Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MUCLecture 2022 5192228
Uploaded by
Hawta Abdulla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesOriginal Title
MUCLecture_2022_5192228
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views16 pagesMUCLecture 2022 5192228
Uploaded by
Hawta AbdullaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Blood Glucose Test
Asst.lec. Zahraa Hasan
What is a blood glucose test?
A blood glucose test measures the amount of
glucose, or sugar, in your blood. When you eat
carbohydrates, your body converts them into
glucose to use as energy. Too much or too little
glucose in the blood can be a sign of a serious
medical condition.
Doctors often order a blood glucose test to help
diagnose a condition called diabetes.
High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) may
be a sign of diabetes, a disorder that can cause
heart disease, blindness, kidney failure and other
complications.
Low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia) can
also lead to major health problems, including
brain damage, if not treated
Symptoms of high blood glucose levels
include:
1- Increased thirst
2- More frequent urination
3- Blurred vision
4- Fatigue
5- Wounds that are slow to heal
Symptoms of low blood glucose levels
include:
1- Anxiety
2- Sweating
3- Trembling
4- Hunger
5- Confusion
The hormones that are involved in the
regulation of blood glucose
Insulin: Stimulates cells to take up glucose from
the blood and so lowers blood glucose
Glucagon: Stimulates hepatocytes to release
glucose into the blood and so raises blood
glucose
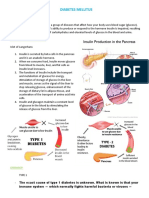
Diabetes is a lifelong condition that causes a person's blood
sugar level to become too high.
There are 2 main types of diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes – where the body's immune system attacks
and destroys the cells that produce insulin.
Type 2 diabetes – where the body does not produce enough
insulin, or the body's cells do not react to insulin.
During pregnancy, some women have such high levels of
blood glucose that their body is unable to produce enough
insulin to absorb it all. This is known as gestational
diabetes.
How to prepare for a blood glucose test:
Blood glucose tests fall into several categories,
including fasting, random (non-fasting), or post-
prandial. Fasting tests are more commonly used to
diagnose diabetes.Before your test, tell your doctor
about the medications you’re taking, including
prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, and herbal
supplements. Certain medications can affect blood
glucose levels. Your doctor may ask you to stop
taking a particular medication or to change the
dosage before your test temporarily.
Medications that can affect your
blood glucose levels include:
1- Diuretics
2- birth control pills
3- hormone therapy
4- aspirin
5- Lithium
6- epinephrine (Adrenalin)
7- phenytoin
Fasting test preparation
For a fasting blood glucose test, you can’t eat or drink
anything except water for 8 hours before your test.
Random testing preparation
Random (non-fasting) blood glucose tests don’t require you
to not eat or drink before the test.
Post-prandial testing preparation
A test given 2 hours after starting a meal is used to measure
postprandial plasma glucose. This test is most often done at
home when you have diabetes. You must do this test 2 hours
after you start eating a meal.
Glycated hemoglobin (A1C )Test
The A1C test measures your average blood sugar
level over the past 2 or 3 months. An A1C below
5.7% is normal, and 6.5% or higher indicates
you have diabetes.
Procedure
To measure blood glucose levels, a doctor will
collect a sample of blood from your vein using a
small needle. If you already have diabetes, you
can perform a blood glucose test at home using a
device that quickly pricks your finger in order to
collect a drop of blood.
Normal range:
Fasting blood sugar test
Normal for person without diabetes: 70–99 mg/dl
,for someone with diabetes: 80–130 mg/dl.
Post-prandial test
Normal for person without diabetes: Less than 140
mg/dl ,for someone with diabetes: Less
than 180 mg/dl.
Random blood sugar test
Normal for person without diabetes: 70–140
mg/dl, for someone with diabetes: 140-200 mg/dl.
