Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unleashing The Power of SD-WAN
Uploaded by
Saqib Afzal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Unleashing the Power of SD-WAN
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesUnleashing The Power of SD-WAN
Uploaded by
Saqib AfzalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Title: Unleashing the Power of SD-WAN: Revolutionizing Conventional Networks
Introduction: In the ever-evolving landscape of networking technologies, Software-
Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) has emerged as a game-changer, offering a
dynamic and flexible approach to managing wide-area networks. This article delves into
the definition, working, significance, drawbacks, value addition, benefits, classification
and models, implementation, and market details of SD-WAN technology.
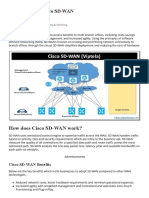
Definition and Working of SD-WAN: SD-WAN, or Software-Defined Wide Area
Networking, is a technology that allows the management of wide-area networks using
software-based controllers or application programming interfaces. Unlike traditional
WANs, which rely heavily on hardware and manual configuration, SD-WAN leverages
software to automate the optimization of traffic routing and improve network
performance.
The working of SD-WAN involves the use of centralized controllers to dynamically direct
traffic across the network. This is achieved by assessing the real-time performance of
each network path and making intelligent decisions based on application requirements
and available resources.
Significance of SD-WAN:
1. Enhanced Performance: SD-WAN optimizes network performance by
dynamically selecting the most efficient path for data transmission, leading to
reduced latency and improved application responsiveness.
2. Cost Savings: The automation and centralized management of SD-WAN reduce
the reliance on expensive hardware and manual configuration, resulting in cost
savings for organizations.
3. Flexibility and Scalability: SD-WAN provides a flexible and scalable network
infrastructure, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing requirements
without the need for extensive hardware upgrades.
Drawbacks of SD-WAN:
1. Security Concerns: While SD-WAN enhances network agility, it introduces
potential security risks. The use of the internet for connectivity may expose
organizations to threats, requiring robust security measures.
2. Complex Implementation: Transitioning to SD-WAN may pose challenges,
especially for organizations with existing complex network architectures. Proper
planning and expertise are crucial to ensuring a smooth implementation.
Value Addition and Benefits to Conventional WAN:
1. Centralized Management: SD-WAN offers centralized control, allowing
administrators to manage the entire network from a single interface, simplifying
operations.
2. Improved Application Performance: By prioritizing and optimizing traffic, SD-
WAN ensures consistent and reliable performance for critical applications,
enhancing the end-user experience.
3. Dynamic Adaptability: SD-WAN adapts to changing network conditions in real-
time, optimizing bandwidth usage and ensuring efficient data transfer across the
network.
Classification and Models: SD-WAN can be classified into two main deployment
models:
1. On-Premises SD-WAN: The SD-WAN infrastructure is deployed and managed
within the organization's data center.
2. Cloud-based SD-WAN: The SD-WAN infrastructure is hosted and managed in
the cloud, providing scalability and reducing on-site hardware requirements.
Implementation: Successful SD-WAN implementation involves careful planning and
execution. Organizations must assess their existing network infrastructure, define
business requirements, and choose an appropriate deployment model. Collaborating
with experienced SD-WAN service providers can streamline the implementation process.
Market Vendors and Products: Several vendors dominate the SD-WAN market, each
offering unique features and capabilities. Some key players and their market shares
include:
1. Cisco: A market leader, offering Cisco SD-WAN solutions with a significant
market share.
2. VMware (VeloCloud): Acquired by VMware, VeloCloud provides robust SD-
WAN solutions, capturing a substantial market share.
3. Silver Peak (now part of Aruba, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise company):
Known for its Unity EdgeConnect SD-WAN solution, Silver Peak has gained
traction in the market.
Summary: SD-WAN technology represents a significant advancement in the networking
landscape, offering organizations unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and performance
optimization. Despite potential drawbacks, the benefits of SD-WAN, including enhanced
application performance, cost savings, and centralized management, make it a
compelling choice for businesses seeking to modernize their wide-area networks. As the
market continues to evolve, organizations must carefully assess their needs and select
the SD-WAN solution that aligns with their unique requirements.
