthdennise reyesNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and CardioDocument26 pagesHypothalamus and CardioPunky LoperaNo ratings yet
- Anabolic Hormones and Dietary SupplementsDocument15 pagesAnabolic Hormones and Dietary SupplementsMalabaris Malaya Umar SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Theories of AgingDocument19 pagesTheories of AgingCatria BerloiseNo ratings yet
- Prelims Nutri LabDocument26 pagesPrelims Nutri LabangelsonarguellesNo ratings yet
- Archer Rapid Review Nclex SylabusDocument9 pagesArcher Rapid Review Nclex SylabusMariaNo ratings yet
- Copy-Nutrition Across The Life SpanDocument7 pagesCopy-Nutrition Across The Life SpanChristian Clyde Noel JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Multiorgan DysfunctionDocument24 pagesMultiorgan DysfunctionJazzy Kathlene DumableNo ratings yet
- AnorexiantsDocument3 pagesAnorexiantsJamaica Mae AguilarNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Review MSDocument39 pagesThe Endocrine System Review MSMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Rle Nicu ResearchDocument3 pagesNCM 107 Rle Nicu ResearchIsha Catimbang GenerilloNo ratings yet
- MDWF 2040 Practice Guideline Postpartum AnemiaDocument4 pagesMDWF 2040 Practice Guideline Postpartum Anemiaapi-442131145No ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders Julie Mann, NP - Case StudyDocument10 pagesEndocrine Disorders Julie Mann, NP - Case Studysimonedarling75% (4)
- BIOL 4380 Motivation + Sex BIOL 4380 Motivation + SexDocument17 pagesBIOL 4380 Motivation + Sex BIOL 4380 Motivation + SexJiaying ChenNo ratings yet
- Aroosa Qamar PharmacologyDocument17 pagesAroosa Qamar PharmacologyAdan IsrarNo ratings yet
- SeizuresDocument3 pagesSeizuresShairaNo ratings yet
- Emilio Aguinaldo College: School of NursingDocument3 pagesEmilio Aguinaldo College: School of Nursingbryan.zabala.mnlNo ratings yet
- Degenerative DiseasesDocument5 pagesDegenerative DiseasesJoanna SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Making Weight in Boxing PDFDocument33 pagesMaking Weight in Boxing PDFjonh AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Rr22 - Ncmp1o7 - Pedia PrelimsDocument18 pagesRr22 - Ncmp1o7 - Pedia PrelimsNicole Faith L. NacarioNo ratings yet
- J.B. Family Case Presentation Group 1Document67 pagesJ.B. Family Case Presentation Group 1Jeno Luis AcubNo ratings yet
- CH 41 Drugs Affecting The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesCH 41 Drugs Affecting The Male Reproductive Systemericka abasNo ratings yet
- Disorders in The Ovaries and PancreasDocument49 pagesDisorders in The Ovaries and PancreaswyneNo ratings yet
- Mar 14 - Fisiologi Hormon PankreasDocument36 pagesMar 14 - Fisiologi Hormon PankreasLailatuz ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Fundamentals Care Plan 1Document12 pagesRunning Head: Fundamentals Care Plan 1Xe StrmNo ratings yet
- Silliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesDocument8 pagesSilliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesRyan Robert V. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- Dietary SupplementsDocument24 pagesDietary Supplementsapi-610233914No ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Disorders Assessment Nursing Interventions Diabetes InsipidusDocument27 pagesEndocrine System: Disorders Assessment Nursing Interventions Diabetes InsipidusDulle Mullet100% (1)
- Gastroenterology Case Discussion: JANUARY 07, 2021 Dr. Stephen Wong Indigo and VioletDocument19 pagesGastroenterology Case Discussion: JANUARY 07, 2021 Dr. Stephen Wong Indigo and VioletJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyspamfromgia10No ratings yet
- (Pha) Le 5Document19 pages(Pha) Le 5Gabby TanNo ratings yet
- TW Case StudyDocument27 pagesTW Case Studyapi-346311171No ratings yet