Thank you
You might also like
- ORAL REVALIDA (Diabetes Mellitus)Document5 pagesORAL REVALIDA (Diabetes Mellitus)Aubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 8: Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument10 pagesCase Study 8: Coronary Artery Diseaseintrovoyz041100% (3)
- ORAL REVALIDA (Diabetes Mellitus)Document5 pagesORAL REVALIDA (Diabetes Mellitus)Aubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Resistance SolutionDocument132 pagesInsulin Resistance Solutionolgaremon100% (3)
- What Is A Blood Glucose TestDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Blood Glucose TestRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- How Is Diabtes DiagnoseDocument10 pagesHow Is Diabtes DiagnoseBethChay LacsonNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose Test ExplainedDocument3 pagesBlood Glucose Test ExplainedDiana MuañaNo ratings yet
- Print Article - Glucose Tests - Glucose Test - Blood Sugar - Blood Glucose - Fasting Blood Glucose - Oral Glucose Tolerance Test - OGTT - GTT - Urine Glucose - Lab Tests OnlineDocument9 pagesPrint Article - Glucose Tests - Glucose Test - Blood Sugar - Blood Glucose - Fasting Blood Glucose - Oral Glucose Tolerance Test - OGTT - GTT - Urine Glucose - Lab Tests OnlineHinaRaviNo ratings yet
- Case Study of DMDocument6 pagesCase Study of DMbuzz Q0% (1)
- Diabetis Mellitus Case StudyDocument16 pagesDiabetis Mellitus Case StudyJim Davis RNNo ratings yet
- Clinical 2Document12 pagesClinical 2yalewzeleke3710No ratings yet
- Data KlinikDocument68 pagesData KlinikSiti Zamilatul AzkiyahNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Diabetes: How Is Diabetes Diagnosed?Document1 pageDiagnosing Diabetes: How Is Diabetes Diagnosed?Karim Abo El FetouhNo ratings yet
- DM Case Study - Nursing CribDocument6 pagesDM Case Study - Nursing CribFrancis VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument5 pagesDiabetesMarina RamharackNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesDiabetes MellituscrisrimartNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: EndocrinologyDocument8 pagesDiabetes: EndocrinologyZhanyar Omer Mustafa F210050No ratings yet
- Case Study of Diabetes MellitusDocument19 pagesCase Study of Diabetes Mellituschai delgadoNo ratings yet
- Blood Sugar TestDocument4 pagesBlood Sugar TestanisyaNo ratings yet
- Oral Glucose Tolerance TestDocument4 pagesOral Glucose Tolerance TestCyna Jane Yao AlcularNo ratings yet
- OGTT Test ExplainedDocument2 pagesOGTT Test ExplainedMin KookieNo ratings yet
- SERBAN ANCUTA NICOLETA - ProjectDocument7 pagesSERBAN ANCUTA NICOLETA - ProjectSoare Ancuta-NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesType 2 Diabetes MellitusCadiz Etrama Di RaizelNo ratings yet
- Type2 Diabetes HandoutDocument1 pageType2 Diabetes Handouthendra_darmawan_4No ratings yet
- Types of Diabetes Mellitus and There SymptomsDocument6 pagesTypes of Diabetes Mellitus and There SymptomsApril Joy DoradoNo ratings yet
- Urine Glucose TestDocument6 pagesUrine Glucose TestSelim HanNo ratings yet
- Blood Sugar TestDocument6 pagesBlood Sugar Testyunini27No ratings yet
- The Test: How Is It Used?Document5 pagesThe Test: How Is It Used?julia_jayronwaldoNo ratings yet
- FBS Test ExplainedDocument5 pagesFBS Test ExplainedKhamron BridgewaterNo ratings yet
- M M M MDocument8 pagesM M M MAudrey MaeNo ratings yet
- What Is The Oral Glucose Tolerance TestDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Oral Glucose Tolerance TestBianca Camille100% (1)
- Tips Managing Blood Sugar For DiabeticsDocument2 pagesTips Managing Blood Sugar For Diabeticsadi assabetNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of High Blood Glucose Levels IncludeDocument9 pagesSymptoms of High Blood Glucose Levels IncludeAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- What Is DiabetesDocument7 pagesWhat Is DiabetesBryan Erazo Menendez MaciasNo ratings yet
- What Is DiabetesDocument6 pagesWhat Is Diabetesmkthakur6410No ratings yet