You might also like
- VeloCloud Lab Hol 2140 91 Ism - PDF - enDocument19 pagesVeloCloud Lab Hol 2140 91 Ism - PDF - enpaulo_an7381No ratings yet
- Annamacharya Institute of Technology: Basics of Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesAnnamacharya Institute of Technology: Basics of Cloud ComputingAbhinavreddy BNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela) - IP With EaseDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela) - IP With EasemvsnkraoNo ratings yet
- (23d4ead4 83ce 4aab 8acb 487dfcdc6d1a) Telstra SD WAN Guide FinalDocument46 pages(23d4ead4 83ce 4aab 8acb 487dfcdc6d1a) Telstra SD WAN Guide FinaldheevettiNo ratings yet
- SD-WAN Explained: The Ultimate Guide To SD-WAN ArchitectureDocument25 pagesSD-WAN Explained: The Ultimate Guide To SD-WAN ArchitecturehogadNo ratings yet
- Sd-Wan For Enterprises: Vmware Special EditionDocument5 pagesSd-Wan For Enterprises: Vmware Special EditionEduardo SoberanisNo ratings yet
- SD Wan 1592482748Document6 pagesSD Wan 1592482748Florick Le MahamatNo ratings yet
- SD WanDocument32 pagesSD WanAbdalrawoof AlsherifNo ratings yet
- Sd-Wan Overview: Vmware Special EditionDocument6 pagesSd-Wan Overview: Vmware Special EditionEduardo SoberanisNo ratings yet
- SDWan A Simplified Network For Distributed Enterprises EbookDocument20 pagesSDWan A Simplified Network For Distributed Enterprises EbookSaravanan Veerayah JayaramanNo ratings yet
- Gartner Market Guide For SD WanDocument23 pagesGartner Market Guide For SD WanedyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document16 pagesChapter 5Hina SaeedNo ratings yet
- Trend Report SD WAN Trends 161110Document12 pagesTrend Report SD WAN Trends 161110Pichai Ng-arnpairojhNo ratings yet
- AAG - Key SD WAN Use CasesDocument3 pagesAAG - Key SD WAN Use Caseshcm daukhiNo ratings yet
- Finding The Best SD-WAN Solution For Your Enterprise: Guide For Evaluating SD-WAN ProductsDocument7 pagesFinding The Best SD-WAN Solution For Your Enterprise: Guide For Evaluating SD-WAN Productseleazar_lostNo ratings yet
- 04wp SD Wan - Solutions EkinopsDocument8 pages04wp SD Wan - Solutions EkinopsTransmission NOCNo ratings yet
- IDC MarketScape - Worldwide SD-WAN Infrastructure 2021 Vendor AssessmentDocument10 pagesIDC MarketScape - Worldwide SD-WAN Infrastructure 2021 Vendor AssessmentstratocaserNo ratings yet
- Virtualized Network Services: Transcend Connectivity and Empower IT With SD-WAN 2.0Document9 pagesVirtualized Network Services: Transcend Connectivity and Empower IT With SD-WAN 2.0Barry ZhuNo ratings yet
- Design WAN For Cloud BrochureDocument5 pagesDesign WAN For Cloud BrochurefghghjyeeNo ratings yet
- Nss Labs Security Controls in The Us EnterpriseDocument16 pagesNss Labs Security Controls in The Us EnterpriseYoel ArmasNo ratings yet
- Top 51 QA For Cisco SDWAN Interview 1689267706Document14 pagesTop 51 QA For Cisco SDWAN Interview 1689267706Marco LopesNo ratings yet
- SDWAN@nettrainDocument12 pagesSDWAN@nettrainelahi elahiNo ratings yet
- Eight Questions To Ask When Considering An SD Wan WPDocument9 pagesEight Questions To Ask When Considering An SD Wan WPAlphonseNo ratings yet
- Cisco Sdwan Design GuideDocument102 pagesCisco Sdwan Design GuideSheik ShareefNo ratings yet
- Cisco Sdwan Design GuideDocument102 pagesCisco Sdwan Design GuideJohn TsigkrisNo ratings yet
- SDWAN (Software Defined-WAN) Technology Evaluation and ImplementationDocument17 pagesSDWAN (Software Defined-WAN) Technology Evaluation and ImplementationWasayefNo ratings yet
- Despre SDN 2Document4 pagesDespre SDN 2RobertNo ratings yet
- Cisco Sdwan Design GuideDocument102 pagesCisco Sdwan Design GuideChien DauNo ratings yet
- Automating SD-WAN Branch Configuration With HCLTech TIS Powered by Aruba Edge ConnectDocument12 pagesAutomating SD-WAN Branch Configuration With HCLTech TIS Powered by Aruba Edge Connect39.Anandadeep Bala XII S4No ratings yet
- SDWAN DeploymentDocument145 pagesSDWAN DeploymentJean Jacques BelyNo ratings yet
