Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eag02 P
Eag02 P
Uploaded by
SUSAN PETER TERUOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eag02 P
Eag02 P
Uploaded by
SUSAN PETER TERUCopyright:
Available Formats
Understanding
Environmental
Accounting
Introduction to the Environmental
Accounting Guidelines
Ministry of the Environment, Japan
What is Environmental Accounting
Environmental accounting aims at achieving sustainable development, maintaining a favorable relationship with
the community, and pursuing effective and efficient environmental conservation activities. These accounting
procedures allow a company to identify the cost of environmental conservation during the normal course of business,
identify benefit gained from such activities, provide the best possible means of quantitative measurement (in
monetary value or physical units) and support the communication of its results.
Identifies cost and benefit of environmental
conservation activities, and provides the best
possible means of quantitative measurement
and supports communications
Environmental
conservation Environmental
cost
Financial accounting Environmental Environmental
performance Economic benefit conservation performance
associated with benefit
environmental
conservation
activities
Functions of Environmental Accounting
Internal Functions
As one step of a company’s environmental information system, internal function makes it possible to manage
environmental conservation cost and analyze the cost of environmental conservation activities versus the benefit
obtained, and promotes effective and efficient environmental conservation activities through suitable decision-
making.
External Functions
By disclosing the quantitatively measured results of its environmental conservation activities, external functions
allow a company to influence the decision-making of stakeholders, such as consumers, investors, and local
residents.
[Companies] [Society ]
Internal functions External functions
Corporate management tool Communication with the local community
Environmental
(trust, assessment, accountability)
accounting used as
Party receiving an environmental
the information Party receiving
information system the information
by companies
Management,
related Consumers, business
departments, partners, investors, financial
employees institutions, local residents,
NGOs, government, citizen
State of Environmental Accounting by Japanese Companies
Based on the results of the “2001 Environment-Conscious Corporate Survey” conducted by the Ministry of the
Environment (July, 2002), the survey targeted companies listed on the first and second sections of the Tokyo,
Osaka and Nagoya Stock Exchanges and non-listed companies with 500 or more employees (6,360 Companies).
http://www.env.go.jp/policy/j-hiroba/kigyo/index.html (Japanese version)
Companies Implementing Environmental Accounting
Of the 2,898 companies which responded to the survey, some 16.9% (491 companies) have adopted
environmental accounting, while another 20.0% (580 companies) were considering such measures.
Use of Environmental Accounting Data
In response to the question as to how they use environmental accounting data within the company, 55.6% was
used in “Benefit-to-cost analyses of environmental conservation activities” which was also the most common reply
given. It was followed by “Management of expense to attain targets of voluntary environmental management” at
45.6% and “Reduction of environmental cost” at 40.3%.
Disclosure of Environmental Accounting Data
Of the 1,351 companies have disclosed environmental data outside their companies, 27.2% or 367 companies
have released the environmental accounting data to the general public.
Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2002
In March 2002, the Ministry of the Environment issued “Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2002,” which is a
revision of “the Guidelines for Introducing an Environmental Accounting System (2000).” The new guidelines were
revised as follows:
A. Greater clarification of external functions;
B. Greater elaboration of environmental conservation cost;
C. Clarification of environmental conservation benefit;
D. Clarification of economic benefit associated with environmental conservation activities.
Overview of Environmental Accounting
Financial performance Environmental performance
(1) Environmental Conservation Cost (2) Environmental Conservation Benefit
Business Area Cost Input of resources into business operations
Upstream/Downstream Cost Energy consumption
Administration Cost Water usage
R&D Cost Input of various resources
Social Activity Cost Environmental impact and waste emissions from
Environmental Remediation Cost business operations
Other Cost Emissions to the air
Emissions to water bodies and ground
Waste emissions
(3) Economic Benefit Associated with The goods and services produced by business
Environmental Conservation Activities operations
Actual Benefit Environmental impact during usage and
disposal, etc.
Revenue
Transports
Expense Saving Environmental impact caused by transports, etc.
Estimated Benefit
Disclosure Format
The Guidelines introduce three different formats for that companies may use for environmental accounting disclosure. The
following format comprehensive cost and benefit.
