Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brief of Cost Management
Uploaded by
Masbooks0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesBrief of Cost Management
Uploaded by
MasbooksCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Project Cost Management Terms
Directions: Hide this side of the
flashcards or fold page in half. Read the
term, recite the definition, and then look
at this side of the flashcards to check
your answer.
The actual amount of monies the project
Actual cost (AC)
has spent to date.
An approach that relies on historical
information to predict the cost of the
Analogous estimating current project. It is also known as top-
down estimating and is the least reliable
of all the cost-estimating approaches.
An estimating approach that starts from
zero, accounts for each component of the
WBS, and arrives at a sum for the
Bottom-up estimating project. It is completed with the project
team and can be one of the most time-
consuming and most reliable methods to
predict project costs.
This estimate is also somewhat broad
and is used early in the planning
processes and also in top-down
Budget estimate
estimates. The range of variance for the
estimate can be from –10 percent to +25
percent.
A cost-estimating approach that uses a
Commercial database database, typically software-driven, to
create the cost estimate for a project.
A contingency allowance to account for
overruns in costs. Contingency
allowances are used at the project
Contingency reserve manager’s discretion and with
management’s approval to counteract
cost overruns for scheduled activities and
risk events.
PMP Exam Prep Seminar ©Instructing.com Page 1
Costs are parallel to each WBS work
package. The costs of each work
package are aggregated to their
Cost aggregation
corresponding control accounts. Each
control account then is aggregated to the
sum of the project costs.
A time-lapse exposure of when the
project monies are to be spent in relation
Cost baseline
to cumulative values of the work
completed in the project.
The cost aggregation achieved by
assigning specific dollar amounts for
each of the scheduled activities or, more
Cost budgeting
likely, for each of the work packages in
the WBS. Cost budgeting applies the cost
estimates over time.
A system that examines any changes
associated with scope changes, the cost
Cost change control system of materials, and the cost of any other
resources, and the associated impact on
the overall project cost.
The cost management plan dictates how
Cost management plan
cost variances will be managed.
The monies spent to recover from not
adhering to the expected level of quality.
Examples may include rework, defect
Cost of poor quality repair, loss of life or limb because safety
precautions were not taken, loss of sales,
and loss of customers. This is also known
as the cost of nonconformance to quality.
The monies spent to attain the expected
level of quality within a project. Examples
Cost of quality
include training, testing, and safety
precautions.
Measures the project based on its
Cost performance index (CPI) financial performance. The formula is CPI
= EV/AC.
PMP Exam Prep Seminar ©Instructing.com Page 2
The difference of the earned value
amount and the cumulative actual costs
Cost variance (CV)
of the project. The formula is CV = EV –
AC.
This estimate type is one of the most
accurate. It’s used late in the planning
processes and is associated with bottom-
Definitive estimate up estimating. You need the WBS in
order to create the definitive estimate.
The range of variance for the estimate
can be from –5 percent to +10 percent.
Costs are attributed directly to the project
work and cannot be shared among
Direct costs
projects (for example, airfare, hotels,
long-distance phone charges, and so on).
Earned value is the physical work
completed to date and the authorized
Earned value (EV) budget for that work. It is the percentage
of the BAC that represents the actual
work completed in the project.
These forecasting formulas predict the
likely completed costs of the project
Estimate at completion (EAC)
based on current scenarios within the
project.
An earned value management formula
that predicts how much funding the
project will require to be completed.
Estimate to complete (ETC)
Three variations of this formula are based
on conditions the project may be
experiencing.
Costs that remain constant throughout
the life of the project (the cost of a piece
Fixed costs of rented equipment for the project, the
cost of a consultant brought on to the
project, and so on).
An organization’s approach to managing
cash flow against the project deliverables
Funding limit reconciliation
based on a schedule, milestone
accomplishment, or data constraints.
PMP Exam Prep Seminar ©Instructing.com Page 3
Costs that are representative of more
than one project (for example, utilities for
Indirect costs the performing organization, access to a
training room, project management
software license, and so on).
An event that will likely happen within the
project, but when it will happen and to
Known unknown
what degree is unknown. These events,
such as delays, are usually risk-related.