- What Is The Cisco SD-WAN Solution?Document56 pagesWhat Is The Cisco SD-WAN Solution?Azizuddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Software Defined NetworkingDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To Software Defined NetworkingPhyo May ThetNo ratings yet
- Fortinet Secure-Sdwan-7.0-Concept-GuideDocument19 pagesFortinet Secure-Sdwan-7.0-Concept-GuideSayed Ashraf Husaini KaziNo ratings yet
- SD WAN Architecture 1621768797Document10 pagesSD WAN Architecture 1621768797Shakeel AminNo ratings yet
- Juniper - Five Must Haves For Next Gen SD WAN SolutionsDocument7 pagesJuniper - Five Must Haves For Next Gen SD WAN SolutionsJNo ratings yet
- Huawei SD-WAN Solution DatasheetDocument9 pagesHuawei SD-WAN Solution Datasheetkareem saleemNo ratings yet
- SD WanDocument4 pagesSD WanFernala Sejmen-BanjacNo ratings yet
- Software Defined Wide Area Network: Puja A. Dhakulkar, Pranjali S. Dubey, Ankita A. Gaikwad, Sneha P. DhokaneDocument6 pagesSoftware Defined Wide Area Network: Puja A. Dhakulkar, Pranjali S. Dubey, Ankita A. Gaikwad, Sneha P. DhokanekamalgaihreNo ratings yet
- Software Defined NetworkingDocument23 pagesSoftware Defined NetworkingNiamNo ratings yet
- Three Key Requirements of Enterprise SD-WAN: Integrated Security, Multicloud Connectivity, and Application ReliabilityDocument7 pagesThree Key Requirements of Enterprise SD-WAN: Integrated Security, Multicloud Connectivity, and Application Reliabilitymasterlinh2008No ratings yet
- SD WanDocument6 pagesSD Wanmukul rajNo ratings yet
- Fortinet 1 4JLJ8BNDocument6 pagesFortinet 1 4JLJ8BNkentmultanNo ratings yet
- Cisco SD-WAN Design GuideDocument103 pagesCisco SD-WAN Design GuideMohmed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Business Goals, Constraints and Sizing of WAN NetworkDocument22 pagesAnalyzing Business Goals, Constraints and Sizing of WAN NetworkdereNo ratings yet
- Analytics of SD-WAN: Telecommunication DepartmentDocument4 pagesAnalytics of SD-WAN: Telecommunication DepartmentAttia EbreakNo ratings yet
- What Is SD-WANDocument7 pagesWhat Is SD-WANMoazzam TiwanaNo ratings yet
- Traditional and Software Defined NetworksDocument6 pagesTraditional and Software Defined NetworksMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- How Service Providers Can Optimize Managed SD WAN and SD Branch Delivery and ManagementDocument15 pagesHow Service Providers Can Optimize Managed SD WAN and SD Branch Delivery and ManagementEdiz İşlerNo ratings yet
- Huawei SD-WAN Solution DatasheetDocument6 pagesHuawei SD-WAN Solution DatasheetEduardo SoberanisNo ratings yet
- SolutionGuide SDWAN For VxRail HCI FINAL PDFDocument18 pagesSolutionGuide SDWAN For VxRail HCI FINAL PDFNguyen Hoang AnhNo ratings yet
- SD WAN Three Use Cases For TransformingDocument8 pagesSD WAN Three Use Cases For TransformingduartefrancoNo ratings yet
- Key PointsDocument10 pagesKey PointsMahi KulkarniNo ratings yet
- SO SDBranchDocument5 pagesSO SDBranchhcm daukhiNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Go MainstreamDocument12 pagesWhitepaper Go Mainstream张裴No ratings yet
- What Is Network Virtualization? Everything You Need To KnowDocument8 pagesWhat Is Network Virtualization? Everything You Need To KnowjonahNo ratings yet
- Notes For SDNDocument11 pagesNotes For SDNtguna21No ratings yet
- Learning SD-WAN with Cisco: Transform Your Existing WAN Into a Cost-effective NetworkFrom EverandLearning SD-WAN with Cisco: Transform Your Existing WAN Into a Cost-effective NetworkNo ratings yet
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) - a definitive guideFrom EverandSoftware Defined Networking (SDN) - a definitive guideRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- OSPFDocument17 pagesOSPFSaqib AfzalNo ratings yet
- SRX ContentsDocument1 pageSRX ContentsSaqib AfzalNo ratings yet
- Layer 4 Network SwitchDocument1 pageLayer 4 Network SwitchSaqib AfzalNo ratings yet