- Random Blood SugarDocument19 pagesRandom Blood SugarSounak NandyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Normal Blood Sugar LevelDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Normal Blood Sugar LevelexpertjatakNo ratings yet
- Reference Summary: X-Plain Diabetes - IntroductionDocument0 pagesReference Summary: X-Plain Diabetes - IntroductionUSMP FN ARCHIVOSNo ratings yet
- HypoglycemiaDocument17 pagesHypoglycemiaJohnjohn Mateo100% (1)
- Bab B.ingDocument11 pagesBab B.ingWidya Ageng SholehaNo ratings yet
- Managing Diabetes with Diet and ExerciseDocument32 pagesManaging Diabetes with Diet and ExerciseNor Hikmah HarisNo ratings yet
- Natural Remedies To Pre-Diabetes: Reverse Type 2 Diabetes Naturally in 90 DaysFrom EverandNatural Remedies To Pre-Diabetes: Reverse Type 2 Diabetes Naturally in 90 DaysNo ratings yet
- DM Brochure For NCM 106Document12 pagesDM Brochure For NCM 106Kimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exams Random Blood Glucose LevelDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Exams Random Blood Glucose LevelSheena IñigoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Global STI Kim EnricoDocument5 pagesDiabetes Global STI Kim EnricoKim Enrico JumarangNo ratings yet
- Do I Have Prediabetes or Diabetes Guide To Diagnosis and ManagementDocument5 pagesDo I Have Prediabetes or Diabetes Guide To Diagnosis and ManagementRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument10 pagesDiabetes MellitusJoseph BallackNo ratings yet
- Laboratory DiagnosisDocument2 pagesLaboratory DiagnosisLourdette TorrefielNo ratings yet
- Understanding HypoglycemiaDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Hypoglycemianurizzah_885541No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Pathophysiology ExplainedDocument2 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Pathophysiology ExplainedG FernandezNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MelitusDocument6 pagesDiabetes Melitusharisman trialviNo ratings yet
- Signs of Insulin ResistanceDocument4 pagesSigns of Insulin ResistanceRatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument11 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitusjohn jumborockNo ratings yet
- Energy Needs and Insulin's Role in Cellular Glucose UptakeDocument4 pagesEnergy Needs and Insulin's Role in Cellular Glucose UptakeBeRnAlieNo ratings yet
- Oral Glucose Tolerance TestDocument29 pagesOral Glucose Tolerance TestAhmedmmhNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis 508Document12 pagesDiagnosis 508Tri HarjonoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Alert Day - March 26, 2013Document2 pagesDiabetes Alert Day - March 26, 2013Scott CoursonNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Treatment: The most important information you need to improve your healthFrom EverandDiabetes: Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Treatment: The most important information you need to improve your healthNo ratings yet
- Blood Sugar Subsistence Formula: Full Guide to Control Your Blood SugarFrom EverandBlood Sugar Subsistence Formula: Full Guide to Control Your Blood SugarNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Hypoglycemia Symptoms, with Curated Recipes and a Sample 7-Day Meal PlanFrom EverandHypoglycemia Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing Hypoglycemia Symptoms, with Curated Recipes and a Sample 7-Day Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Type 1 Diabetes: Symptoms, Risks, Treatments and Support for DiabeticsFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Type 1 Diabetes: Symptoms, Risks, Treatments and Support for DiabeticsNo ratings yet
- physicalDocument16 pagesphysicalHawta AbdullaNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument11 pagesPresentationHawta AbdullaNo ratings yet
- All-Experiments 3RDDocument105 pagesAll-Experiments 3RDHawta AbdullaNo ratings yet