An approach that assumes the cost per
unit decreases the more units workers
Learning curve
complete, because workers learn as they
complete the required work.
A market condition where the market is
Oligopoly so tight that the actions of one vendor
affect the actions of all the others.
The total cost of the opportunity that is
Opportunity cost refused to realize an opposing
opportunity.
An approach using a parametric model to
extrapolate what costs will be needed for
Parametric estimating a project (for example, cost per hour and
cost per unit). It can include variables and
points based on conditions.
Planned value is the work scheduled and
the budget authorized to accomplish that
Planned value (PV) work. It is the percentage of the BAC that
reflects where the project should be at
this point in time.
The final variance, which is discovered
Project variance only at the project’s completion. The
formula is VAR = BAC – AC.
PMP Exam Prep Seminar ©Instructing.com Page 4
This is a statistical approach to predicting
what future values may be, based on
historical values. Regression analysis
creates quantitative predictions based on
Regression analysis variables within one value to predict
variables in another. This form of
estimating relies solely on pure statistical
math to reveal relationships between
variables and to predict future values.
Cost reserves are for unknown unknowns
within a project. The management
Reserve analysis reserve is not part of the project cost
baseline, but is included as part of the
project budget.
This rough estimate is used during the
initiating processes and in top-down
Rough order of magnitude estimates. The range of variance for the
estimate can be from –25 percent to +75
percent.
Measures the project based on its
Schedule performance index (SPI) schedule performance. The formula is
SPI = EV/PV.
The difference between the earned value
Schedule variance (SV) and the planned value. The formulas is
SV = EV – PV.
Many vendors can provide what your
Single source project needs to purchase, but you prefer
to work with a specific vendor.
Only one vendor can provide what your
project needs to purchase. Examples
Sole source
include a specific consultant, specialized
service, or unique type of material.
Monies that have already been invested
Sunk costs
in a project.
PMP Exam Prep Seminar ©Instructing.com Page 5
A formula to forecast the likelihood of a
project to achieve its goals based on
what’s happening in the project right now.
There are two different flavors for the
TCPI, depending on what you want to
accomplish. If you want to see if your
To-Complete Performance Index project can meet the budget at
completion, you’ll use this formula: TCPI
= (BAC – EV)/(BAC – AC). If you want to
see if your project can meet the newly
created estimate at completion, you’ll use
this version of the formula: TCPI = (BAC
– EV)/(EAC – AC).
Costs that change based on the
conditions applied in the project (the
Variable costs number of meeting participants, the
supply of and demand for materials, and
so on).
The difference between what was
Variance
expected and what was experienced.
A forecasting formula that predicts how
much of a variance the project will likely
Variance at completion (VAC) have based on current conditions within
the project. The formula is VAC = BAC –
EAC.
PMP Exam Prep Seminar ©Instructing.com Page 6
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Urba 1304 221 1 EfDocument4 pagesUrba 1304 221 1 EfLeidy De La CruzNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Business CaseDocument12 pagesBusiness CaseRobbieJim100% (2)
- Diseño Geometrico-PuentesDocument13 pagesDiseño Geometrico-PuentesMilo Olivas50% (2)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Gravimetria PresentaciónDocument52 pagesGravimetria PresentaciónJesus espitia100% (2)
- 10277Br Retentor-EcoTurn Portuguese PDFDocument2 pages10277Br Retentor-EcoTurn Portuguese PDFEdilson AlvesNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Act Central U4Document6 pagesAct Central U4Ronald Salgado100% (1)