Understanding Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2002
In order to promote effective use of Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2002, the Ministry of the Environment
has produced the Guidebook, “Understanding Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2002,” which explains the
original Guidelines using a Q&A format and also presents examples of accounting entries and cases by theme. The
Ministry promotes the guidelines widely to companies who have already adopted environmental accounting as well
as those who are considering adoption of such methods.
The above Guidebook may also be downloaded from the Ministry of Environment's Web site at:
http://www.env.go.jp/policy/kaikei/guide2002.html (Japanese version)
Structure of the Guidebook 2002
Chapter 1: Revisions to Environmental Accounting Guidelines
Chapter 2: Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2002
Chapter 3: Understanding the 2002 Guidelines - 1 [Q&A]
Chapter 4: Understanding the 2002 Guidelines - 2 [Cases]
Reference: Latest trends in environmental accounting
Glossary
Relationships between Environmental Report, Environmental
Performance Indicators and Environmental Accounting
In order to promote voluntary efforts towards environmental conservation, the Ministry of the Environment has issued
the “Environmental Accounting Guidelines 2002,” the “Environmental Reporting Guidelines,” as well as the
“Environmental Performance Indicators for Businesses.” The mutual relationship between these three guidelines is
indicated as follows:
Stakeholders (Consumers/Investors/Local Residents)
Communication
Production of Environmental
Environmental Report Reporting Guidelines
Environmental
External Functions of Accounting Internal Functions of
Environmental Guidelines Environmental
Accounting
Environmental Conservation
Cost & Economic Benefit
(Monetary Value)
Information Disclosure by Internal Environmental
Environmental Report Environmental Conservation Management
Benefit
(Physical Units)
[Self Evaluation]
Incorporate Incorporate
Data Collection & Analysis
Selection of Environmental Performance Indicators
Environmental Performance
Environmental impact indicators
Indicators for Businesses
Environmental management indicators
Environmental Management System
Harmonizing with International Trends
d
Throughout the world various governmental organizations, international organizations, researchers, and corporate
accounting specialists are engaged in efforts to research and development of environmental accounting. In Japan,
the Ministry of the Environment is following overseas trends while making a direct appeal of the status of
environmental accounting in Japan.
• Participate in the UNDSD environmental management accounting initiative.
Since 1999, the Ministry of the Environment has participated in an expert working group on the “Government's role in
promoting environmental management accounting” initiated by the United Nations Division for Sustainable
Development (UNDSD) environmental management accounting initiative. During such meetings, the Ministry of the
Environment grasps worldwide trends in this field and gives presentations on the practices in Japan. Detailed
information can be found at the following Web site:
http://www.un.org/esa/sustdev/estema1.htm
• Environmental Management Accounting Network-Asia Pacific (EMAN-AP)
The Environmental Management Accounting Network-Asia Pacific (EMAN-AP) is a network comprising of
researchers and practitioners of environmental accounting from 14 countries and regions in the Asian Pacific region,
including Japan. Established in September 2001, the network promotes the adoption and use of environmental
management accounting methods, and contributes to the promotion of sustainable development in the Asian-Pacific
region. In respect to the EMAN-AP project, the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES) the Kansai
Research Center acts as the coordinating office in Japan. Detailed information can be found at the following Web
site:
http://www.eman-ap.net/
Liaison for Inquiries Regarding Environmental Accounting
and Your Comments
Aiming to produce world-class environmental accounting guidelines, the Ministry of the Environment intends to
continue to enhance the methods introduced through such guidelines in cooperation with corporate practitioners and
specialists of environmental accounting. We value your comments and welcome any feedback you may have in this