- Configure DHCP On Cisco IOS DevicesDocument8 pagesConfigure DHCP On Cisco IOS DevicesSaqib AfzalNo ratings yet
- Causes & CountersDocument186 pagesCauses & CountersMuhammad Bilal JunaidNo ratings yet
- Firewall Configuration For Data Centre NetworkDocument13 pagesFirewall Configuration For Data Centre NetworkVidhu Ranjan GopalNo ratings yet
- 01 Computer Communication and Networks V PDFDocument30 pages01 Computer Communication and Networks V PDFkartikNo ratings yet
- CANopen Manual 920-0025LDocument101 pagesCANopen Manual 920-0025LVictor ManuelNo ratings yet
- Capstone Project 2 Business Problem Requirement Document: Enterprise Network Security Based On Cisco SolutionsDocument12 pagesCapstone Project 2 Business Problem Requirement Document: Enterprise Network Security Based On Cisco Solutionshoàng huyNo ratings yet
- 02 LTE KPI ArchitectureDocument104 pages02 LTE KPI ArchitectureVahid ZibakalamNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent's CDMA Portfolio: Sales Training Overview Mike Hobby November 2006Document34 pagesAlcatel-Lucent's CDMA Portfolio: Sales Training Overview Mike Hobby November 2006Yousuf ShaikhNo ratings yet
- GW1000-ABEIP: Datalink Ethernet IP To DH+ Datalink AB Ethernet To DH+Document25 pagesGW1000-ABEIP: Datalink Ethernet IP To DH+ Datalink AB Ethernet To DH+Alamsyah SyamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Anil Sharma ResumeDocument5 pagesAnil Sharma Resumebindu sharmaNo ratings yet
- OSI Network Layers Quiz - ProProfs QuizDocument6 pagesOSI Network Layers Quiz - ProProfs Quizraghad mejeedNo ratings yet
- Practice Testanswers 6Document6 pagesPractice Testanswers 6Marina GeorgiouNo ratings yet
- PDS-LR3G-IP67 GeoWAN 4G GatewayDocument5 pagesPDS-LR3G-IP67 GeoWAN 4G GatewayPeter BergerNo ratings yet
- NanoPBX ManualDocument41 pagesNanoPBX ManuallogbearNo ratings yet
- GPON Doctor - General Presentation Sep 2009Document10 pagesGPON Doctor - General Presentation Sep 2009Saurabh AmritaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 v7 Modules 7 - 9 Full Exam AnswersDocument27 pagesCCNA 2 v7 Modules 7 - 9 Full Exam AnswersAndu HariNo ratings yet
- NAT Gateway and NAT InstanceDocument17 pagesNAT Gateway and NAT InstanceBhanu VikasNo ratings yet
- Ccna Basic Questions and AnswersDocument174 pagesCcna Basic Questions and AnswersyeshtewatiyaNo ratings yet
- Connecting Networks 6.0 - Chapter 5 Skills Integration Challenge AnswersDocument4 pagesConnecting Networks 6.0 - Chapter 5 Skills Integration Challenge AnswersCCNAv70% (3)
- Linux For Hacking For Install Test and Hack Tools.Document589 pagesLinux For Hacking For Install Test and Hack Tools.DIY DinhoBrNo ratings yet
- MPMC - UnitIV - Serial Communication and Bus interface-Part-IDocument35 pagesMPMC - UnitIV - Serial Communication and Bus interface-Part-Ineha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Serial and Parallel CommunicationDocument82 pagesSerial and Parallel Communicationilham djafarNo ratings yet
- Thesis Turbo CodesDocument5 pagesThesis Turbo CodesjenniferreitherspringfieldNo ratings yet
- QAM Implementation Using LabVIEWDocument21 pagesQAM Implementation Using LabVIEWVijaya Shree100% (2)
- 3G NOC RAN-Back Office CV ExampleDocument2 pages3G NOC RAN-Back Office CV ExampleharyantojogjaboyNo ratings yet
- 3G Counter Level - BianDocument124 pages3G Counter Level - BianAnonymous TTVlXoNo ratings yet
- airMAX - Training - Guide 10 15 12 PDFDocument84 pagesairMAX - Training - Guide 10 15 12 PDFMorhne RufinNo ratings yet
- Wireless Access Point Configuration in PfSenseDocument3 pagesWireless Access Point Configuration in PfSenseAung Kyaw ThuNo ratings yet
- EE359 Wireless Communications: Professor Homayoun HashemiDocument48 pagesEE359 Wireless Communications: Professor Homayoun HashemiArnab BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- FT Broch v2 A4USDocument4 pagesFT Broch v2 A4USRanel AbantoNo ratings yet
- TCP Congestion ControlDocument20 pagesTCP Congestion ControlErik XuNo ratings yet