- NCM 102 Case Analysis 1 NotesDocument12 pagesNCM 102 Case Analysis 1 NotesJosefina Isabel GullasNo ratings yet
- NDT Lec Midterms 3Document36 pagesNDT Lec Midterms 3mayangernszNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Vascular DisordersDocument5 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Vascular DisordersVinzii DrtNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Mini Test # 70 - Enzyme CofactorsDocument4 pagesMini Test # 70 - Enzyme CofactorsShreya BahamniNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY (Calcium)Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY (Calcium)NicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability and Efficiency of Rutin As An Antioxidant: A Human Supplementation StudyDocument10 pagesBioavailability and Efficiency of Rutin As An Antioxidant: A Human Supplementation StudyMema FathyNo ratings yet
- A Special Person EssayDocument5 pagesA Special Person Essayz1v1mud0z0p2100% (3)
- Digoxin Drug CardDocument1 pageDigoxin Drug CardMahsa Ahmadzadeh100% (2)
- Renal Function TestsDocument43 pagesRenal Function TestsAbdulelah MurshidNo ratings yet
- 11.multisystem Process Disorders 5 Blocks @eduwaves360Document1,060 pages11.multisystem Process Disorders 5 Blocks @eduwaves360AbigailNo ratings yet
- Nama BHP & Kode Barang Lab EkadaDocument3 pagesNama BHP & Kode Barang Lab EkadaPipit latuNo ratings yet
- NRDP 201529Document21 pagesNRDP 201529Zurielle LuboaNo ratings yet
- In Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Meroditerpenoids of Stypopodium Flabelliforme Against FOXO1Document4 pagesIn Silico Molecular Docking Studies of Meroditerpenoids of Stypopodium Flabelliforme Against FOXO1Rakesh DavellaNo ratings yet
- Surgery 2 PancreasDocument28 pagesSurgery 2 PancreasPARADISE JanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice IvDocument24 pagesNursing Practice IvJohn wewNo ratings yet
- Intradermo Presurizada en Grasa AbdominalDocument15 pagesIntradermo Presurizada en Grasa AbdominalGrecia Contreras BenitezNo ratings yet
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism-Literature Update 2018Document8 pagesPseudohypoparathyroidism-Literature Update 2018radu nicolaeNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis Prevention: Exercise Your BonesDocument8 pagesOsteoporosis Prevention: Exercise Your BonesAdhiraj singhNo ratings yet
- Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma NEJMDocument14 pagesPheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma NEJMLeo AcNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism - MCQs 4 BDocument10 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism - MCQs 4 BSaroja Veeresh100% (1)
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument6 pagesRoot Cause Analysisapi-548490535No ratings yet
- 50 TOP PHARMACODYNAMICS Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pages50 TOP PHARMACODYNAMICS Multiple ChoiceLibby Khalid100% (1)
- The Limbic SystemDocument7 pagesThe Limbic Systemkerima juliaNo ratings yet
- AutocoidDocument7 pagesAutocoidIdrissa ContehNo ratings yet
- Steps RationaleDocument3 pagesSteps RationaleKangMunching PotatoGamingNo ratings yet
- J Sajb 2019 11 007Document7 pagesJ Sajb 2019 11 007Dhanang Prawira NugrahaNo ratings yet
- The Liver and Its DisordersDocument41 pagesThe Liver and Its Disordersreuben kwotaNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & Minerals: Metadichol and Vitamin C Increase, An Open-Label StudyDocument5 pagesVitamins & Minerals: Metadichol and Vitamin C Increase, An Open-Label StudySilambarasu KaruppiahNo ratings yet
- Research ThesisDocument18 pagesResearch ThesisJanAndrianCaingat100% (2)
- A1C To Blood Glucose Conversion TableDocument1 pageA1C To Blood Glucose Conversion TableJeff LentiniNo ratings yet
- Osmosis ScriptDocument130 pagesOsmosis ScriptJihanNo ratings yet