connection, and therefore respectfully ask your comments to the following address:
Environmental and Economy Div. of
Environmental Policy Bureau, Ministry of the
Environment
TEL: +81-(0)3-5521-8240 FAX: +81-(0)3-3580-9568
E-mail: env-acctg@env.go.jp
Issued by Ministry of the Environment September 2002
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Chandrasekhar S. The Mathematical Theory of Black Holes PDFDocument667 pagesChandrasekhar S. The Mathematical Theory of Black Holes PDFBudhaditya Bhattacharjee94% (17)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Christian Missionaries and Female Education in Bengal During East India Company's Rule: A Discourse Between Christianised Colonial Domination Versus Women EmancipationDocument11 pagesChristian Missionaries and Female Education in Bengal During East India Company's Rule: A Discourse Between Christianised Colonial Domination Versus Women EmancipationSanjay Samuel RaiNo ratings yet
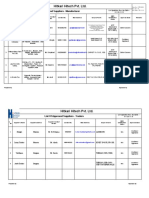
- Hitkari Hitech Pvt. LTD.: List of Approved Suppliers - ManufacturerDocument3 pagesHitkari Hitech Pvt. LTD.: List of Approved Suppliers - ManufacturerRakesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Final Research ReportDocument84 pagesFinal Research ReportSamarthNo ratings yet
- Unit2 Copyright Slot3 Session7 8 9Document31 pagesUnit2 Copyright Slot3 Session7 8 9Z FuuNo ratings yet
- SRS Annual Report 2020-21Document268 pagesSRS Annual Report 2020-21GadsdcaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument15 pagesConceptual FrameworkJacie TupasNo ratings yet
- People v. AyogDocument14 pagesPeople v. AyogRein DomNo ratings yet
- Two Greek Philosophers Plato & AristotleDocument15 pagesTwo Greek Philosophers Plato & AristotleMonique ReyesNo ratings yet
- Audix tr40Document2 pagesAudix tr40wc9j7dy42xNo ratings yet
- ESL Worksheet: School RoomsDocument2 pagesESL Worksheet: School RoomsDouglas P PerkinsNo ratings yet
- Oedipus The King Plot SummaryDocument4 pagesOedipus The King Plot SummaryYonatan HaileNo ratings yet
- Ashes PvE Beginner RulebookDocument32 pagesAshes PvE Beginner Rulebookprojectumbridge projectumbridgeNo ratings yet
- SM 11Document75 pagesSM 11Mai Anh ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Ba 2518436880Document1 pageBa 2518436880Phu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Autumn Leaves AnalysisDocument6 pagesAutumn Leaves AnalysisJack Noké100% (4)
- United States v. Dailey, 4th Cir. (2002)Document3 pagesUnited States v. Dailey, 4th Cir. (2002)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- DR Abbas Batkhela 02-02-2024Document3 pagesDR Abbas Batkhela 02-02-2024Smart ProNo ratings yet
- 2.8 - Figurative Language Answers Exercise 3B PDFDocument5 pages2.8 - Figurative Language Answers Exercise 3B PDFLi NahNo ratings yet
- What Is Plant Physiology BOTANYDocument12 pagesWhat Is Plant Physiology BOTANYfatima manzoorNo ratings yet
- Effects of Drama Serials On HousewivesDocument54 pagesEffects of Drama Serials On HousewivesMahid MudassarNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of The Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageCommunicable Diseases of The Reproductive SystemSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Cpoc Resolution Adopting KasimbayananDocument2 pagesCpoc Resolution Adopting Kasimbayananjanice teradoNo ratings yet
- AmeriCorps Healthcare Allowance GuideDocument8 pagesAmeriCorps Healthcare Allowance GuideToriGuyNo ratings yet
- Sandip University Top Leading University in Nashik, MaharashtraDocument12 pagesSandip University Top Leading University in Nashik, MaharashtraRavi SarafNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 5: "Illustrating and Verifying A Relation and A Function"Document27 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 5: "Illustrating and Verifying A Relation and A Function"Eiay CommsNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Arts in Public Governance: Outcomes-Based Syllabus in Introduction To Labor LawDocument5 pagesBachelor of Arts in Public Governance: Outcomes-Based Syllabus in Introduction To Labor LawAndrew Belgica0% (1)
- Language AnalysisDocument13 pagesLanguage AnalysisMuhammad Iqbal100% (4)
- The Philippine National RailwaysDocument32 pagesThe Philippine National RailwayspixiedustNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Action Research Data Collection MethodsDocument10 pagesTopic 8 Action Research Data Collection MethodsFatin Syazwani100% (2)