- Aprender A Pensar en La Solucion de Problema y en La Toma de DecisionesDocument11 pagesAprender A Pensar en La Solucion de Problema y en La Toma de DecisionesXimena PérezNo ratings yet
- Thomas Warren BurbankAirportDocument2 pagesThomas Warren BurbankAirporttpwarren23No ratings yet
- Acceptance FormDocument5 pagesAcceptance Formtpwarren23No ratings yet
- Project Management, Research, and Product DevelopmentDocument2 pagesProject Management, Research, and Product Developmenttpwarren23No ratings yet
- 4q2012 ExcelDocument826 pages4q2012 Exceltpwarren23No ratings yet
- 4q2012 ExcelDocument826 pages4q2012 Exceltpwarren23No ratings yet
- CLEVIDIPINE CleviprexDocument17 pagesCLEVIDIPINE Cleviprextpwarren23No ratings yet
- Juntos Por Un Futuro SostenibleDocument1 pageJuntos Por Un Futuro SostenibleMary MartínezNo ratings yet
- Funciones y Atribuciones Del Comité Paritario de Higiene y Seguridad y Su Ejecucion PrácticaDocument4 pagesFunciones y Atribuciones Del Comité Paritario de Higiene y Seguridad y Su Ejecucion Prácticaceciodette40No ratings yet
- Retroalimentación IndividualDocument5 pagesRetroalimentación IndividualJMontes ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Productos Amway - Hogar EcologicoDocument18 pagesProductos Amway - Hogar EcologicoNicolas PaezNo ratings yet
- Reavaliação Do Trem-Tipo Ferroviário BrasileiroDocument6 pagesReavaliação Do Trem-Tipo Ferroviário BrasileiroYgor SilvaNo ratings yet
- PTG5Document2 pagesPTG5Josue CarlinNo ratings yet
- Profesional Fronteras ComercialesDocument1 pageProfesional Fronteras ComercialesErick BritoNo ratings yet
- Négation Formes Et PlaceDocument1 pageNégation Formes Et PlaceIsabelle KantoussanNo ratings yet
- Content Networking - Architecture, Protocols, and PracticeDocument14 pagesContent Networking - Architecture, Protocols, and PracticeScaliba TaylorNo ratings yet
- Tema 1. Procesos de Desarrollo y Adolescencia - TareasDocument31 pagesTema 1. Procesos de Desarrollo y Adolescencia - TareasMenchu Ruiz LópezNo ratings yet
- Sigmund Freud - Diez Cosas Que Quizá No Sabías Del Padre Del PsicoanálisisDocument10 pagesSigmund Freud - Diez Cosas Que Quizá No Sabías Del Padre Del PsicoanálisisIng. Procoro CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Rus - Stub Ansi Asme b1.8 88Document43 pagesRus - Stub Ansi Asme b1.8 88Perfect Signature0% (1)
- PythonDocument2 pagesPythonVaibhaw ShiwarkarNo ratings yet
- Area Tecnologia e Informatica Taller Grado DecimoDocument3 pagesArea Tecnologia e Informatica Taller Grado DecimoarteagasagNo ratings yet
- Intro Matlab Calc Numerico PDFDocument18 pagesIntro Matlab Calc Numerico PDFJhan Rojas PérezNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Escenario 3 PRIMER BLOQUE-TEORICO - VIRTUAL LIDERAZGO Y PENSAMIENTO ESTRATÉGICODocument14 pagesQuiz - Escenario 3 PRIMER BLOQUE-TEORICO - VIRTUAL LIDERAZGO Y PENSAMIENTO ESTRATÉGICOViviana EstepaNo ratings yet
- Types of SoilDocument9 pagesTypes of SoilNilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- Guia de Instalacion Del QT 500Document7 pagesGuia de Instalacion Del QT 500cande_loNo ratings yet
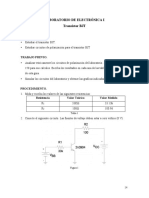
- Laboratorio 3Document8 pagesLaboratorio 3JesusCastroNo ratings yet
- Plano de Aula Lpo1 11ats01Document18 pagesPlano de Aula Lpo1 11ats01nereide bezerraNo ratings yet
- Sol Mpi 2 Taller Previo EpDocument8 pagesSol Mpi 2 Taller Previo EpClaudia Juarez MunaycoNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Building Design and Analysis: Project: Proposed Two-Storey Residential HouseDocument106 pagesReinforced Concrete Building Design and Analysis: Project: Proposed Two-Storey Residential HouseRonaldo BatlaganNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Aprendizaje SocialDocument10 pagesTrabajo Aprendizaje SocialVilma RojasNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solution - I Software Testing Chapter 4Document4 pagesExercise Solution - I Software Testing Chapter 4Fatima AsadNo ratings yet