- 2014 (Aerobic Homocoupling of Arylboronic Acids Catalysed by Copper Terephthalate Metal-OrganicDocument11 pages2014 (Aerobic Homocoupling of Arylboronic Acids Catalysed by Copper Terephthalate Metal-OrganicHawta AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Citing and Referencing PowerpointDocument18 pagesCiting and Referencing PowerpointlynNo ratings yet
- CaffeieneDocument8 pagesCaffeieneHawta AbdullaNo ratings yet
- CaffeieneDocument8 pagesCaffeieneHawta AbdullaNo ratings yet
- All-Experiments 3RDDocument5 pagesAll-Experiments 3RDHawta AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Fasting Glucose Vs A1CDocument1 pageFasting Glucose Vs A1CBrent HussongNo ratings yet
- FBS Test ExplainedDocument5 pagesFBS Test ExplainedKhamron BridgewaterNo ratings yet
- Best of Vegan + Best of Paleo PeganDocument5 pagesBest of Vegan + Best of Paleo PeganVladutzz DimaNo ratings yet
- Normal Glucose Levels - The Ultimate Guide From LDocument2 pagesNormal Glucose Levels - The Ultimate Guide From LAgha Muhammad RazaNo ratings yet
- Zu1861 PDFDocument2 pagesZu1861 PDFYan KaiNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose TestDocument2 pagesBlood Glucose TestNoorain YousuffNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus An OverviewDocument4 pagesDiabetes Mellitus An OverviewALNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MallitusDocument33 pagesDiabetes Mallitushammu hothi100% (2)
- Lonsberry OcManDM10hdntDocument87 pagesLonsberry OcManDM10hdnthossam ridaNo ratings yet
- DAV PUBLIC SCHOOL PROJECT ON DIABETES MELLITUSDocument31 pagesDAV PUBLIC SCHOOL PROJECT ON DIABETES MELLITUSalex david100% (14)
- General Practitioner - Endocrinology MCQsDocument17 pagesGeneral Practitioner - Endocrinology MCQsAsif Newaz100% (2)
- Assignment On Diabetes: Submitted ToDocument19 pagesAssignment On Diabetes: Submitted ToEhesanulHaqueSaifNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Treatment ProtocolDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Treatment ProtocolPuja ZarkarNo ratings yet
- Major NCDs in the Philippines: Heart Disease, Cancer, Lung Disease & DiabetesDocument53 pagesMajor NCDs in the Philippines: Heart Disease, Cancer, Lung Disease & DiabetesNaddy RetxedNo ratings yet
- Ajcpath112 0665Document10 pagesAjcpath112 0665RiyanNo ratings yet
- Fasting Blood Sugar LevelsDocument7 pagesFasting Blood Sugar LevelsApple RamosNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose Test: Written By:marwa Azad Ahmed Supervised By:dr - Lubna.SameerDocument8 pagesBlood Glucose Test: Written By:marwa Azad Ahmed Supervised By:dr - Lubna.Sameerفنر محمدNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InformationDocument171 pagesDiabetes Informationtheia28No ratings yet
- (CC1) LAB-W14-Carbohydrates (Diagnosis)Document3 pages(CC1) LAB-W14-Carbohydrates (Diagnosis)Aira UsiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Diagnosis, Risk Factors and ManagementDocument39 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Diagnosis, Risk Factors and Managementimee cNo ratings yet
- RBS and FBSDocument5 pagesRBS and FBSAllenne Rose Labja Vale100% (1)
- Diagnosing Insulin Resistance by Simple Quantitative Methods in Subjects With Normal Glucose MetabolismDocument6 pagesDiagnosing Insulin Resistance by Simple Quantitative Methods in Subjects With Normal Glucose MetabolismKiaraliz Rivera RosaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma GlucoseDocument3 pagesLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Fasting Plasma Glucosemasood syedNo ratings yet
- A. Classification and Characteristics of Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesA. Classification and Characteristics of Diabetes MellitusNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Non-Communicable Diseases - Lifestyle Related Diseases: Wilma N. Beralde, RM, RN, ManDocument53 pagesNon-Communicable Diseases - Lifestyle Related Diseases: Wilma N. Beralde, RM, RN, ManNaddy RetxedNo ratings yet
- Consensus criteria for diagnosing GDM following landmark HAPO studyDocument6 pagesConsensus criteria for diagnosing GDM following landmark HAPO studyRaul Garcia Salas CastilloNo ratings yet